m (Scipediacontent moved page Draft Content 310579432 to Santovena-Casal Bernal-Bravo 2019a) |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
Analyzing the influence of social media on the learning process is no longer a novel idea; however, due to its importance for students and consequently for teachers, research continues to explore the pedagogical potential of social media. The main objective of the present study was to analyze the influence of teacher roles (guide or facilitator) on students’ social participation in Twitter and their perceived academic experience. The sample consisted of 525 future teachers, all of the Master’s degree students at Spain’s National Distance Education University (UNED). We used a mixed triangulation design, a theoretical model, quantitative methods (descriptive analysis and contrast of means) and qualitative methods (content analysis following the principles of grounded theory). Our results showed that the teacher’s role as a facilitator exerted a more positive influence on how students assessed their experience and on their participation on Twitter than the role as a guide. We conclude that the use of social media sites in education offers a motivating and satisfying framework that is not provided by other more traditional means such as forums, and that a role that facilitates independent learning is a better strategy when using social media in the classroom. | Analyzing the influence of social media on the learning process is no longer a novel idea; however, due to its importance for students and consequently for teachers, research continues to explore the pedagogical potential of social media. The main objective of the present study was to analyze the influence of teacher roles (guide or facilitator) on students’ social participation in Twitter and their perceived academic experience. The sample consisted of 525 future teachers, all of the Master’s degree students at Spain’s National Distance Education University (UNED). We used a mixed triangulation design, a theoretical model, quantitative methods (descriptive analysis and contrast of means) and qualitative methods (content analysis following the principles of grounded theory). Our results showed that the teacher’s role as a facilitator exerted a more positive influence on how students assessed their experience and on their participation on Twitter than the role as a guide. We conclude that the use of social media sites in education offers a motivating and satisfying framework that is not provided by other more traditional means such as forums, and that a role that facilitates independent learning is a better strategy when using social media in the classroom. | ||
| − | [[Media: | + | [[Media:Santovena-Casal_Bernal-Bravo_2019a-69577.pdf|<span style="color:#0645AD; font-weight: bold">Download the PDF version</span>]] |
==== 1. Introduction and status of the issue ==== | ==== 1. Introduction and status of the issue ==== | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Santovena-Casal_Bernal-Bravo_2019a-69577-en015.png|center|px|]] |
Figure 1. Proposed model. | Figure 1. Proposed model. | ||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Santovena-Casal_Bernal-Bravo_2019a-69577-en016.png|center|px|]] |
Figure 2. Teacher participation on Twitter: Tweets sent over the four-week period. | Figure 2. Teacher participation on Twitter: Tweets sent over the four-week period. | ||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Santovena-Casal_Bernal-Bravo_2019a-69577-en017.png|center|px|]] |
For the study of Twitter participation, the sample was made up of the messages sent and registered in a Google TAGS spreadsheet v6 (Hawksey, 2013) connected to Twitter API: 26188 tweets. Tweets were selected using the hashtags that identify each discussion. Twitter API, despite some limitations, makes it possible to recover tweets depending on the number of tweets sent during the past month, eliminating the oldest messages in order to facilitate the creation of new ones. Despite their temporary nature, these data are nonetheless an interesting research objective (Bruns & Stieglitz, 2012; Gerlitz & Rieder, 2013); the API must be trusted, given that it is the only means of obtaining large-scale data (Bruns & Stieglitz, 2012). The researchers have no other way to confirm data quality and accuracy; this is an unavoidable limitation that does not invalidate the results. As indicated by Gerlitz and Rieder (2013), Twitter sampling is based on nonprobabilistic sampling that is not representative, given that sample selection is always limited by the application used. | For the study of Twitter participation, the sample was made up of the messages sent and registered in a Google TAGS spreadsheet v6 (Hawksey, 2013) connected to Twitter API: 26188 tweets. Tweets were selected using the hashtags that identify each discussion. Twitter API, despite some limitations, makes it possible to recover tweets depending on the number of tweets sent during the past month, eliminating the oldest messages in order to facilitate the creation of new ones. Despite their temporary nature, these data are nonetheless an interesting research objective (Bruns & Stieglitz, 2012; Gerlitz & Rieder, 2013); the API must be trusted, given that it is the only means of obtaining large-scale data (Bruns & Stieglitz, 2012). The researchers have no other way to confirm data quality and accuracy; this is an unavoidable limitation that does not invalidate the results. As indicated by Gerlitz and Rieder (2013), Twitter sampling is based on nonprobabilistic sampling that is not representative, given that sample selection is always limited by the application used. | ||
| Line 96: | Line 96: | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Santovena-Casal_Bernal-Bravo_2019a-69577-en018.png|center|px|]] |
Figure shows the results of Dimension 1, “Learning process and acquisition of knowledge”. The teaching methodology was highly rated by 70% of the students. They considered that participation on Twitter helped them acquire knowledge about the subject matter (59.6%), theoretical knowledge (42.7%), practical knowledge (53%), collaborative and participative knowledge (70%) and that they had experienced different types of learning in this class: critical (76%) and reflective (76%), constructivist (73.7%), connectivist (73.5%), social (81.9%) and participative (70%), active (61.6%). | Figure shows the results of Dimension 1, “Learning process and acquisition of knowledge”. The teaching methodology was highly rated by 70% of the students. They considered that participation on Twitter helped them acquire knowledge about the subject matter (59.6%), theoretical knowledge (42.7%), practical knowledge (53%), collaborative and participative knowledge (70%) and that they had experienced different types of learning in this class: critical (76%) and reflective (76%), constructivist (73.7%), connectivist (73.5%), social (81.9%) and participative (70%), active (61.6%). | ||
| Line 121: | Line 121: | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Santovena-Casal_Bernal-Bravo_2019a-69577-en019.png|center|px|]] |
Figure 3. General concept map “Perceived academic experience”. | Figure 3. General concept map “Perceived academic experience”. | ||
| Line 130: | Line 130: | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Santovena-Casal_Bernal-Bravo_2019a-69577-en020.png|center|px|]] |
Figure 4. Concept map “We-centered perspective”. | Figure 4. Concept map “We-centered perspective”. | ||
| Line 244: | Line 244: | ||
El análisis de la influencia de las redes sociales en el proceso de aprendizaje ya no es una novedad. Sin embargo, debido a su importancia para el alumnado y en consecuencia para el profesorado, la literatura científica sigue prestando atención al potencial pedagógico de las redes sociales. El objetivo principal de esta investigación fue analizar la influencia del rol del profesorado (guía y facilitador) sobre la participación social en Twitter y la experiencia académica percibida de los estudiantes. La muestra estuvo formada por 525 futuros profesores, estudiantes de posgrado en la Universidad Nacional de Educación a Distancia. Se utilizó un diseño mixto de triangulación, un modelo teórico, una parte cuantitativa (análisis descriptivo y contraste sobre medias) y otra cualitativa (análisis de contenido, siguiendo los principios de la teoría fundamentada). Los resultados mostraron que el rol facilitador del profesor influye positivamente en la valoración de la experiencia por parte de los estudiantes y en la participación en Twitter, en mayor medida que el rol guía. Por un lado, se concluye que el uso de las redes sociales, en el ámbito educativo, proporciona un marco motivacional y de satisfacción que no lo aportan otros medios más tradicionales, como los foros, y, por otro, que un rol que facilita un proceso de aprendizaje independiente es mejor estrategia cuando hablamos de redes sociales en el aula. | El análisis de la influencia de las redes sociales en el proceso de aprendizaje ya no es una novedad. Sin embargo, debido a su importancia para el alumnado y en consecuencia para el profesorado, la literatura científica sigue prestando atención al potencial pedagógico de las redes sociales. El objetivo principal de esta investigación fue analizar la influencia del rol del profesorado (guía y facilitador) sobre la participación social en Twitter y la experiencia académica percibida de los estudiantes. La muestra estuvo formada por 525 futuros profesores, estudiantes de posgrado en la Universidad Nacional de Educación a Distancia. Se utilizó un diseño mixto de triangulación, un modelo teórico, una parte cuantitativa (análisis descriptivo y contraste sobre medias) y otra cualitativa (análisis de contenido, siguiendo los principios de la teoría fundamentada). Los resultados mostraron que el rol facilitador del profesor influye positivamente en la valoración de la experiencia por parte de los estudiantes y en la participación en Twitter, en mayor medida que el rol guía. Por un lado, se concluye que el uso de las redes sociales, en el ámbito educativo, proporciona un marco motivacional y de satisfacción que no lo aportan otros medios más tradicionales, como los foros, y, por otro, que un rol que facilita un proceso de aprendizaje independiente es mejor estrategia cuando hablamos de redes sociales en el aula. | ||
| − | [[Media: | + | [[Media:Santovena-Casal_Bernal-Bravo_2019a-69577_ov.pdf|<span style="color:#0645AD; font-weight: bold">Descarga aquí la versión PDF</span>]] |
==== 1. Introducción y estado de la cuestión ==== | ==== 1. Introducción y estado de la cuestión ==== | ||
| Line 271: | Line 271: | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Santovena-Casal_Bernal-Bravo_2019a-69577_ov-es015.png|center|px|]] |
Figura 1. Modelo propuesto. | Figura 1. Modelo propuesto. | ||
| Line 282: | Line 282: | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Santovena-Casal_Bernal-Bravo_2019a-69577_ov-es016.png|center|px|]] |
Figura 2. Participación del profesor en Twitter: Tweets enviados a lo largo de las semanas. | Figura 2. Participación del profesor en Twitter: Tweets enviados a lo largo de las semanas. | ||
| Line 295: | Line 295: | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Santovena-Casal_Bernal-Bravo_2019a-69577_ov-es017.png|center|px|]] |
Para el estudio de la participación en Twitter, la muestra estuvo formada por los mensajes enviados y registrados en Google TAGS hoja de cálculo v6 (Hawksey, 2013) que depende de la API de Twitter: 26.188 tweets. La selección de los tweets se realizó a través de los hashtags que identifican cada debate. La API de Twitter, aunque presenta limitaciones, posibilita la recuperación de los tweets dependiendo del número de tweets enviados durante el último mes, eliminando los más antiguos para facilitar la generación de los nuevos. A pesar de su carácter temporal, estos datos no dejan de ser un objetivo de investigación interesante (Bruns & Stieglitz, 2012; Gerlitz & Rieder, 2013), debiendo confiar en la API puesto que es el único medio que facilita la obtención de datos a gran escala (Bruns & Stieglitz, 2012). Los investigadores no disponen de otra forma de confirmar la calidad y precisión de los datos y, por tanto, es una limitación inevitable que no invalida los resultados. Como indican Gerlitz y Rieder (2013), el muestreo realizado en Twitter se basa en un muestreo no probabilístico, no representativo, puesto que la selección de la muestra siempre está limitada por la aplicación utilizada. | Para el estudio de la participación en Twitter, la muestra estuvo formada por los mensajes enviados y registrados en Google TAGS hoja de cálculo v6 (Hawksey, 2013) que depende de la API de Twitter: 26.188 tweets. La selección de los tweets se realizó a través de los hashtags que identifican cada debate. La API de Twitter, aunque presenta limitaciones, posibilita la recuperación de los tweets dependiendo del número de tweets enviados durante el último mes, eliminando los más antiguos para facilitar la generación de los nuevos. A pesar de su carácter temporal, estos datos no dejan de ser un objetivo de investigación interesante (Bruns & Stieglitz, 2012; Gerlitz & Rieder, 2013), debiendo confiar en la API puesto que es el único medio que facilita la obtención de datos a gran escala (Bruns & Stieglitz, 2012). Los investigadores no disponen de otra forma de confirmar la calidad y precisión de los datos y, por tanto, es una limitación inevitable que no invalida los resultados. Como indican Gerlitz y Rieder (2013), el muestreo realizado en Twitter se basa en un muestreo no probabilístico, no representativo, puesto que la selección de la muestra siempre está limitada por la aplicación utilizada. | ||
| Line 334: | Line 334: | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Santovena-Casal_Bernal-Bravo_2019a-69577_ov-es018.png|center|px|]] |
La Figura muestra los resultados de la dimensión 1 «Proceso de aprendizaje y adquisición de conocimiento». La propuesta pedagógica fue altamente valorada por el 70% de los estudiantes. Considerando que la participación en Twitter les ha facilitado la adquisición de conocimiento sobre materia (59,6%), teórico (42,7%), práctico (53%), colaborativo y participativo (70%) y que en la investigación han desarrollado diferentes tipos de aprendizaje: crítico (76%) y reflexivo (76%), constructivista (73,7%), conectivista (73,5%), social (81,9%) y participativo (70%), activo (61,6%). | La Figura muestra los resultados de la dimensión 1 «Proceso de aprendizaje y adquisición de conocimiento». La propuesta pedagógica fue altamente valorada por el 70% de los estudiantes. Considerando que la participación en Twitter les ha facilitado la adquisición de conocimiento sobre materia (59,6%), teórico (42,7%), práctico (53%), colaborativo y participativo (70%) y que en la investigación han desarrollado diferentes tipos de aprendizaje: crítico (76%) y reflexivo (76%), constructivista (73,7%), conectivista (73,5%), social (81,9%) y participativo (70%), activo (61,6%). | ||
| Line 361: | Line 361: | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Santovena-Casal_Bernal-Bravo_2019a-69577_ov-es019.png|center|px|]] |
Figura 3. Mapa conceptual general «Experiencia académica percibida». | Figura 3. Mapa conceptual general «Experiencia académica percibida». | ||
| Line 370: | Line 370: | ||
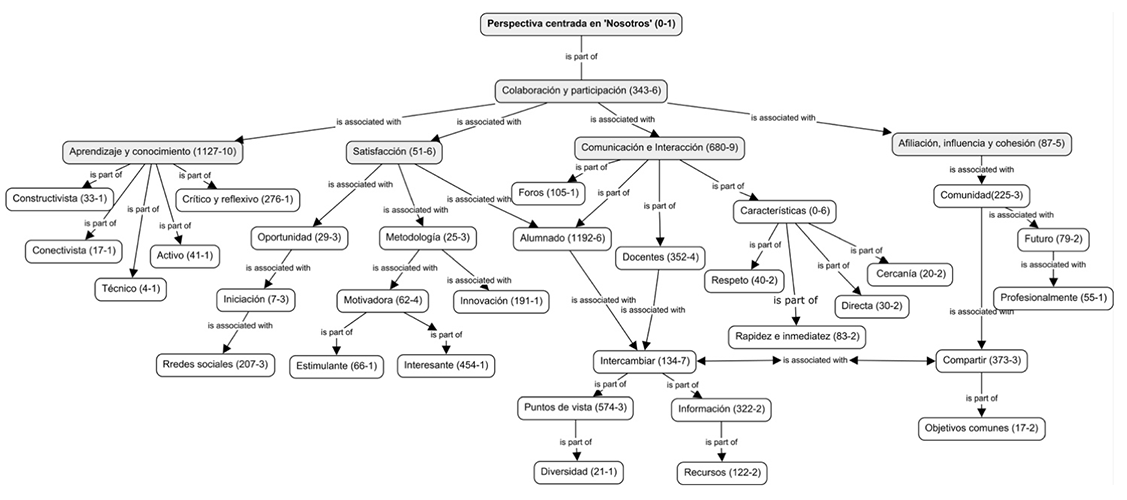
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Santovena-Casal_Bernal-Bravo_2019a-69577_ov-es020.png|center|px|]] |
Figura 4. Mapa conceptual «Perspectiva centrada en Nosotros». | Figura 4. Mapa conceptual «Perspectiva centrada en Nosotros». | ||
Latest revision as of 15:20, 27 March 2019
Pulsa aquí para ver la versión en Español (ES)
Abstract
Analyzing the influence of social media on the learning process is no longer a novel idea; however, due to its importance for students and consequently for teachers, research continues to explore the pedagogical potential of social media. The main objective of the present study was to analyze the influence of teacher roles (guide or facilitator) on students’ social participation in Twitter and their perceived academic experience. The sample consisted of 525 future teachers, all of the Master’s degree students at Spain’s National Distance Education University (UNED). We used a mixed triangulation design, a theoretical model, quantitative methods (descriptive analysis and contrast of means) and qualitative methods (content analysis following the principles of grounded theory). Our results showed that the teacher’s role as a facilitator exerted a more positive influence on how students assessed their experience and on their participation on Twitter than the role as a guide. We conclude that the use of social media sites in education offers a motivating and satisfying framework that is not provided by other more traditional means such as forums, and that a role that facilitates independent learning is a better strategy when using social media in the classroom.
1. Introduction and status of the issue
Most experts accept the need to develop new educational models where learning is adapted to characteristics of the networked society (complexity, connectivity, and speed) (Jenkins, 2012). Thinking is developed within the context of social participation: experiences of interacting with others establish our way of being present in the world, something that is critical to learning (Gee, 2004). These new ways of learning must be frustrating and interesting at the same time, and avoid thinking processes that only rely on what is easy and simple (Gee, 2004).
Research studies about online learning have underscored the importance of interaction (between students, with the teacher, and with the content) and its positive influence on academic performance (Kurucay & Inan, 2017). Student-student and student-teacher interaction reinforce a sense of belonging (Luo, Zhang, & Qi, 2017) and, consequently, a sense of cohesion. Discussion and reflection among students facilitate learning and improve their perceived academic experience (Lee & Bonk, 2016). Students seem to give more importance to relations with other students than with the teacher (Smith, 2016), and student-student interaction is a verified predictor of student satisfaction (Ali & Ahmad, 2011).
Historically, many authors (Ausubel, 1981) have acknowledged the important role of the teacher, who is responsible for providing opportunities for debate and knowledge creation in an interactive setting. When teachers provide online students with different moments for learning and differing degrees of interaction, they are ensuring a positive outcome (Battalio, 2007). Ouyang and Scharber (2017) underscored the importance of modifying the teacher’s role over the school year to facilitate student cohesion and learning. These authors found that during the first part of the school year, there was a greater need for participation and interaction from teachers (a leadership role), evolving into a more passive position with time (facilitator and observer role). In fact, the mere presence or absence of the teacher influences student satisfaction (Battalio, 2007; Ladyshewsky, 2013), as well as their participation and the communication process itself (Jaggars & Xu, 2016). In short, depending on the teacher’s behavior, there are significant differences in the students’ behavior (An, Shin, & Lim, 2015; Marcos-García, Martínez-Monés, & Dimitriadis, 2015).
Technology (such as social media) naturally facilitates these connected learning experiences. According to Jenkins (2012), not only does the student need information and resources but more importantly, rich environments involving different types of learning. Application of social media in education has produced contradictory outcomes.
On the one hand, social media is recognized as having pedagogical potential (Scott, Sorokti, & Merrell, 2016) and capacity for knowledge exchange within the educational context (Wong, Sing-Chai, & Poh-Aw, 2017), and as instrumental in facilitating communication, exchange of resources, and collaboration (Tuzel & Hobbs, 2017). Social media, as an alternative to more traditional learning models, can promote engagement, interaction between students (Alhazmi & Rahman, 2013), and motivation (Gutiérrez-Porlán, Román-García, & Sánchez-Vera, 2018). Eid and Al-Jabri (2016) found a positive relationship between the level of students’ motivation and the exchange of information and discussion on Twitter. Moreover, the use of social media has been related to students having a positive academic perception (Alhazmi & Rahman, 2013; Lee & Bonk, 2016), to their perception of interaction and communication processes (Smith, 2016), to satisfaction and usefulness (AL-Rahmi & Othman, 2013) and to group cohesion and belonging to a group with shared interests (Carpenter & Krutka, 2014). Twitter may facilitate the creation of a community with shared interests, extending interpersonal relations both inside and outside the educational sphere (Carpenter & Krutka, 2014). The social interaction processes and patterns of information exchange that can take place on Twitter positively influence the sense of community among students (Blight, Ruppel, & Schoenbauer, 2017).
On the other hand, authors recognize that while social networks like Facebook offer great opportunities for communicating and socializing, they may become a source of distraction (Gupta & Irwin, 2016) and therefore have a negative effect on academic performance (Bellur, Nowaka, & Hullb, 2015). They affirm that the more time is invested in Facebook, the lower the level of achievement (Paul, Baker, & Cochran, 2012), due to less time being spent on studying (Kirschner & Karpinski, 2010). With regard to Twitter, Tang and Hew (2017: 1) state that: “Although Twitter shows promise in improving interactions among learners and teachers, causality between Twitter use and learning performance remains to be conclusively established”. Furthermore, several research studies have indicated that microblogging represents few actual conversations, it reinforces one-directional discourse (Arrabal, & de Aguilera, 2016): individualistic action more than group action or interaction, monologues more than dialogues (Santoveña-Casal, 2017). Finally, it is worth mentioning that the use of Twitter in academic activities prompts complaints from students about increased workload (Chen & Chen, 2012), difficulty expressing oneself due to the character limitation (Prestridge, 2014) and difficulty in handling the large quantities of information (Lin, Hoffman, & Borengasser, 2013).
Briefly, then, the objective of the present study was to analyze how the teacher role (guide or facilitator) –as played out over four academic discussions on Twitter– affected social participation online and the perceived academic experience. The following hypotheses are being tested:
• H1. The type of role enacted by the teacher (guide or facilitator) influences the student’s academic participation using Twitter.
• H2. The type of role enacted by the teacher (guide or facilitator) influences the student’s perceived academic experience.
• H3. Social participation on a network (Twitter) positively influences how students assess the academic experience, the learning process, the interaction process (student-student and student-teacher) and their feeling of belonging, of influence and of group cohesion.
The research model, including its three hypotheses, is presented in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Proposed model.
2. Material and method
2.1. Context
This study took place within an official Master’s degree program for future teachers at Spain’s National Distance Education University (UNED). Students were to interact and exchange opinions in two mandatory discussions over the Twitter social network. Two additional, optional discussions were also offered.
The teacher’s role in the discussions was modified over the course of the semester. We adopted the classification from Marcos-García, Martínez-Monés, and Dimitriadis (2015) and from Ouyang and Scharber (2017), who categorize teacher roles as guide, facilitator or observer. In this class, the roles of Guide and Facilitator were used exclusively, making a change midway through the discussions (Figure 2).
Figure 2. Teacher participation on Twitter: Tweets sent over the four-week period.
a) The Guide role implies that the teacher is at the center of learning and is the leader who heads up the process. She/he guides the students, offers instructions, provides the material necessary for learning. Enacting the role of guide, the teacher interacted with students through the Twitter conversations, and sent links, educational resources, and news, for the purpose of enriching the discussion.
b) The Facilitator role implies that the teacher monitors student activity, and acts as a mediator if there are conflicts. On Twitter, the teacher adopted a secondary role, limiting the number of messages sent. She/he did not intervene in the conversations or send supplementary resources.
2.2. Population and sample
The population was made up of all students pursuing a Master’s degree (720). To study the perceived academic experience, the sample included students who answered the questionnaire (the same questionnaire applied at two different moments), for a total of 525 students: 249 answered the questionnaire upon completion of Discussion 1 and Discussion 2 where the role of guide was adopted, and 276 students answered upon completion of Discussion 3 and Discussion 4 where the facilitator role was adopted. Women represented 66.3% (N= 348) of the sample. The participants ranged from 21 to 53 years in age, with a mean of 32.5 years. Table 1 shows the sampling error that was found based on simple random sampling in the most disadvantaged case (p=q= 0.5).
For the study of Twitter participation, the sample was made up of the messages sent and registered in a Google TAGS spreadsheet v6 (Hawksey, 2013) connected to Twitter API: 26188 tweets. Tweets were selected using the hashtags that identify each discussion. Twitter API, despite some limitations, makes it possible to recover tweets depending on the number of tweets sent during the past month, eliminating the oldest messages in order to facilitate the creation of new ones. Despite their temporary nature, these data are nonetheless an interesting research objective (Bruns & Stieglitz, 2012; Gerlitz & Rieder, 2013); the API must be trusted, given that it is the only means of obtaining large-scale data (Bruns & Stieglitz, 2012). The researchers have no other way to confirm data quality and accuracy; this is an unavoidable limitation that does not invalidate the results. As indicated by Gerlitz and Rieder (2013), Twitter sampling is based on nonprobabilistic sampling that is not representative, given that sample selection is always limited by the application used.
2.3. Design and data collection instruments
The study is based on a mixed triangulation design, a theoretical model, quantitative methods (descriptive analysis and contrast of means) and qualitative methods (content analysis following the principles of grounded theory). We used SPSS v24 for statistical analysis and Atlas Ti HM for content analysis.
The quantitative study was based on descriptive analysis and contrast of means (test for independent samples) in order to learn how the variable of teacher’s role (Guide or Facilitator) influenced the dependent variables (Perceived academic experience and Participation on Twitter). Given the lack of normal sample distribution of variables, and in order to confirm Student’s t data, we used the Mann-Whitney U. In addition, we determined effect sizes for the tests (Cohen’s D and correlation coefficient r).
In order to analyze the perceived academic experience, a Likert-type, ad hoc survey was used to collect students’ opinion. Supplementary open-ended questions were also included to add qualitative information to the closed response questions. Content validity was based on the scientific literature, in variables considered fundamental by authors like Kurucay and Inan (2017) (demographic data, satisfaction, interaction, perception of collaboration, perception of learning) and Luo, Zhang, & Qi (2017) (student-student interaction, student-teacher interaction, interaction with the content, belonging and influence). In addition, we requested the collaboration of a group of experts (4 teachers) who indicated changes that should be made to a preliminary version of the questionnaire.
This version was applied to a sample of 40 students, which helped to confirm that the instructions and questions were well understood. A Cronbach alpha of .960 was obtained for reliability, far above the recommended minimum (.70). Later, exploratory factor analysis was applied (using Varimax rotation and main components), and each individual item was grouped within the corresponding construct, for a total explained variance of 66.7%. The following dimensions were found:
• Dimension 1. Learning process and acquisition of knowledge: .943. This assesses the academic experience on Twitter, in this class subject, as a space for knowledge acquisition that is constructivist, reflective and critical, connectivist, individualistic, social and participative, active. It also assesses the teaching methodology in general.
• Dimension 2. Belonging and influence in class, and group cohesion: .921.
• Dimension 3. General aspects: .879. This analyzes quality, satisfaction and usefulness of the experience and the value added from the communication and interaction process, in general, and on Twitter in particular.
• Dimension 4. Student-student interaction: .855. This examines the frequency of Twitter use; the degree at which information is shared, regarding the class subject and regarding problems with other students; Twitter’s contribution to improved interpersonal relations between the students, interpersonal skills and online communication skills and the degree that these have made it possible to form a community or shared-interest group.
• Dimension 5. Student-teacher interaction: .896. This examines to what extent students request information from the teacher with regard to class content, the class itself and the activity on Twitter.
• Dimension 6. Use of forums: .518. This analyzes the frequency of forum usage and their added value.
The qualitative study is based on content analysis of the responses to open-ended questions on the questionnaire. The content analysis follows indications from García-Llamas, González and Ballesteros (2001): 1) Defining the content universe and sample selection; 2) Deciding on the unit of analysis and establishing the categories. The main categories are established by the dimensions identified in the scientific literature (Kurucay & Inan, 2017; Luo, Zhang, & Qi, 2017). These categories are organized in the superfamily (Perceived academic experience) and in two families that fall under it: the We-focused perspective, to which the Collaboration and participation code is assigned; and the I-focused perspective, to which the Criticism and Difficulties code is assigned. The results of the code categorization are presented in a concept map, indicating their materialization (frequency of appearance) and density (number of codes that relate to each). In addition, we include the literal text of the student comments that were used, indicating the number of the main document of analysis and the line from which the comment is taken.
3. Results
3.1. Social participation on Twitter
High participation on Twitter was recorded, with 26,188 tweets, 5,639 retweets, and 6,089 links within the messages. Students participated especially during the second and third week when the discussions were mandatory. Moreover, they participated more on Twitter when the teacher adopted the Facilitator role when they sent 56.3% of the total messages. A significantly greater number of student messages on Twitter was observed when the teacher enacted a facilitator role [F(2.8) t=–3.06, Sig. (bilateral)=.002]. The data are confirmed by Mann-Whitney U, but the effect size is null (r=0.07 and d=0.14).
3.2. Perceived academic experience
Student assessment of this learning experience was very positive. Over 64% of the students rated all the dimensions high or very high, and this rating was significantly more positive when the teacher adopted the facilitator role: Quality [F(9.6) t=2.7, Sig. (bilateral)=.006], Usefulness [F(6.7) t=2.1, Sig. (bilateral)=.034], Satisfaction [F(10.8) t=2.9, Sig. (bilateral)=.004], and Value added to the Twitter communication process [F (4.02) t=4.0, Sig. (bilateral)=.000]. The Mann-Whitney U confirms these significant differences (Table 2). The effect size is small for Quality of the learning experience (r=0.12; d=0.24), Satisfaction (r=0.12; d=0.25) and Value added to the Twitter communication process (r=0.16; d=0.34); and null for Usefulness (r=0.09; d=0.09).
Figure shows the results of Dimension 1, “Learning process and acquisition of knowledge”. The teaching methodology was highly rated by 70% of the students. They considered that participation on Twitter helped them acquire knowledge about the subject matter (59.6%), theoretical knowledge (42.7%), practical knowledge (53%), collaborative and participative knowledge (70%) and that they had experienced different types of learning in this class: critical (76%) and reflective (76%), constructivist (73.7%), connectivist (73.5%), social (81.9%) and participative (70%), active (61.6%).
When the teacher adopted the facilitator role, students ratings of their learning through Twitter and in the class as a whole were significantly higher in the following variables:
a) Twitter facilitates acquisition of knowledge [F(17.22) t=4.7, Sig. (bilateral)=.000], related to the material [F(15.4) t=4.6, Sig. (bilateral)=.000], theoretical [F(.48) t=4.02, Sig. (bilateral)=.000] and practical [F(1.7) t=4.02, Sig. (bilateral)=.039].
b) This class facilitates critical and reflective learning [F(8.2) t=2.9, Sig. (bilateral)=.003], constructivist learning [F(5.5) t=2.6, Sig. (bilateral)=.007], social learning [F(2.04) t= 2.9, Sig. (bilateral)= .003] and individualistic learning [F(0.090) t=2.6, Sig. (bilateral)=.009].
c) Assessment of this teaching method [F(8..) t=2.6, Sig. (bilateral)=.009].
The Mann-Whitney U confirms these significant differences. For all variables, the effect size is small (r between 0.1 and 0.25 and d between 0.41 and 0.21), or null for Twitter facilitates practical knowledge acquisition (r=0.08; d=0.17).
Regarding Dimension 2, “Belonging, influence in class and group cohesion”, we observed that students see themselves as part of the class group, and they feel they have good ties to other students, in a high or very high degree. Regarding Group cohesion, students manifested the intent, to a high or very high degree, to prolong their participation in the online degree program and/or the social network, to access the online course and/or social media in the future. On the other hand, they consider that their influence on the class and/or the online degree is low. No significant differences were found in any of the aspects analyzed in this dimension as a function of the teacher’s role. Data are confirmed by the Mann-Whitney U. Two dimensions were found in relation to the interaction processes: student-student interaction (Dimension 4) and student-teacher interaction (Dimension 5).
51.6% of the students confirmed that they use Twitter almost always; 42.5% confirmed that they interact with their classmates by sharing class information; 45.7% claimed to share knowledge frequently with their classmates.
Most students considered that participation on Twitter helped them improve, in a high or very high degree, their interpersonal relations with classmates (69.3%), their interpersonal and online communication skills (63%) and they affirmed that they were able to form a community or shared interests group (71.5%). Significant differences as a function of the teacher’s role were only found for perceived improvement in interpersonal relations between the students [F(10.3) t=3.2, Sig. (bilateral)=.001], with greater improvement reported when the teacher adopted a facilitator role. Data are confirmed by the Mann-Whitney U. The effect size was small (r= 0.14; d=0.28).
Elsewhere, regarding the process of interacting with the teacher, students perceived that they had little interaction with the teacher, and this tendency is heightened when the teacher adopted the facilitator role: 54.5% affirmed that they had never requested information about the class itself or its content. Significant differences were found in: Interacting with the teacher to request information about content, about the class itself, and about the activity. Differences were confirmed with Mann-Whitney U. The effect size is small (r between 0.10 and 0.12 and d between 0.22 and 0.25).
In Dimension 6, “Use of forums” most of the students claimed to use them infrequently (52.4%). Moreover, the value that forums add to the class was considered high or very high by only 33% of the students, and low, very low or null by 34% of the students. When the teacher adopted a facilitator role, students claimed to use them more often. The effect size was small. Data are confirmed by the Mann-Whitney U.
Figure 3. General concept map “Perceived academic experience”.
Content analysis of students’ descriptions of the perceived academic experience revealed three main aspects (Figure 3). First, two different perspectives on the academic experience stand out: students who gave a positive rating to participation on Twitter made a we-centered assessment, in the processes of collaborating and participating with their fellow Master’s degree students. By contrast, those who criticized and perceived more difficulty in the academic experience made a self-focused analysis. Second, an interrelationship was observed between the main dimensions: general aspects (satisfaction), student-student and student-teacher interaction process, learning and knowledge acquisition process, and belonging and influence in the class and group cohesion. Third, there were no differences in student comments about the teacher’s role, nor was there a better rating of the teacher in the phase of Guide role as compared to the phase of the Facilitator role.
Students gave a very high rating not only to the activity performed on Twitter but also to the class in general. They primarily emphasized its innovative and motivating nature, considering it of great interest, entertaining, rewarding, attractive, fun [“This methodology seems much more attractive to me than the traditional forum-based methodology” (6:668)]. They commented on the importance of getting started in Twitter and overcoming one’s hesitation and initial reluctance to use it [“Despite being reluctant to use Twitter, and even more so for a class, it turned out to be very enriching for me” (14:1171)]. Student-student interaction stood out as the determining factor for satisfaction [“the satisfying effects that it had on interaction and communication with my classmates” (1:120)]. They considered it to be the first time they were able to have direct, spontaneous, close and democratic contact with other Master’s degree students [“I very much liked the chance to interact directly with my classmates, and to have a much closer relationship” (1:747)] and to learn different points of view [“a large number of participants gave rise to a broad range of opinions and viewpoints” (1:465)]. Student-student interaction led to a feeling of belonging and cohesion within the group, the feeling of being part of a community was a much-emphasized aspect [“The feeling of belonging is what most prompted me to do this activity on a regular basis” (7:598)]. Furthermore, through the communication and discussion process, students acquired theoretical and practical knowledge; they exchanged ideas, information, and knowledge in a fun, motivating way [“it was a different way to learn, very dynamic and motivating” (1:548)] (Figure 4).
Figure 4. Concept map “We-centered perspective”.
There were a few criticisms of the activity, but they are interesting to analyze. They focused on the workload involved in participation, the excessive time required for participating on Twitter [“… the experience … seems like a heavy workload to me (in terms of hours spent)” (6:642)]. They criticized the mandatory nature of the task, and students were worried about invasion of privacy from using the networks in the academic sphere [(“it seems that no matter how many security filters you use, any hacker can steal your identity, or your private like may simply become public” (5:760)]. They also criticized the chaos involved with so many people participating, the large volume of tweets, and the absolute lack of control over the communication [“The Twitter activity is chaotic, too many open discussions” (2:552)] and the anxiety involved in this process [“I enjoyed it… but there were times when … I felt stressed by the large number of interactions” (2:547)]. It is interesting to note that the students who negatively assessed the activity made I-centered comments, [“I have always seen this as something that I cannot really control, and therefore I do not want to make it part of my life” (5:579); “I don’t feel comfortable expressing myself on media…” (6:622)]. In fact, these students acknowledge null or little belonging and group cohesion [“I did not come here to make friends, I do not believe in the value of relationships per se” (8:499)].
4. Discussion and conclusions
The main objective of this study was to analyze how the teacher role (guide or facilitator) –played out over four academic discussions on Twitter– influenced social participation online and the perceived academic experience. Results indicate that the teacher role did not influence students’ social participation, and it had little influence on the perceived academic experience, though it is highly interesting for the educational context.
Several authors (Durlak, 2009; Frías, Pascual, & García-Pérez, 2000) consider that a small effect size can have great practical importance in a specific context, and above all, as stated by Glass, McGaw, and Smith (1981), the practical importance of an effect depends entirely on its relative costs and benefits. We consider that the data offered by this research study has high practical value for education. Given that adopting a facilitator role on Twitter, a more passive role, seems to improve students’ perception of the teaching methodology, their degree of satisfaction, how they rate the communication and interaction process over Twitter, as well as the contribution of microblogging to the acquisition of learning and knowledge and improved interpersonal relations. According to Battalio (2007), when teachers provide students with different educational moments with varying degrees of interaction, they ensure a positive outcome in online learning. Moreover, this type of methodology does not involve a high cost, and its benefits can be very large.
We observed that the teacher’s role did not influence the feeling of belonging, influence or cohesion. In fact, students stated that they practically never approached the teacher to ask questions. This tendency was more marked when the teacher adopted a facilitator role, and by contrast, there was a more perceived improvement in interpersonal relations on Twitter between the students. As seen in research by Smith (2016), students give greater importance to student-student interactions than to student-teacher interaction in learning over social media. It is probable that adopting a more passive role, leaving room for interaction between students, is an adequate methodology for learning on social media. In fact, students underscored the importance of interaction between students and how this relationship influenced their feeling of belonging to the group. These data are confirmed by content analysis where student-student interactions were described as motivating and highly satisfying. Results concur with research by Ali and Ahmad (2011), who established interaction between students as a predictor of satisfaction.
In the same line as previous research studies, we conclude that networked social participation (Twitter) positively influences how students rate the academic experience (Alhazmi & Rahman, 2013; Lee & Bonk, 2016), the learning process, and their feeling of belonging and group cohesion (Blight, Ruppel, & Schoenbauer, 2017; Carpenter & Krutka, 2014). The students gave very positive ratings for the innovative nature of the methodology; they indicated the value of Twitter as a motivational space, positively relating discussion, information exchange and resource exchange to motivation, as indicated by Eid and Al-Jabri (2016).
Students assigned a high value to Twitter as a means for communicating and interacting, thereby contradicting other research studies that emphasize the scarcity of conversations registered on the network (Arrabal, & de Aguilera, 2016) and a tendency to carry on monologues more than dialogues (Santoveña-Casal, 2017). The social network may be considered an environment that facilitates the adoption of new educational models based on connected learning and social participation, aspects underscored by Jenkins (2012) and Gee (2004) as fundamental to the networked society. Furthermore, students have explicitly commented on the importance of getting started on Twitter and overcoming hesitation and initial fears. Twitter produced feelings of frustration along with a high level of interest in the task aspects that Gee (2004) points to as fundamental to new forms of learning.
At the same time, this network is not without drawbacks when used in the educational context. In the same line as other research studies, some students criticized the extra workload that was involved (Chen & Chen, 2012) and the sensation of chaos and stress when struggling to manage the shared information (Lin, Hoffman, & Borengasser, 2013). Students who made a negative assessment usually expressed their criticism and difficulties from a focus on self, on their problems controlling the communication process, their anxiety problems, or an absolute lack of interest in others. This is an especially interesting aspect to be analyzed in future research: how do personality variables influence academic participation on social media? What role does internal and external locus of control have in these experiences?
In summary, it seems that participation on Twitter enables communication and interaction, facilitates social participation and increases academic satisfaction in students; however, how students are influenced by the change in teacher role remains to be conclusively established. Studying the role of the teacher that has a special interest since it sheds light on new online methodologies. In conclusion, the use of social media in university education offers motivational value not provided by other more traditional media like forums; on the other hand, a teacher role that reinforces an independent learning process is probably a better strategy when we speak of social media in the classroom.
References
Al-Rahmi, W.M., & Othman, M.S. (2013). Evaluating student’s satisfaction of using social media through collaborative learning in higher education. International Journal of Advances in Engineering & Technology, 6(4),1541-1551. https://bit.ly/2vJbwXl
Alhazmi, A.K., & Rahman, A.A. (2013). Facebook in higher education: Students’ use and perceptions AISS. Advances in Information Sciences and Service Sciences, 5(15), 32-41. https://bit.ly/2Ph5QMv
Ali, A., & Ahmad, I. (2011). Key factors for determining students’ satisfaction in distance learning courses: A study of Allama Iqbal Open University. Contemporary Educational Technology, 2(2), 118-134. https://bit.ly/2vLRjzU
An, H., Shin, S., & Lim, K. (2009). The effects of different instructor facilitation approaches on students’ interactions during asynchronous online discussions. Computers & Education, 53, 749-760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2009.04.015
Arrabal, G., & de-Aguilera, M. (2016). Communicating in 140 characters. How journalists in Spain use Twitter. [Comunicar en 140 caracteres. Cómo usan Twitter los comunicadores en España]. Comunicar, 46, 9-17. https://doi.org/10.3916/C46-2016-01
Ausubel, D. (1981). Psicología educativa. Un punto de vista cognoscitivo. México: Trillas. https://bit.ly/2Bf5djx
Battalio, J. (2007). Interaction online: A reevaluation. Quarterly Review of Distance Education, 8(4), 339-352. https://bit.ly/2PgsXqm
Bellur, S., Nowaka, K.L., & Hullb, K.S. (2015). Make it our time: In class multitaskers have lower academic performance. Computers in Human Behavior, 53, 63-70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2015.06.027
Blight, M.G., Ruppel, E.K., & Schoenbauer, K.V. (2017). Cyberpsychology. Behavior, and Social Networking, 20(5), 314-319. https://doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2016.0505
Bruns, A., & Stieglitz, S. (2012). Quantitative Approaches to Comparing Communication Patterns on Twitter. Journal of Technology in Human Services, 30(3-4), 160-185. https://doi.org/10.1080/15228835.2012.744249
Carpenter, J.P., & Krutka, D.G. (2014). How and why educators use Twitter: A survey of the field. Journal of Research on Technology in Education, 46(4), 414-434. https://doi.org/10.1080/15391523.2014.925701
Chen, L., & Chen, T.L. (2012). Use of Twitter for formative evaluation: Reflections on trainer and trainees’ experiences: Colloquium. British Journal of Educational Technology, 43(2), E49-E52, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8535.2011.01251.x
Chen, L., & Chen, T.L. (2012). Use of Twitter for formative evaluation: Reflections on trainer and trainees’ experiences: Colloquium. British Journal of Educational Technology, 43(2), E49-E52, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8535.2011.01251.x
Durlak, J.A. (2009). How to select, calculate, and interpret effect sizes. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 34(9), 917-928. https://doi.org/10.1093/jpepsy/jsp004
Eid, M.I.M., & Al-Jabri, I.M. (2016). Social networking, knowledge sharing, and student learning: The case of university students. Computers & Education, 99, 14-27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2016.04.007
Frías, M.D., Pascual, J., & García-Pérez, J.F. (2000). Tamaño del efecto del tratamiento y significación estadística. Psicothema, 12(2), 236-240. https://bit.ly/2MvuiuM
García-Llamas, J.L., González, M.A., & Ballesteros, B. (2001). Introducción a la investigación en educación II. Madrid: UNED. https://bit.ly/2OGQzmK
Gee, J.P. (2008). Lo que nos enseñan los videojuegos sobre el aprendizaje y el alfabetismo. Málaga: Aljibe. https://bit.ly/2vVVhX9
Gerlitz, C., & Rieder, B. (2013). Mining One Percent of Twitter: Collections, Baselines, Sampling. Journal of Media and Culture, 16(2). https://bit.ly/2vVVhX9
Glass, G.V., McGaw, B., & Smith, M.L. (1981). Meta-analysis in social research. London: Sage. https://bit.ly/2MRfNyu
Gupta, N., & Irwin, J.D. (2016). In-class distractions: The role of Facebook and the primary learning task. Computers in Human Behavior, 55(B), 1165-1178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2014.10.022
Gutiérrez-Porlán, I., Román-García, M., & Sánchez-Vera, M. (2018). Strategies for the communication and collaborative online work by university students. [Estrategias para la comunicación y el trabajo colaborativo en red de los estudiantes universitarios]
Hawksey, M. (2013). Twitter archiving Google spreadsheet (TAGS). https://bit.ly/1GmM3nV
Jaggars, S.S., & Xu, D. (2016). How do online course design features influence student performance? Computers & Education, 95, 270-284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2016.01.014
Jenkins, H. (2012). Connected learning: Reimagining the experience of education in the information age. Blog Confessions of an ace-fan. https://bit.ly/2OH2tgp
Kirschner, P.A., & Karpinski, A.C. (2010). Facebook and academic performance. Computers in Human Behavior, 26(6), 1237-1245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2010.03.024
Kurucay, M., & Inan, A. (2017). Examining the effects of learner-learner interactions on satisfaction and learning in an online undergraduate course. Computers & Education, 115, 20-37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2017.06.010
Ladyshewsky, R.K. (2013). Instructor presence in online courses and student satisfaction. International Journal for the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning, 7(1). https://doi.org/10.20429/ijsotl.2013.070113
Lee J., & Bonk, C.J. (2016). Social network analysis of peer relationships and online interactions in a blended class using blogs. The Internet and Higher Education, 28, 35-44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2015.09.001
Lin, M.F.G., Hoffman, E.S., & Borengasser, C. (2013). Is social media too social for class? A case study of Twitter use. TechTrends, 57(2), 39-45. https://bit.ly/2vO1AM0
Luo, N., Zhang, M., & Qi, D. (2017). Effects of different interactions on students’ sense of community in e-learning environment. Computers & Education,115, 153-160, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2017.08.006
Marcos-García, J.A., Martínez-Monés, A., & Dimitriadis, Y. (2015). DESPRO: A method based on roles to provide collaboration analysis support adapted to the participants in CSCL situations. Computers & Education, 82, 335-353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.com
Ouyang, F., & Scharger, C. (2017). The influences of an experienced instructor’s discussion design and facilitation on an online learning community development: A social network analysis study. The Internet and Higher Education, 35, 34-47. https://doi.or
Paul, J.A., Baker, H.M., & Cochran, J.D. (2012). Effect of online social networking on student academic performance. Computers in Human Behavior, 28, 2117-2127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2012.06.016
Prestridge, S. (2014). A focus on students’ use of Twitter–their interactions with each other, content and interface. Active Learning in Higher Education, 15(2), 101-115. https://doi.org/10.1177/1469787414527394
Santoveña-Casal, S. (2017). Conversations, debates and affiliation networks on Twitter. Turkish Online Journal of Educational Technology (TOJET), 16(3), 47-59. https://bit.ly/2nKRJ5o
Scott, K.S., Sorokti, K.H., & Merrell, J.D. (2016). Learning ‘beyond the classroom’ within an enterprise social network system. The Internet and Higher Education, 29, 75-90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2015.12.005
Smith, E.E. (2016). A real double-edged sword: Undergraduate perceptions of social media in their learning. Computers & Education, 103, 44-58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2016.09.009
Tang, Y., & Hew, F.K. (2017). Using Twitter for education: Beneficial or simply a waste of time? Computers & Education,106, 97-118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2016.12.004
Tuzel, S., & Hobbs, R. (2017). The Use of Social Media and Popular Culture to Advance Cross-Cultural Understanding. [El uso de las redes sociales y la cultura popular para una mejor comprensión intercultural]. Comunicar, 51, 63-72. https://doi.org/10.391
Wong, L., Sing-Chai, C., & Poh-Aw, G. (2017). Seamless language learning: Second language learning with social media. [Aprendizaje de idiomas «sin costuras»: Aprendizaje de segundas lenguas y redes sociales]. Comunicar, 50, 9-21. https://doi.org/10.3916/
Click to see the English version (EN)
Resumen
El análisis de la influencia de las redes sociales en el proceso de aprendizaje ya no es una novedad. Sin embargo, debido a su importancia para el alumnado y en consecuencia para el profesorado, la literatura científica sigue prestando atención al potencial pedagógico de las redes sociales. El objetivo principal de esta investigación fue analizar la influencia del rol del profesorado (guía y facilitador) sobre la participación social en Twitter y la experiencia académica percibida de los estudiantes. La muestra estuvo formada por 525 futuros profesores, estudiantes de posgrado en la Universidad Nacional de Educación a Distancia. Se utilizó un diseño mixto de triangulación, un modelo teórico, una parte cuantitativa (análisis descriptivo y contraste sobre medias) y otra cualitativa (análisis de contenido, siguiendo los principios de la teoría fundamentada). Los resultados mostraron que el rol facilitador del profesor influye positivamente en la valoración de la experiencia por parte de los estudiantes y en la participación en Twitter, en mayor medida que el rol guía. Por un lado, se concluye que el uso de las redes sociales, en el ámbito educativo, proporciona un marco motivacional y de satisfacción que no lo aportan otros medios más tradicionales, como los foros, y, por otro, que un rol que facilita un proceso de aprendizaje independiente es mejor estrategia cuando hablamos de redes sociales en el aula.
1. Introducción y estado de la cuestión
La necesidad de desarrollar nuevos modelos educativos, basados en un aprendizaje adaptado a las características de la sociedad en red (complejidad, conectividad y velocidad), es aceptado por la mayoría de los expertos (Jenkins, 2012). En este contexto de participación social, tiene lugar el desarrollo del pensamiento, puesto que las experiencias en interacción con otros establecen nuestra forma de estar en el mundo, lo que es lo decisivo para el aprendizaje (Gee, 2004). Estas nuevas formas de aprender deberán ser frustrantes e interesantes al mismo tiempo y evitar procesos de pensamiento basados exclusivamente en lo cómodo y sencillo (Gee, 2004).
En cursos en línea, las investigaciones han destacado la importancia de la interacción (entre los estudiantes, con el profesor y con los contenidos) y su influencia positiva en el rendimiento académico (Kurucay & Inan, 2017). La interacción alumno-alumno y alumno-profesor refuerza el sentido de pertenencia (Luo, Zhang, & Qi, 2017) y, por tanto, el sentimiento de cohesión de los estudiantes. La discusión y reflexión entre los estudiantes facilita el aprendizaje y mejora la percepción académica (Lee & Bonk, 2016). Los estudiantes parecen dar más importancia a las relaciones entre estudiantes que con el profesor (Smith, 2016), constatándose la interacción alumno-alumno como predictor de la satisfacción de los estudiantes (Ali & Ahmad, 2011).
La importancia del rol del profesor, como responsable de aportar oportunidades de debate y creación de conocimiento en un entorno social de interacción ha sido recogido tradicionalmente por múltiples autores (Ausubel, 1981). Al proporcionar a los estudiantes diferentes momentos educativos con diversos grados de interacción, los profesores garantizan que los estudiantes en línea tengan un resultado positivo (Battalio, 2007). Ouyang y Scharber (2017) destacaron la importancia de modificar el rol del profesor a lo largo del curso y así facilitar la cohesión y el aprendizaje en los estudiantes. Estos autores encontraron que durante las primeras etapas del curso era necesario una mayor participación e interacción del profesorado (rol de liderazgo), para posteriormente adoptar una posición más pasiva (rol facilitador y observador). De hecho, la simple presencia o ausencia del profesor influye en la satisfacción del estudiante (Battalio, 2007; Ladyshewsky, 2013), así como en la participación y en el proceso de comunicación (Jaggars & Xu, 2016). En síntesis, dependiendo del comportamiento del profesor se producen cambios significativos en la conducta de los estudiantes (An, Shin, & Lim, 2015; Marcos-García, Martínez-Monés, & Dimitriadis, 2015).
Las tecnologías –como las redes sociales– facilitan estas experiencias de aprendizaje conectado de manera natural. Como afirma Jenkins (2012), no solo es aportar al estudiante información y recursos, sino lo que es más importante, entornos ricos con diferentes tipos de aprendizajes. Al aplicar las redes sociales en educación los resultados han sido contradictorios.
Por un lado, se reconoce el potencial pedagógico de las redes sociales (Scott, Sorokti, & Merrell, 2016), su capacidad para intercambiar conocimiento dentro del contexto educativo (Wong, Sing-Chai, & Poh-Aw, 2017), y como herramientas que facilitan la comunicación, el intercambio de recursos y la colaboración (Tuzel & Hobbs, 2017). Las redes sociales como alternativa a modelos de aprendizaje más tradicionales pueden promover el compromiso, la interacción entre los estudiantes (Alhazmi & Rahman, 2013) y la motivación (Gutiérrez-Porlán, Román-García, & Sánchez-Vera, 2018). Eid y Al-Jabri (2016) encontraron una relación positiva entre el nivel de motivación de los estudiantes y el intercambio de información y debate en Twitter. Además, se han hallado relaciones entre utilizar las redes sociales y una percepción académica positiva de los estudiantes (Alhazmi & Rahman, 2013; Lee & Bonk, 2016), percepciones sobre las interacciones y los procesos de comunicación (Smith, 2016), sobre la satisfacción y utilidad (Al-Rahmi & Othman, 2013) y sobre la cohesión y pertenencia a un grupo con intereses compartidos (Carpenter & Krutka, 2014). Twitter puede facilitar la creación de una comunidad con intereses compartidos, ampliando las relaciones interpersonales, tanto dentro como fuera del ámbito educativo (Carpenter & Krutka, 2014). Los procesos de interacción social y los patrones de intercambio de información, que pueden desarrollarse en Twitter, influyen positivamente en el sentido de comunidad de los estudiantes (Blight, Ruppel, & Schoenbauer, 2017).
Por otro lado, los autores reconocen que a pesar de que las redes sociales, como Facebook, ofrece grandes oportunidades para comunicarse y socializar, puede constituir una fuente de distracción (Gupta & Irwin, 2016) y afectar, por tanto, negativamente al rendimiento académico (Bellur, Nowaka, & Hullb, 2015). Afirman que, a mayor tiempo invertido en Facebook, menor rendimiento se alcanza (Paul, Baker, & Cochran, 2012), debido a que dedican menos tiempo a estudiar (Kirschner & Karpinski, 2010). Con relación a Twitter, Tang y Hew (2017) dicen que «aunque Twitter parece prometedor para mejorar las interacciones entre los alumnos y los profesores, la correlación entre el uso de Twitter y el rendimiento del aprendizaje queda por establecer de manera concluyente». Además, diversas investigaciones han indicado que el «microblogging» registra escasas conversaciones, reforzando discursos unidireccionales (Arrabal, & de Aguilera, 2016), acciones individualistas más que colectivas y de interacción, monólogos más que los diálogos (Santoveña-Casal, 2017). Finalmente, cabe destacar que el uso de Twitter en actividades académicas conlleva quejas por parte de los estudiantes relativas al aumento de la carga de trabajo (Chen & Chen, 2012), con los problemas para expresarse debido a la limitación de caracteres (Prestridge,2014) y a las dificultades para manejar las grandes cantidades de información (Lin, Hoffman, & Borengasser, 2013).
En definitiva, el objetivo del presente trabajo fue analizar cómo afecta el rol del profesor (guía y facilitador), desarrollado a lo largo de cuatro debates académicos en Twitter, en la participación social en red y en la experiencia académica percibida. Se busca poner a prueba las siguientes hipótesis:
• H1. El tipo de rol desempeñado por el profesor (guía o facilitador) influye en la participación académica del estudiante a través de Twitter.
• H2. El tipo de rol desempeñado por el profesor (guía o facilitador) influye en la experiencia académica percibida del estudiante.
• H3. La participación social en red (Twitter) influye positivamente en la valoración de la experiencia académica, del proceso de aprendizaje, del proceso de interacción (alumno-alumno y alumno-profesor) y en el sentimiento de afiliación, influencia y cohesión grupal.
El modelo de la investigación incluyendo las tres hipótesis se presenta en la Figura 1.
Figura 1. Modelo propuesto.
2. Material y método
Este estudio se realizó en un máster oficial destinado a futuros profesores en la Universidad Nacional de Educación a Distancia (UNED). Los estudiantes debían interactuar e intercambiar opiniones en dos debates obligatorios a través de la red social Twitter. Además, se desarrollaron dos debates voluntarios.
El rol del profesorado en los debates fue modificado a lo largo del semestre. Se parte de la propuesta de Marcos-García, Martínez-Monés y Dimitriadis (2015) y Ouyang y Scharber (2017) que clasifican los roles en guía, facilitador y observador. En la investigación se ponen en marcha exclusivamente el rol Guía y el rol Facilitador que cambia a lo largo de los cuatro debates (Figura 2).
Figura 2. Participación del profesor en Twitter: Tweets enviados a lo largo de las semanas.
a) El rol guía implica que el profesor sea el centro del aprendizaje, el líder responsable del proceso. Orienta a los estudiantes, facilita indicaciones, aporta el material necesario para el aprendizaje. Con el rol guía, el profesor interactuó con los estudiantes a través de las conversaciones generadas en Twitter y envió links, recursos educativos y noticias con el objetivo de enriquecer el debate.
b) El rol facilitador implica que el profesor realiza un seguimiento de la actividad desarrollada por los estudiantes y actúa como mediador si existen conflictos. En Twitter, el profesor adoptó un papel secundario, reduciendo el número de mensajes. No intervino en las conversaciones, ni envió recursos complementarios.
2.2. Población y muestra
La población estuvo formada por todos los estudiantes del máster (720). Para el estudio de la experiencia académica percibida, la muestra la constituyó los estudiantes que respondieron al cuestionario (un mismo cuestionario aplicado en dos momentos temporales diferentes), un total de 525 estudiantes: 249 (responden al cuestionario una vez finalizado el debate 1 y el debate 2 durante los cuales se adoptó el rol guía) y 276 estudiantes (responden al cuestionario una vez finalizado el debate 2 y el debate 3 durante los que se adoptó el rol facilitador). El 66,3% (N= 348) son mujeres. Los participantes fluctuaron de 21 a 53 años, una media de 32,5. La Tabla 1 muestra el error muestral que se halla sobre la base de un muestreo aleatorio simple en el caso más desfavorecido del muestreo (p=q= 0.5).
Para el estudio de la participación en Twitter, la muestra estuvo formada por los mensajes enviados y registrados en Google TAGS hoja de cálculo v6 (Hawksey, 2013) que depende de la API de Twitter: 26.188 tweets. La selección de los tweets se realizó a través de los hashtags que identifican cada debate. La API de Twitter, aunque presenta limitaciones, posibilita la recuperación de los tweets dependiendo del número de tweets enviados durante el último mes, eliminando los más antiguos para facilitar la generación de los nuevos. A pesar de su carácter temporal, estos datos no dejan de ser un objetivo de investigación interesante (Bruns & Stieglitz, 2012; Gerlitz & Rieder, 2013), debiendo confiar en la API puesto que es el único medio que facilita la obtención de datos a gran escala (Bruns & Stieglitz, 2012). Los investigadores no disponen de otra forma de confirmar la calidad y precisión de los datos y, por tanto, es una limitación inevitable que no invalida los resultados. Como indican Gerlitz y Rieder (2013), el muestreo realizado en Twitter se basa en un muestreo no probabilístico, no representativo, puesto que la selección de la muestra siempre está limitada por la aplicación utilizada.
2.3. Diseño e instrumentos de recogida de datos
El estudio se basa en un diseño mixto de triangulación, un modelo teórico, una parte cuantitativa (análisis descriptivo y contraste sobre medias) y otra cualitativa (análisis de contenido, siguiendo los principios de la teoría fundamentada). Se utilizó el paquete SPSS 24 (análisis estadístico) y el software Atlas Ti HM (análisis de contenido).
El estudio cuantitativo se desarrolló sobre la base de un análisis descriptivo y contraste de medias (Prueba t para muestras independientes) para conocer la influencia de la variable Rol del profesor (Guía o Facilitador) sobre las variables dependientes (Experiencia académica percibida y Participación en Twitter). Ante la falta de normalidad de la distribución de las variables en la muestra y para confirmar los datos de T de Student se usa la U de Mann-Whitney. Además, se halla los tamaños del efecto de las pruebas (D de Cohen y Coeficiente de correlación r).
Para el análisis de la experiencia académica percibida, se utilizó una encuesta ad hoc, tipo Likert, para la recogida de la opinión de los estudiantes. Además, se añadieron preguntas abiertas complementarias para ampliar la información cualitativa a las preguntas de respuesta cerrada. La validez del contenido se basa en la literatura científica, en las variables consideradas fundamentales por autores como Kurucay e Inan (2017) (datos demográficos, satisfacción, interacción, percepción de colaboración, percepción de aprendizaje), y Luo, Zhang y Qi (2017) (Interacción alumno-alumno, interacción alumno-profesor, interacción con el contenido, afiliación e influencia). Además, se solicitó la colaboración de un grupo de expertos (cuatro profesores) que indicaron cambios a realizar en la versión preliminar del cuestionario.
Se aplica esta versión a una muestra de 40 estudiantes, lo que ayudó a comprobar que las instrucciones y preguntas eran comprendidas, obteniendo una fiabilidad de Alfa de Cronbach de .960 muy superior a lo recomendado (.70). Posteriormente, se aplicó el análisis factorial exploratorio (utilizando la rotación varimax y los componentes principales) y cada ítem individual se agrupó dentro del constructo correspondiente, logrando una varianza total explicada de 66,7%. Las dimensiones encontradas fueron:
• Dimensión 1. «Proceso de aprendizaje y adquisición de conocimiento»: .943. Valora la experiencia académica en Twitter y de la asignatura como espacios para la adquisición de conocimiento constructivista, reflexivo y crítico, conectivista, individualista, social y participativo, y activo. Además, se valora la propuesta pedagógica en general.
• Dimensión 2. «Afiliación e influencia en la asignatura y Cohesión en el grupo»: .921.
• Dimensión 3. «Aspectos generales»: .879. Analiza la calidad, satisfacción y utilidad de la experiencia y el valor añadido del proceso de comunicación e interacción, en general y Twitter, en particular.
• Dimensión 4. «Interacción alumno-alumno»: .855. Estudia la frecuencia de uso de Twitter, grado en que ha compartido información sobre asignatura y sobre problemas con otros estudiantes, la aportación de Twitter a la mejora de las relaciones interpersonales entre los estudiantes, las habilidades interpersonales y de comunicación en red y el grado en que les ha permitido formar una comunidad o grupo con intereses compartidos.
• Dimensión 5. «Interacción alumno-profesor» .896. Estudia el grado en que ha solicitado información al profesor sobre contenidos, la asignatura y la actividad en Twitter.
• Dimensión 6. «Uso de los foros»: .518. Se analiza la frecuencia de uso de los foros y su valor añadido.
El estudio cualitativo se basó en un análisis de contenido de las respuestas a las preguntas abiertas del cuestionario. Se desarrolla siguiendo lo indicado por García-Llamas, González y Ballesteros (2001: 1) definición del universo de contenidos y selección de la muestra; 2) Decisión de la unidad de análisis y establecimiento de las categorías. Las categorías principales las establece las dimensiones destacadas en la literatura científica Kurucay y Inan (2017), y Luo, Zhang y Qi (2017). Estas categorías son organizadas en la superfamilia (Experiencia académica percibida) y dos familias dependientes de la anterior: Perspectiva centrada en Nosotros del que forma parte el código Colaboración y participación y, la familia, Perspectiva centrada en Yo, del que depende el código Crítica y dificultades. Los resultados de la categorización de los códigos se presentan en un mapa conceptual, indicando la fundamentación (frecuencia de aparición) y densidad (el número de códigos con los que se relaciona). Además, los comentarios textuales utilizados de los estudiantes se presentan indicando el número del documento principal de análisis y la línea de donde se extrae el comentario.
3. Resultados
3.1. Participación social en Twitter
Se registró una alta participación en Twitter, con 26.188 tweets, 5.639 retwits y 6.089 enlaces en los mensajes, participaron sobre todo durante la segunda y tercera semana, cuando los debates eran obligatorios. Además, participaron más en Twitter cuando el profesor adoptó el rol facilitador, enviando el 56,3% de los mensajes. Se observa que los estudiantes enviaron significativamente más mensajes a Twitter cuando el profesor desarrolla un rol facilitador [F(2,8) t=–3,06, Sig. (bilateral)=,002]. Los datos son confirmados por U de Mann-Whitney, pero el tamaño del efecto es nulo (r=0,07 y d=0,14).
3.2. Experiencia académica percibida
Se observa una valoración muy positiva de la experiencia pedagógica por parte de los estudiantes. Más del 64% de los estudiantes valoran alto o muy alto todas las dimensiones, siendo esta valoración significativamente más positiva cuando el profesor adopta el rol facilitador para la calidad [F(9,6) t=2,7, Sig. (bilateral)=,006], Utilidad [F(6,7) t=2,1, Sig. (bilateral)=,034], Satisfacción [F(10,8) t=2,9, Sig. (bilateral)=,004], y para Valor añadido al proceso de comunicación de Twitter [F (4,02) t=4,0, Sig. (bilateral)=,000]. U de Mann-Whitney confirma estas diferencias significativas (Tabla 2). El tamaño del efecto es pequeño para Calidad de la propuesta (r=0,12; d=0,24), Satisfacción (r=0,12; d=0,25) y Valor añadido al proceso de comunicación de Twitter (r=0,16; d=0,34) y nulo para Utilidad (r=0,09; d=0,09).
La Figura muestra los resultados de la dimensión 1 «Proceso de aprendizaje y adquisición de conocimiento». La propuesta pedagógica fue altamente valorada por el 70% de los estudiantes. Considerando que la participación en Twitter les ha facilitado la adquisición de conocimiento sobre materia (59,6%), teórico (42,7%), práctico (53%), colaborativo y participativo (70%) y que en la investigación han desarrollado diferentes tipos de aprendizaje: crítico (76%) y reflexivo (76%), constructivista (73,7%), conectivista (73,5%), social (81,9%) y participativo (70%), activo (61,6%).
Se observa que cuando el profesor adopta el rol facilitador, los estudiantes tienen una valoración significativamente más alta del aprendizaje adquirido con Twitter y en la asignatura en las variables:
a) Twitter facilita la adquisición de conocimiento [F(17,22) t=4,7, Sig. (bilateral)=,000], relacionado con la materia [F(15,4) t=4,6, Sig. (bilateral)= ,000], teórico [F(,48) t=4,02, Sig. (bilateral)=,000] y práctico [F(1,7) t=4,02, Sig. (bilateral)=,039].
b) Asignatura facilita el aprendizaje crítico y reflexivo [F(8,2) t=2,9, Sig. (bilateral)=,003], constructivista [F(5,5) t=2,6, Sig. (bilateral)=,007], social [F(2,04) t= 2,9, Sig. (bilateral)= ,003] e individualista [F(0,090) t=2,6, Sig. (bilateral)=,009].
c) Valoración de la propuesta pedagógica [F(8,8) t=2,6, Sig. (bilateral)=,009].
U de Mann-Whitney confirma las diferencias significativas. Para todas las variables el tamaño del efecto es pequeño (r entre 0,1 y 0,25 y d entre 0,41 y 0,21) y nulo para Twitter facilitando la adquisición de conocimiento práctico (r=0,08; d=0,17).
Con relación a la dimensión 2 «Afiliación, influencia en la asignatura y cohesión en el grupo» se observa que los estudiantes se ven como parte del grupo-clase, sienten que tienen un buen vínculo con otros estudiantes en un grado alto o muy alto. Referente a la Cohesión en el grupo, en un grado alto o muy alto, los estudiantes tienen intención de prolongar su participación en el curso virtual y/o la red social, acceder al curso virtual y/o redes sociales en el futuro. Por otra parte, consideran que la influencia que tiene sobre la asignatura y/o el curso virtual es baja. No se encuentran diferencias significativas en ninguno de los aspectos analizados en esta dimensión en función del rol del profesor. Los datos se confirman con U de Mann-Whitney. Se han encontrado dos dimensiones relativas a los procesos de interacción: interacción alumno-alumno (dimensión 4) y alumno-profesor (dimensión 5).
El 51,6% de los estudiantes confirman que utilizan Twitter casi siempre y el 42,5% que a menudo interactúan con sus compañeros compartiendo información de la asignatura. El 45,7% afirma compartir conocimiento con sus compañeros a menudo.
La mayoría de los estudiantes han valorado que la participación en Twitter les permite mejorar, en un grado alto o muy alto, las relaciones interpersonales con los compañeros (69,3%), las habilidades interpersonales y de comunicación en red (63%) y afirman que les ha permitido formar una comunidad o grupo con intereses compartidos (71,5%). Solo se encuentran diferencias significativas, en función del rol del profesor para la percepción de mejora de las relaciones interpersonales entre los estudiantes [F(10,3) t=3,2, Sig. (bilateral)=,001], siendo superior cuando el profesor desarrolla un rol facilitador. Los datos se confirman con U de Mann-Whitney. El tamaño del efecto es pequeño (r=0,14; d=0,28).
Por otra parte, respecto al proceso de interacción con el profesorado, los estudiantes perciben que han interactuado poco con el profesor y esta tendencia se acentúa cuando el profesor adopta el rol de facilitador: el 54,5% afirma que nunca ha solicitado información relacionada con los contenidos ni sobre la asignatura. Se encuentran diferencias significativas en: Interacción con el profesor para solicitar información sobre los contenidos, sobre la asignatura y sobre la actividad. Se confirman las diferencias con U de Mann-Whitney. El tamaño del efecto es pequeño (r entre 0,10 y 0,12 y d entre 0,22 y 0,25).
En la dimensión 6 «Uso de los foros», se observa que la mayoría de los estudiantes afirman utilizarlos en pocas ocasiones (52,4%). Además, el valor añadido de los foros a la asignatura se ha considerado alto o muy alto solo el 33% de los estudiantes y bajo, muy bajo o nulo por el 34% de los estudiantes. Cuando el profesor desempeña un rol facilitador, los estudiantes afirman usarlos con mayor frecuencia. El tamaño del efecto es pequeño. U de Mann-Whitney confirma estos datos.
El análisis de contenido de las descripciones de los estudiantes sobre la experiencia académica percibida muestra tres aspectos principales (Figura 3). En primer lugar, destacan dos perspectivas diferentes a la hora de evaluar la experiencia académica: aquellos estudiantes que han estimado de manera positiva la participación en Twitter realizan una valoración centrada en nosotros, en los procesos de colaboración y participación con sus compañeros del máster. En contraste, aquellos que critican y han percibido más dificultades en la experiencia académica, realizan un análisis centrado en sí mismo. En segundo lugar, se observa una interrelación entre las principales dimensiones: aspectos generales (satisfacción), proceso de interacción alumno-alumno y alumno-profesor, proceso de aprendizaje y adquisición de conocimiento y afiliación e influencia en la asignatura y cohesión en el grupo. En tercer lugar, no se observa diferencias en los comentarios de los estudiantes referente al rol del profesor, ni se identifica una mejor valoración del profesor en la fase de rol guía en contraste con la fase de rol facilitador.
Figura 3. Mapa conceptual general «Experiencia académica percibida».
Los estudiantes valoran muy positivamente, no solo la actividad realizada en Twitter, sino también la asignatura en general. Han destacado principalmente su carácter innovador, motivador, de gran interés, considerada entretenida, gratificante, atractiva, divertida [«Esta metodología me resulta mucho más atractiva que la tradicional a partir de los foros» (6:668)]. Comentan lo importante que ha sido iniciarse en Twitter y superar las reticencias y el rechazo inicial a utilizarlo [«A pesar de tener cierta reticencia a usar Twitter y más para una asignatura, me ha resultado muy enriquecedor» (14:1171)]. La interacción alumno-alumno destaca como variable determinante de la satisfacción [«resaltar los satisfactorios efectos que ha tenido sobre la interacción y la comunicación con mis compañeros» (1:120)]. Consideran que es la primera vez que pueden tener un contacto directo, espontáneo, cercano y democrático con otros estudiantes del máster [«Me ha gustado mucho la posibilidad de interactuar de forma directa con los compañeros, permitiendo así una relación mucho más cercana» (1:747)] y conocer diversos puntos de vista [«la gran cantidad de participantes propiciaba un amplio abanico de opiniones y puntos de vista» (1:465)]. La interacción alumno-alumno les ha permitido generar un sentimiento de afiliación y cohesión dentro del grupo, el sentimiento de formar parte de una comunidad ha sido un aspecto especialmente destacado [«El sentimiento de afiliación es el elemento que más me ha hecho seguir la actividad de forma periódica» (7:598)]. Además, a través de este proceso de comunicación y de debate, los estudiantes han adquirido conocimientos teóricos, prácticos, intercambiando ideas, información y conocimientos, de un modo divertido y motivador [«ha supuesto otra forma diferente de aprender muy dinámica y motivadora» (1:548)] (Figura 4).
Se han recibido pocas críticas a la actividad, pero es interesante analizarlas. Se han centrado en la sobrecarga de trabajo que conlleva la participación, el excesivo tiempo que requiere la participación en Twitter [«La experiencia (…) me parece mucha carga de trabajo (en horas de dedicación)» (6:642)]. Critican la obligatoriedad de la tarea y los estudiantes se muestran preocupados por la invasión de la privacidad al usar las redes en el ámbito académico [«Me parece que por más filtros de seguridad que pongas cualquier hacker puede robarte tu identidad, o simplemente que se haga pública tu vida privada» (5:760)]. También critican el caos que implica la participación de mucha gente y el gran volumen de tweets, la falta absoluta de control sobre la comunicación [«La actividad del Twitter es caótica, demasiados debates abiertos» (2:552)] y la ansiedad que implica este proceso [«He disfrutado (…) pero ha habido momentos que me ha generado (…) estrés por el alto número de interacciones» (2:547)]. Es interesante destacar que los estudiantes que valoran negativamente la actividad realizan comentarios centrados en el Yo, en sí mismos [«Siempre lo he visto como algo que yo realmente no puedo controlar y que por ende no quiero hacerlo parte de mi vida» (5:579); «No me siento cómoda en la exposición en redes sociales» (6:622)]. De hecho, estos estudiantes reconocen la nula o escasa afiliación y cohesión con el grupo [«No he venido aquí a hacer amigos, no creo que el valor per se de las relaciones» (8:499)].
Figura 4. Mapa conceptual «Perspectiva centrada en Nosotros».
4. Discusión y conclusiones
El objetivo principal de este trabajo fue analizar la influencia del rol del profesor (guía y facilitador), desarrollado a lo largo de cuatro debates académicos en Twitter, en la participación social en red y en la experiencia académica percibida. Los resultados indican que el rol docente no influye en la participación social de los estudiantes y que su influencia sobre la percepción de la experiencia académica es pequeña, aunque de alto interés para el contexto educativo.
Varios autores (Durlak, 2009; Frías, Pascual, & García-Pérez, 2000) consideran que un tamaño del efecto pequeño puede ser de gran importancia práctica en un contexto concreto y, sobre todo, como dicen Glass, McGaw y Smith (1981), la importancia práctica de un efecto depende enteramente de sus costos y beneficios relativos. Se considera que los datos aportados en esta investigación tienen alto valor práctico para la educación, puesto que parece que la adopción de un rol facilitador en Twitter, un rol más pasivo, mejora la percepción de los estudiantes de la propuesta pedagógica, su grado de satisfacción, la valoración del proceso de comunicación e interacción desarrollado en Twitter, así como la contribución del «microblogging» a la adquisición de aprendizaje y conocimiento y la mejora de las relaciones interpersonales. Como dice Battalio (2007), cuando los profesores proporcionan a los estudiantes diferentes momentos educativos con diversos grados de interacción, garantizan un resultado positivo en el aprendizaje en línea. Además, este tipo de metodología no supone un costo elevado y sus beneficios pueden ser muy altos.
Se observa que el rol del profesor no influye en el sentimiento de afiliación, influencia y cohesión. De hecho, los estudiantes afirman que prácticamente no han acudido al profesor para plantearles dudas. Esta tendencia se acentúa cuando el profesor adopta un rol facilitador y, en contraste, aumenta la percepción de mejora de las relaciones interpersonales entre los estudiantes en Twitter. En la línea de Smith (2016), los estudiantes otorgan mayor importancia a las interacciones alumno-alumno, más que alumno-profesor en el aprendizaje a través de las redes sociales. Es probable que adoptar un rol más pasivo, dejando espacio libre para la interacción entre los estudiantes sea una metodología más adecuada para el aprendizaje en redes sociales. De hecho, el alumnado ha destacado la importancia de la interacción entre estudiantes y cómo esta relación influye en su sentimiento de pertenencia al grupo. Estos datos se confirman con el análisis de contenido donde describen las interacciones alumno-alumno como motivadoras y de alto grado de satisfacción. Resultados coincidentes con la investigación de Ali y Ahmad (2011) que establecían la interacción entre estudiantes como predictor de la satisfacción.
En la misma línea que investigaciones previas, se concluye que la participación social en red (Twitter) influye positivamente en la valoración de la experiencia (Alhazmi & Rahman, 2013; Lee & Bonk, 2016), en el proceso de aprendizaje y en el sentimiento de afiliación y cohesión grupal (Blight, Ruppel, & Schoenbauer, 2017; Carpenter & Krutka, 2014). Los estudiantes han valorado muy positivamente el carácter innovador de la metodología y han indicado el valor de Twitter como espacio motivacional, estableciendo una relación positiva entre el debate, el intercambio de información y recursos con la motivación, como señalaron Eid y Al-Jabri (2016).
Los estudiantes han otorgado un alto valor a Twitter como medio para comunicarse e interactuar, contradiciendo otras investigaciones que han destacado las escasas conversaciones que se registran en la Red (Arrabal, & de Aguilera, 2016) y la tendencia a desarrollar monólogos más que diálogos (Santoveña-Casal, 2017). La red social puede considerarse un entorno que facilita la adopción de nuevos modelos educativos basados en un aprendizaje conectado y la participación social, aspectos destacados por Jenkins (2012) y Gee (2004) como fundamentales en la sociedad en red. Además, los estudiantes han comentado explícitamente lo importante que ha sido iniciarse en Twitter y superar las reticencias y miedos iniciales. En Twitter se generan sentimientos de frustración junto a un alto grado de interés en la tarea. Aspectos destacados por Gee (2004) como fundamentales en las nuevas formas de aprender.
Aunque es una red que no está exenta de inconvenientes cuando se utiliza en el marco educativo. En la misma línea que otras investigaciones, los estudiantes han criticado la sobrecarga de trabajo que supone (Chen & Chen, 2012) y la sensación de caos y estrés ante las dificultades para gestionar la información compartida (Lin, Hoffman, & Borengasser, 2013). Los estudiantes que realizan una valoración negativa suelen expresar sus críticas y dificultades centrándose en sí mismos, en sus problemas de control del proceso de comunicación, sus problemas de ansiedad o en su falta absoluta de interés por el otro. Este es un aspecto especialmente interesante para analizar en futuras investigaciones: ¿cómo influye las variables de personalidad en la participación académica en redes sociales? ¿Qué papel tiene el locus de control interno y externo en estas experiencias?
En síntesis, parece que la participación en Twitter permite la comunicación e interacción, facilita la participación social y el aumento de la satisfacción académica en los estudiantes, pero todavía queda por establecer de manera concluyente cómo influye el cambio de rol del profesor en el alumnado. El estudio del rol del docente tiene especial interés, puesto que aporta luz a nuevas metodologías en red. Se concluye, por un lado, que el uso de redes sociales en educación universitaria aporta un valor motivacional a los estudiantes que no lo proporciona otros medios más tradicionales como los foros y, por otro, que un rol que refuerza un proceso de aprendizaje independiente es probablemente mejor estrategia cuando hablamos de redes sociales en el aula.
Referencias
Al-Rahmi, W.M., & Othman, M.S. (2013). Evaluating student’s satisfaction of using social media through collaborative learning in higher education. International Journal of Advances in Engineering & Technology, 6(4),1541-1551. https://bit.ly/2vJbwXl
Alhazmi, A.K., & Rahman, A.A. (2013). Facebook in higher education: Students’ use and perceptions AISS. Advances in Information Sciences and Service Sciences, 5(15), 32-41. https://bit.ly/2Ph5QMv
Ali, A., & Ahmad, I. (2011). Key factors for determining students’ satisfaction in distance learning courses: A study of Allama Iqbal Open University. Contemporary Educational Technology, 2(2), 118-134. https://bit.ly/2vLRjzU
An, H., Shin, S., & Lim, K. (2009). The effects of different instructor facilitation approaches on students’ interactions during asynchronous online discussions. Computers & Education, 53, 749-760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2009.04.015
Arrabal, G., & de-Aguilera, M. (2016). Communicating in 140 characters. How journalists in Spain use Twitter. [Comunicar en 140 caracteres. Cómo usan Twitter los comunicadores en España]. Comunicar, 46, 9-17. https://doi.org/10.3916/C46-2016-01
Ausubel, D. (1981). Psicología educativa. Un punto de vista cognoscitivo. México: Trillas. https://bit.ly/2Bf5djx
Battalio, J. (2007). Interaction online: A reevaluation. Quarterly Review of Distance Education, 8(4), 339-352. https://bit.ly/2PgsXqm
Bellur, S., Nowaka, K.L., & Hullb, K.S. (2015). Make it our time: In class multitaskers have lower academic performance. Computers in Human Behavior, 53, 63-70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2015.06.027
Blight, M.G., Ruppel, E.K., & Schoenbauer, K.V. (2017). Cyberpsychology. Behavior, and Social Networking, 20(5), 314-319. https://doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2016.0505
Bruns, A., & Stieglitz, S. (2012). Quantitative Approaches to Comparing Communication Patterns on Twitter. Journal of Technology in Human Services, 30(3-4), 160-185. https://doi.org/10.1080/15228835.2012.744249
Carpenter, J.P., & Krutka, D.G. (2014). How and why educators use Twitter: A survey of the field. Journal of Research on Technology in Education, 46(4), 414-434. https://doi.org/10.1080/15391523.2014.925701
Chen, L., & Chen, T.L. (2012). Use of Twitter for formative evaluation: Reflections on trainer and trainees’ experiences: Colloquium. British Journal of Educational Technology, 43(2), E49-E52, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8535.2011.01251.x
Chen, L., & Chen, T.L. (2012). Use of Twitter for formative evaluation: Reflections on trainer and trainees’ experiences: Colloquium. British Journal of Educational Technology, 43(2), E49-E52, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8535.2011.01251.x
Durlak, J.A. (2009). How to select, calculate, and interpret effect sizes. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 34(9), 917-928. https://doi.org/10.1093/jpepsy/jsp004
Eid, M.I.M., & Al-Jabri, I.M. (2016). Social networking, knowledge sharing, and student learning: The case of university students. Computers & Education, 99, 14-27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2016.04.007
Frías, M.D., Pascual, J., & García-Pérez, J.F. (2000). Tamaño del efecto del tratamiento y significación estadística. Psicothema, 12(2), 236-240. https://bit.ly/2MvuiuM
García-Llamas, J.L., González, M.A., & Ballesteros, B. (2001). Introducción a la investigación en educación II. Madrid: UNED. https://bit.ly/2OGQzmK
Gee, J.P. (2008). Lo que nos enseñan los videojuegos sobre el aprendizaje y el alfabetismo. Málaga: Aljibe. https://bit.ly/2vVVhX9
Gerlitz, C., & Rieder, B. (2013). Mining One Percent of Twitter: Collections, Baselines, Sampling. Journal of Media and Culture, 16(2). https://bit.ly/2vVVhX9
Glass, G.V., McGaw, B., & Smith, M.L. (1981). Meta-analysis in social research. London: Sage. https://bit.ly/2MRfNyu
Gupta, N., & Irwin, J.D. (2016). In-class distractions: The role of Facebook and the primary learning task. Computers in Human Behavior, 55(B), 1165-1178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2014.10.022
Gutiérrez-Porlán, I., Román-García, M., & Sánchez-Vera, M. (2018). Strategies for the communication and collaborative online work by university students. [Estrategias para la comunicación y el trabajo colaborativo en red de los estudiantes universitarios]
Hawksey, M. (2013). Twitter archiving Google spreadsheet (TAGS). https://bit.ly/1GmM3nV
Jaggars, S.S., & Xu, D. (2016). How do online course design features influence student performance? Computers & Education, 95, 270-284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2016.01.014
Jenkins, H. (2012). Connected learning: Reimagining the experience of education in the information age. Blog Confessions of an ace-fan. https://bit.ly/2OH2tgp
Kirschner, P.A., & Karpinski, A.C. (2010). Facebook and academic performance. Computers in Human Behavior, 26(6), 1237-1245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2010.03.024
Kurucay, M., & Inan, A. (2017). Examining the effects of learner-learner interactions on satisfaction and learning in an online undergraduate course. Computers & Education, 115, 20-37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2017.06.010
Ladyshewsky, R.K. (2013). Instructor presence in online courses and student satisfaction. International Journal for the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning, 7(1). https://doi.org/10.20429/ijsotl.2013.070113
Lee J., & Bonk, C.J. (2016). Social network analysis of peer relationships and online interactions in a blended class using blogs. The Internet and Higher Education, 28, 35-44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2015.09.001
Lin, M.F.G., Hoffman, E.S., & Borengasser, C. (2013). Is social media too social for class? A case study of Twitter use. TechTrends, 57(2), 39-45. https://bit.ly/2vO1AM0
Luo, N., Zhang, M., & Qi, D. (2017). Effects of different interactions on students’ sense of community in e-learning environment. Computers & Education,115, 153-160, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2017.08.006
Marcos-García, J.A., Martínez-Monés, A., & Dimitriadis, Y. (2015). DESPRO: A method based on roles to provide collaboration analysis support adapted to the participants in CSCL situations. Computers & Education, 82, 335-353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.com
Ouyang, F., & Scharger, C. (2017). The influences of an experienced instructor’s discussion design and facilitation on an online learning community development: A social network analysis study. The Internet and Higher Education, 35, 34-47. https://doi.or
Paul, J.A., Baker, H.M., & Cochran, J.D. (2012). Effect of online social networking on student academic performance. Computers in Human Behavior, 28, 2117-2127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2012.06.016
Prestridge, S. (2014). A focus on students’ use of Twitter–their interactions with each other, content and interface. Active Learning in Higher Education, 15(2), 101-115. https://doi.org/10.1177/1469787414527394
Santoveña-Casal, S. (2017). Conversations, debates and affiliation networks on Twitter. Turkish Online Journal of Educational Technology (TOJET), 16(3), 47-59. https://bit.ly/2nKRJ5o
Scott, K.S., Sorokti, K.H., & Merrell, J.D. (2016). Learning ‘beyond the classroom’ within an enterprise social network system. The Internet and Higher Education, 29, 75-90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2015.12.005
Smith, E.E. (2016). A real double-edged sword: Undergraduate perceptions of social media in their learning. Computers & Education, 103, 44-58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2016.09.009
Tang, Y., & Hew, F.K. (2017). Using Twitter for education: Beneficial or simply a waste of time? Computers & Education,106, 97-118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2016.12.004
Tuzel, S., & Hobbs, R. (2017). The Use of Social Media and Popular Culture to Advance Cross-Cultural Understanding. [El uso de las redes sociales y la cultura popular para una mejor comprensión intercultural]. Comunicar, 51, 63-72. https://doi.org/10.391
Wong, L., Sing-Chai, C., & Poh-Aw, G. (2017). Seamless language learning: Second language learning with social media. [Aprendizaje de idiomas «sin costuras»: Aprendizaje de segundas lenguas y redes sociales]. Comunicar, 50, 9-21. https://doi.org/10.3916/
Document information
Published on 31/12/18
Accepted on 31/12/18
Submitted on 31/12/18
Volume 27, Issue 1, 2019
DOI: 10.3916/C58-2019-07
Licence: CC BY-NC-SA license
Share this document
Keywords
claim authorship
Are you one of the authors of this document?