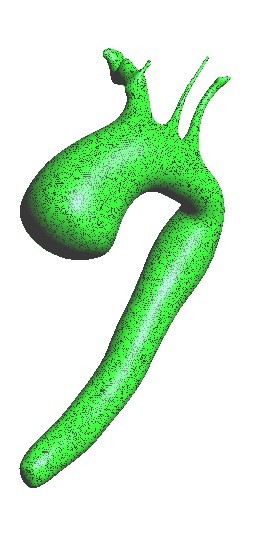| Line 219: | Line 219: | ||
| + | {| style="text-align: center; " | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Image:draft_Samper_526155048-image55.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |style="padding:15px;"|[[Image:draft_Samper_526155048-image56.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
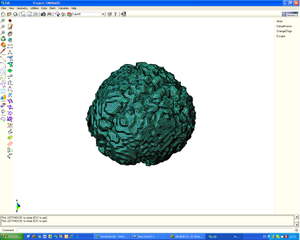
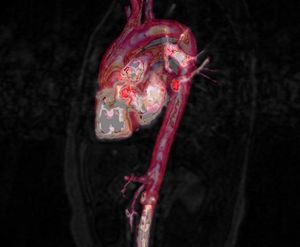
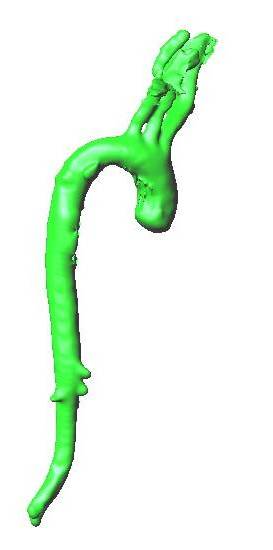
| + | |Deformable isosurface model | ||
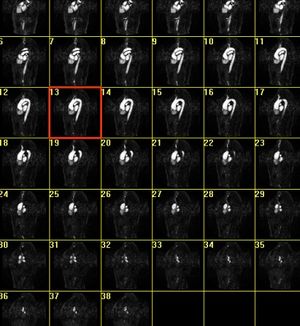
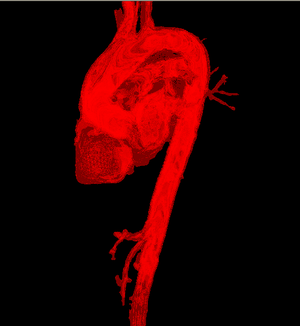
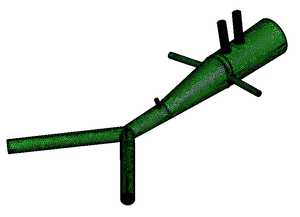
| + | |Meshing of heart and aorta | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Image:draft_Samper_526155048-image58-c.jpeg|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |style="padding:15px;"|[[Image:draft_Samper_526155048-image57-c.jpeg|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
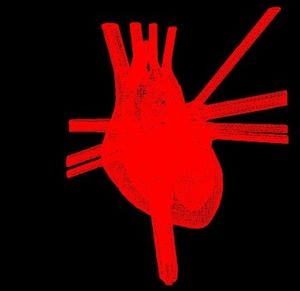
| + | |Meshing of heart | ||
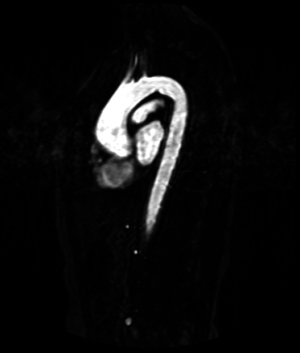
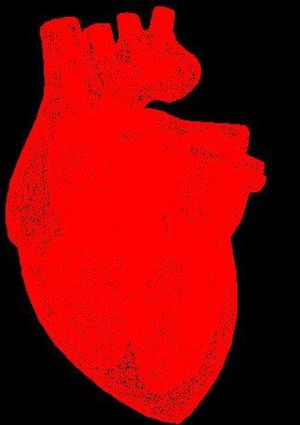
| + | |3D heart | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <big>* Segmentation and 3D reconstruction of medical images. </big> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Image:draft_Samper_526155048-image60.png|center|300px]] | [[Image:draft_Samper_526155048-image60.png|center|300px]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<big>* Meshing of segmented geometries: creation of surface meshes or volume meshes.</big> | <big>* Meshing of segmented geometries: creation of surface meshes or volume meshes.</big> | ||
Revision as of 11:45, 13 June 2018
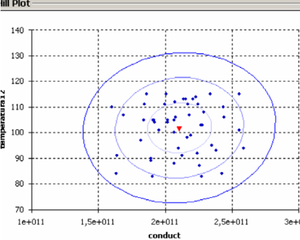
Research Lines & RTD Project in Biomedical Engineering
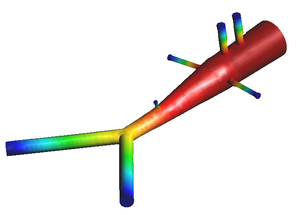
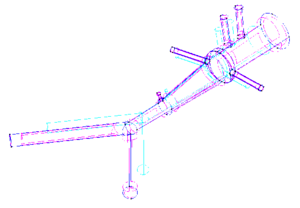
Computational Fluid Dynamics
Solid and Structural Biomechanics
Health Decision Support Systems
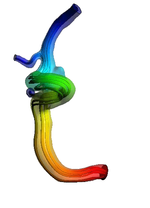
Cardiovascular System
Biomaterials
Artificial Intelligence
Neurosciences
Medical-GiD
Urology
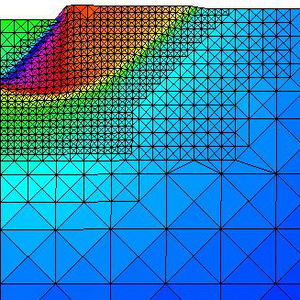
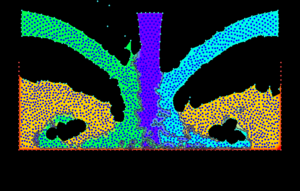
Pre and post processing
Computational Fluid Dynamics
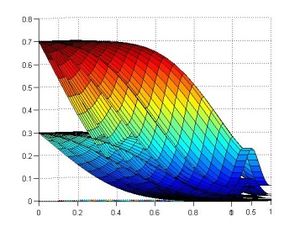
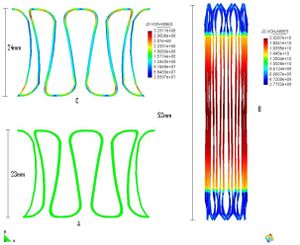
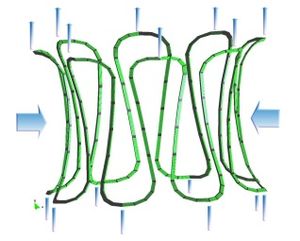
* Stabilized finite element and finite difference methods in incompressible biofluid mechanics.
* Bio-Absorption theory application in vessel structures for atheroma plack and biochemical studies.
* Finite element methods for fluid flow and analysis.
* Numerical methods applied in multidisciplinary problems in fluid biomechanics (fluid structure interaction, thermal flows, absorption theory etc).
* Coupling 3D with 2D or 1D models to improve study details.
Solid and Structural Biomechanics
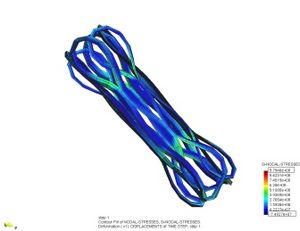
* Finite element methods for linear and non linear analysis of solids structures.
* Coupled problems in solid biomechanics (fluid structure interaction, thermal flows, absorption theory etc).
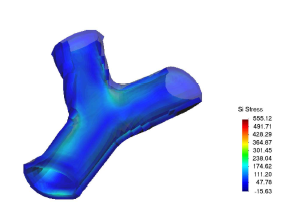
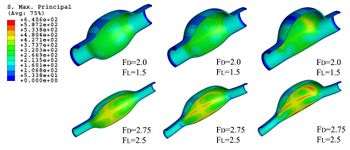
* Finite element methods for biomechanical devices analysis and prototype design (stent, prosthesis, etc).
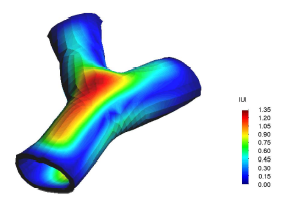
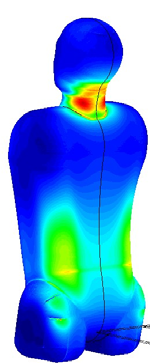
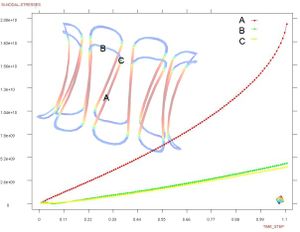
* Finite element methods analysis of solid biology structures (hearth mechanics, vessel stresses response, etc).
Health Decision Support System
* Development of intelligent platform to help physician work, informatization of routinely medical work.
* Finite element use to improve medical diagnosis and to perfect analysis processes.
* Biostatistical models applied ad hoc for several medical problems and cases.
* Bioinformatic technology solutions to coupled finite elements methods with biostatistical tools and artificial intelligence.
* Monte-Carlo methods for stochastic analysis in computational biomechanics and in biofluid dynamics.
* Parameter identification via stochastic methods.
* Coupling of TIC solutions, stochastic methods and finite element methods to improve and get faster medical analysis and decision
Computational Fluid Dynamics
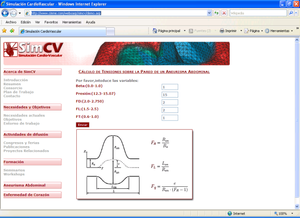
* Development of simulation platform for cardiovascular problems.
* Finite element for the simulation of problematic scenarios (aneurism, lumen obstruction, deformation, etc).
* Finite element for the study of cholesterol and platelets vessel absorption.
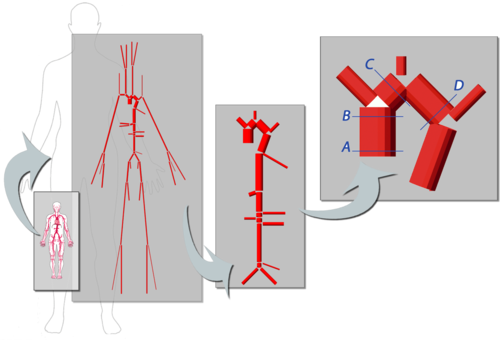
* 1D-Vessel model of whole human body. General information coupled to specific 2D or 3D studies.
* Reconstruction of real geometries starting by DICOM images.
* Automatic 2D and 3D geometries for vessel obstruction or aneurisms formation analysis.
Biomaterials
Development of biocompatible geometries for internal or external devices (stents, internal prosthesis, etc).
* Finite element for stress testes with biomaterials and medical devices.
* Design and study of biocompatible devices for human medical use or experimental use.
*
* New constitutive models for biomaterial and shape memory materials.
* Parameter identifications in constitutive models of biomaterials.
Artifial Intelligence
* Development of artificial neural networks (ANN) for optimization, inverse analysis and medical decision support fast decision taking.
* Integration of artificial neural networks (ANN) in decision support systems combining wireless sensors, computer simulations methods and artificial intelligence technology.
*
Development of artificial intelligence techniques based in agent simulations.
* Applications of artificial neural networks (ANN) technology for parameter identification in constitutive laws
* Development of intelligent finite element methods via Al Technology
| http://www.cimne.com/flood/ |
Neursciences
* Finite element methods for the analysis of brain cellular activity in pathological and physiological scenarios.
* 1D Finite element methods to study the propagations of neuronal signals in complex networks.
*
Statistical methods to fast response in biochemical brain analysis.
* Dementia diseases studies: finite element methods and bioinformatic solutions to reinforce the investigation about the causes of several brain dysfunction.
* Amyloids, Polymers and Cerebral Membrane Characterization
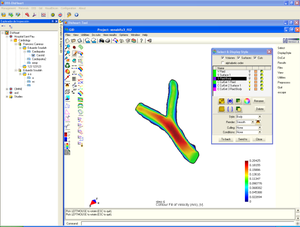
Medical-GiD
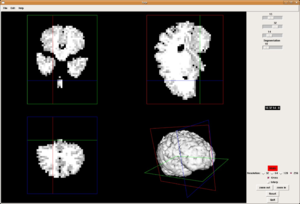
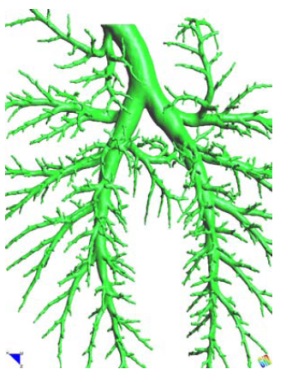
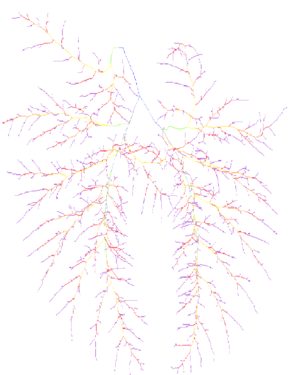
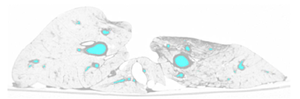
| Magnetic Resonance (2D) | 2D Detail | Edition/Generation |
| Deformable isosurface model | Meshing of heart and aorta |
| Meshing of heart | 3D heart |
* Segmentation and 3D reconstruction of medical images.
* Meshing of segmented geometries: creation of surface meshes or volume meshes.
* Visualization of 4D images (3D + time), creation of flux vectors and study of time developing in the image.
* Anatomical real cases.
* Coupling with simulation programs and with finite element methods solver.
* Friendly platform and portability of the informatics solutions adopted.
Urology
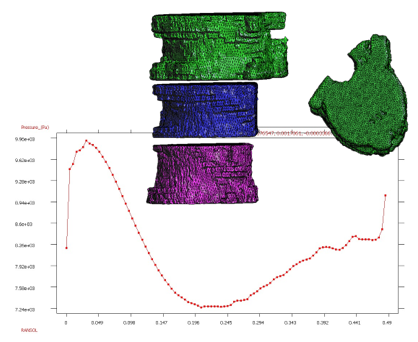
* Finite Element Method for the simulation of the urinary bladder and its parts like the destrusor (little smooth muscle)
* Study of biological materials and its multi-scale hierarchy, creation of simplificated models with classical nonlinear continuum mechanics theory.
*
Characterization of destrusor-tissue model is based in the representation (based on hyperelastic matrix, and viscoelastic fibres)
*
Analisys of the interaction between bladder wall with urine modelled via the Particle Finite Element Method (PFE
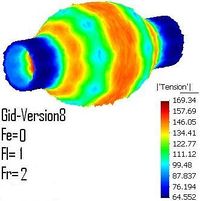
Pre and Post Proccesing
* Development and maintenance of GiD pre and post processing system (www.gidhome.com).
* Development of methods for generating structure and unstructured meshes.
*
Development of input data technology for large scale computational problems.
* Graphical visualization techniques for large scale simulation problems.
* Generation of input data for finite element analysis from medical images.
* Meshless methods for parameterization of geometries for shape optimization problems.
Document information
Published on 01/01/2009
Licence: CC BY-NC-SA license
Share this document
Keywords
claim authorship
Are you one of the authors of this document?