David.franco (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (34 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
'''Machine Learning Techniques applied to the Coronavirus pandemic: a systematic and bibliometric analysis from January 2020 to June 2021'''</div> | '''Machine Learning Techniques applied to the Coronavirus pandemic: a systematic and bibliometric analysis from January 2020 to June 2021'''</div> | ||
--> | --> | ||
| + | ==Abstract== | ||
| − | + | During the pandemic caused by the Coronavirus (Covid-19), Machine Learning (ML) techniques can be used, among other alternatives, to detect the virus in its early stages, which would aid a fast recovery and help to ease the pressure on healthcare systems. In this study, we present a Systematic Literature Review (SLR) and a Bibliometric Analysis of ML technique applications in the Covid-19 pandemic, from January 2020 to June 2021, identifying possible unexplored gaps. In the SLR, the 117 most cited papers published during the period were analyzed and divided into four categories: 22 articles that analyzed the problem of the disease using ML techniques in an X-Ray (XR) analysis and Computed Tomography (CT) of the lungs of infected patients; 13 articles that studied the problem by addressing social network tools using ML techniques; 44 articles directly used ML techniques in forecasting problems; and 38 articles that applied ML techniques for general issues regarding the disease. The gap identified in the literature had to do with the use of ML techniques when analyzing the relationship between the human genotype and susceptibility to Covid-19 or the severity of the infection, a subject that has begun to be explored in the scientific community. | |
| − | '''Keywords | + | '''Keywords''': Machine learning, coronavirus pandemic, systematic literature review, bibliometric analysis, genetic predisposition |
| − | =1. Introduction= | + | ==1. Introduction== |
According to the World Health Organization [1], pandemic is a term used for a determined disease that rapidly spreads through diverse regions (at the continental or world level) through sustained contamination. In this respect, the gravity of the disease is not a determining factor, but rather its contagiousness and geographical proliferation. | According to the World Health Organization [1], pandemic is a term used for a determined disease that rapidly spreads through diverse regions (at the continental or world level) through sustained contamination. In this respect, the gravity of the disease is not a determining factor, but rather its contagiousness and geographical proliferation. | ||
| Line 69: | Line 70: | ||
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 presents the theoretical background of ML applied to the Covid-19 disease. Section 3 discusses the methodological procedures, including the research terms and the flowchart used in the systematic literature review. Section 4 presents and discusses the results, i.e., the survey conducted with the researched articles. Finally, Section 5 concludes the paper and suggests directions for future research in this field. | The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 presents the theoretical background of ML applied to the Covid-19 disease. Section 3 discusses the methodological procedures, including the research terms and the flowchart used in the systematic literature review. Section 4 presents and discusses the results, i.e., the survey conducted with the researched articles. Finally, Section 5 concludes the paper and suggests directions for future research in this field. | ||
| − | =2. Theoretical background: ML techniques for the Covid-19 disease= | + | ==2. Theoretical background: ML techniques for the Covid-19 disease== |
The Covid-19 pandemic has become the most devastating disease of the twenty-first century and has spread to all the 216 countries in the world. Despite the availability of modern and sophisticated medical treatment, the disease is spreading through more outbreaks. | The Covid-19 pandemic has become the most devastating disease of the twenty-first century and has spread to all the 216 countries in the world. Despite the availability of modern and sophisticated medical treatment, the disease is spreading through more outbreaks. | ||
| Line 85: | Line 86: | ||
The present study differs from other works in that it does not focus on a single type of application, but to all the situations widely cited in the literature and seeking answers to why certain patients are so severely affected by the virus, while others are asymptomatic when affected by it. | The present study differs from other works in that it does not focus on a single type of application, but to all the situations widely cited in the literature and seeking answers to why certain patients are so severely affected by the virus, while others are asymptomatic when affected by it. | ||
| − | =3. Methodology= | + | ==3. Methodology== |
This study was based on the methodology proposed by Snyder [17] and Xiao and Watson [18] to delineate the flow of information and procedures necessary to conduct this literature review. The review was guided by the research questions presented in Section 1. The initial search criteria adopted are (“Data Mining” OR “Machine Learning”) AND (“Covid” OR “Coronavirus”). | This study was based on the methodology proposed by Snyder [17] and Xiao and Watson [18] to delineate the flow of information and procedures necessary to conduct this literature review. The review was guided by the research questions presented in Section 1. The initial search criteria adopted are (“Data Mining” OR “Machine Learning”) AND (“Covid” OR “Coronavirus”). | ||
| − | The search was limited to original articles published in peer-reviewed journals form January 2020 to June 2021, and only in English. Three scientific databases were used: ScienceDirect; Scopus; and Web of Science. | + | The search was limited to original articles published in peer-reviewed journals form January 2020 to June 2021, and only in English. Three scientific databases were used: ScienceDirect; Scopus; and Web of Science. [[#img-1|Figure 1]] shows the systematic literature review flowchart. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | [[ | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | <div id='img-1'></div> | ||
| + | {| style="text-align: center; border: 1px solid #BBB; margin: 1em auto; width: auto;max-width: auto;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |style="padding:10px;"| [[File:Steiner_et_al_2022a_6611_Figure_1.png|600px]] | ||
| + | |- style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;" | ||
| + | | colspan="1" style="padding:10px;"| '''Figure 1'''. Systematic literature review flowchart | ||
| + | |} | ||
Based on the initial search criteria, 1,912 articles were identified in the three scientific databases. The most frequently cited articles were then selected, resulting in a total of 130 articles, of which 10 were duplicates and three did not fit the initial search profile (the first lay outside the predefined time interval, the second was an article from the field of pharmaceutics, and the third was not an original article, but a report). These 13 articles were removed in the exclusion of duplicates and search refinement stages, leaving a total of 117 original articles whose contents were analyzed. | Based on the initial search criteria, 1,912 articles were identified in the three scientific databases. The most frequently cited articles were then selected, resulting in a total of 130 articles, of which 10 were duplicates and three did not fit the initial search profile (the first lay outside the predefined time interval, the second was an article from the field of pharmaceutics, and the third was not an original article, but a report). These 13 articles were removed in the exclusion of duplicates and search refinement stages, leaving a total of 117 original articles whose contents were analyzed. | ||
| − | =4. Results and | + | ==4. Results and discussion== |
The results of the study conducted in accordance with the methodology presented in Section 3 are presented here, with the 117 most cited articles from the ScienceDirect, Scopus and Web of Science databases. The systematic review of the articles is presented in Section 4.1 and the bibliometric review in Section 4.2. | The results of the study conducted in accordance with the methodology presented in Section 3 are presented here, with the 117 most cited articles from the ScienceDirect, Scopus and Web of Science databases. The systematic review of the articles is presented in Section 4.1 and the bibliometric review in Section 4.2. | ||
| − | ==4.1. Systematic | + | ===4.1. Systematic literature review=== |
| − | Of the 117 articles analyzed, 22 are studies that used X-rays (XR) and Computed Tomography (CT) of the lungs of patients affected by Covid-19 so that, through ML techniques, they could be differentiated from other lung ailments, predicting their level of severity, and determining which measures should be taken, among other alternatives, as shown in | + | Of the 117 articles analyzed, 22 are studies that used X-rays (XR) and Computed Tomography (CT) of the lungs of patients affected by Covid-19 so that, through ML techniques, they could be differentiated from other lung ailments, predicting their level of severity, and determining which measures should be taken, among other alternatives, as shown in [[#tab-1|Table 1]]. |
Researchers Ardakani et al. [19], for example, suggested a rapid and valid method for Covid-19 diagnosis based on AI techniques. They used 1,020 CT slices from 108 patients with laboratory proven Covid-19 (Covid-19 group) and 86 patients with other atypical and viral pneumonia diseases (non-Covid-19 group). The authors used 10 known Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and concluded that a computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) approach based on CT images has promising potential to distinguish Covid-19 infections from other atypical and viral pneumonia diseases. Their study showed that ResNet-101 can be considered a promising model to characterize and diagnose Covid-19 infections. This model does not involve substantial costs and can be used as an adjuvant method during CT imaging in radiology departments. | Researchers Ardakani et al. [19], for example, suggested a rapid and valid method for Covid-19 diagnosis based on AI techniques. They used 1,020 CT slices from 108 patients with laboratory proven Covid-19 (Covid-19 group) and 86 patients with other atypical and viral pneumonia diseases (non-Covid-19 group). The authors used 10 known Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and concluded that a computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) approach based on CT images has promising potential to distinguish Covid-19 infections from other atypical and viral pneumonia diseases. Their study showed that ResNet-101 can be considered a promising model to characterize and diagnose Covid-19 infections. This model does not involve substantial costs and can be used as an adjuvant method during CT imaging in radiology departments. | ||
| Line 112: | Line 114: | ||
Another example is the work of Cai et al. [20], who analyzed the CT quantification of Covid-19 pneumonia and how are the impacts on the assessment of disease severity through the prediction, using Random Forest Regression (RFR), of clinical outcomes in the management of Covid-19 patients. Meanwhile, the work of Chowdhury et al. [21], proposed a robust technique for automatic detection of Covid-19 pneumonia from digital chest X-ray images applying pre-trained Deep Learning (DL) algorithms while maximizing the detection accuracy. A public database was created by the authors combining several public databases and also by collecting images from recently published papers. | Another example is the work of Cai et al. [20], who analyzed the CT quantification of Covid-19 pneumonia and how are the impacts on the assessment of disease severity through the prediction, using Random Forest Regression (RFR), of clinical outcomes in the management of Covid-19 patients. Meanwhile, the work of Chowdhury et al. [21], proposed a robust technique for automatic detection of Covid-19 pneumonia from digital chest X-ray images applying pre-trained Deep Learning (DL) algorithms while maximizing the detection accuracy. A public database was created by the authors combining several public databases and also by collecting images from recently published papers. | ||
| − | + | [[#tab-1|Table 1]] provides an overview of this research niche involving ML and XR/CT. The first column contains the authors, while the second presents the focus of the study. The third column identifies the ML technique that was employed, and the fourth column shows the databases that were used. | |
| − | <div class="center" style=" | + | <div class="center" style="font-size: 75%;">'''Table 1'''. Papers (22) that analyzed lung XR/CT of Covid-19 patients using ML techniques</div> |
| − | '''Table 1 | + | |
| − | {| style=" | + | <div id='tab-1'></div> |
| + | {| class="wikitable" style="margin: 1em auto 0.1em auto;border-collapse: collapse;font-size:85%;width:auto;" | ||
| + | |-style="text-align:center" | ||
| + | ! style="background-color: #d1e0df;text-align:left;"| Authors (year) !! style="background-color:#d1e0df;text-align:left;"| Focus of the paper !! style="background-color: #d1e0df;text-align:left;"| ML Techniques !! style="background-color: #d1e0df;text-align:left;"| Databases | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Anastasopoulos et al. (2020) [22] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Implement an automated software to solve the substantial increase in chest CT admissions |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|DL |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|GitHub platform with Covid-19 chest CT dataset |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Ardakani et al. (2020) [19] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Develop a rapid and valid method for Covid-19 diagnosis |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|10 Convolutional NN |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|108 patients |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Bharati et al. (2020) [23] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Detect lung diseases from X-ray images through ''VGG Data STN ''with ''CNN ''(VDSNet) |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|DL; VGG; STN; CNN |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Kaggle repository |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Brunese et al. (2020) [24] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Detect Covid-19 from chest X-rays |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Supervised ML techniques |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|85 chest X-rays | |
| − | + | ||
| − | | style=" | + | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Cai et al. (2020) [20] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Analyze CT quantification |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|RFR |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|99 patients from Zhejiang |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Chakraborty & Mali (2021) [25] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Efficiently Interpret and segment Covid-19 radiological images. |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|SUFMACS |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|250 CT images; 250 X-Ray images |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Chowdhury et al. (2020) [21] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Detect Covid-19 pneumonia from digital X-ray images |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|DL |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Kaggle databases |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Elaziz et al. (2020) [26] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Classify chest x-ray images into 2 classes: Covid-19 patient or non-Covid-19 person |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|New FrMEMs; modified Manta-Ray Foraging Optimization based on DE |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|GitHub; Qatar University; University of Dhaka |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Vijay kumar et al. (2020) [27] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Use the analytics of key points from images of Covid-19 for diagnosis and predictions |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|GANs; DL | |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|16 benchmark datasets | |
| − | | style=" | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | | style=" | + | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Loey et al. (2020) [28] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Detect coronavirus in chest X-ray images |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|GAN; DL |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|307 images |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Saha et al. (2021) [29] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Identify Covid-19 patients by evaluating chest X-ray images through an automated detection scheme (EMCNet) |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|DL; RF; SVM; DT; AdaBoost |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Github repository (400 chest X-ray images) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Saygılı (2021) [30] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Achieve rapid and accurate detection of Covid-19 from CT and X-ray images |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|k-NN; SVM; Bag of Tree; K-ELM |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|3 public Covid-19 data sets |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Sedik et al. (2020) [31] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Present two data-augmentation models to enhance learnability of Covid-19 detection |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|CNN: ConvLSTM-based on DL |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|2 datasets consisting of X-ray and CT images |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Sethy et al. (2020) [32] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Detect coronavirus infected patients using X-ray images |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Deep feature; SVM | |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|GitHub repositor (University of Montreal; 381 images) | |
| − | | style=" | + | |
| − | | style=" | + | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | stylestyle="background-color:#f5faf9;"="text-align: left;"|Shiri et al. (2021) [33] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Predict Covid-19 patients using clinical data and lung/lesion radiomic features extracted from chest CT images |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|XGBoost |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|152 patients |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|D. Singh et al. (2020) [34] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Classify Covid-19 patients from chest CT images |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|MODE; ANN; ANFIS; CNN |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|--- |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Somasekar et al. (2020) [14] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Open 3 research directions in the fight against the pandemic: CXR image classification; patient risk prediction; and forecasting of disease |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|DCNN |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|--- |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Tamal et al. (2021) [35] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Detect Covid-19 early and rapidly from CXR |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|SVM; k-NN; EBM Trees | |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|378 images | |
| − | | style=" | + | |
| − | | style=" | + | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Tartaglione et al. (2020) [36] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Provide which information to expect through CXR images |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|DL to Covid classification of CXR images |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Hospitals in Northern Italy |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|X. Wang et al. (2020) [37] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Develop a DL using 3D CT for Covid-19 classification and lesion localization |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|DL |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|540 patients |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Waheed et al. (2020) [38] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Generate synthetic chest X-ray images |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|DL: CNNs |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|3 publicly accessible datasets |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Wu et al. (2021) [39] |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Improve Covid-19 diagnosis using CT | |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|RF | |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Youan Hospital, Beijing. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | | style=" | + | |
| − | | style=" | + | |
| − | | style=" | + | |
|} | |} | ||
| − | '''Acronyms (alphabetical): '''AI (Artificial Intelligence); AF (Atrial Fibrillation); AL (Active Learning); ANFIS (adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system); API (Application Programming Interface); AR (Auto-Regressive Process); ARIMA (Auto-Regressive Integrated Moving Average); BTM (Biterm Topic Model); CDCP (Center for Disease Control and Prevention); CART (Classification And Regression Trees); CXR (Chest X-Ray); CMC (composite Monte-Carlo); CMM (Chinese Materia Medica); CNN (Convolutional Neural Networks); CT (computed tomography); ConvLSTM (Convolutional Long Short-Term Memory); CTree (Conditional Inference Tree); CUBIST (Cubist Regression); DCNN (Deep Convolution Neural Networks); DE (Differential Evolution); DL (deep learning); DT (Decision Trees); EA (Ensemble Algorithm); EBM (Ensemble Bagged Model) Trees); ELM (Extreme Learning Machine); FrMEMs (Fractional Multichannel Exponent Moments); FRI (Fuzzy Rule Induction); GA (Genetic Algorithm); GAN (Generative Adversarial Network); GBA (Gradient Boosting Algorithm); GPR(Gaussian Process Regression); GBM (Gradient Boosted Tree Models); GIWD (Generalized Inverse Weibull distribution); GHOST (Globally Harmonized Observational Surface Treatment); HCA (Hierarchical Clustering Algorithm); IoT (Internet of Things); k-NN (k-Nearest Neighbor); K-ELM (Kernel Extreme Learning Machine); LASSO (least absolute shrinkage and selection operator); LDA (Latent Dirichlet Allocation); LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory); LR (Linear Regression); LoR (Logistic Regression); LOS (Length of Stay); LSTM (Long /Short Term Memory); LR (Linear Regression); ML (Machine Learning); MLDSP (Machine Learning with Digital Signal Processing); MLP (Multilayer perceptron); MLP-ICA (MLP-imperialist competitive algorithm); MODE (Multi-objective Differential Evolution); MNB (Multinomial Naïve Bayes); NLP (Natural Language Processing); NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information); NN (Neural Network); PAC (Passive Aggressive Classifier); PCR (Principal Components Regression); PDR-NML (Partial Derivative Regression and Nonlinear Machine Learning); PLS-DA (Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis); PLSR (Partial Least Squares Regression); PNN+cf (Polynomial Neural Network with Corrective Feedback); PR (Polynomial Regression); RF (Random Forest); RFR (Random Forest Regression); RIDGE (Ridge Regression); RT (Regression Tree); SARIMA (Seasonal Auto-Regressive Integrated Moving Average); SEIRD (Susceptible, Exposed, Infected, Recovered, and Dead); SIR (Susceptible(P-Infected-Recovered epidemiological model); SLR (Simple Linear Regression); SMOM (Social Mimic Optimization Method); SNA (social network analysis); SUFMACS (SUperpixel based Fuzzy Memetic Advanced Cuckoo Search); SVM (Support Vector Machine); SVR (Support Vector Regression); STN (Spatial Transformer Network); SVC (Support Vector Classifier); SVR (Support Vector Regression); TClustVID (Clustered Based Proposed Classification and Topics modeling Approach); TCM (traditional Chinese medicine); TWC (Topological Weighted Centroid); USDA ERS (United States Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service); VGG (Visual Geometry Group based Neural Network); WHO (World Health Organization); VAR (Vector Autoregression); WSIDEA (Weighted Stochastic Data Envelopment Analysis); WSCC (Web of Science Core Collection); XGBoost (Extreme Gradient Boosting). | + | <div class="justified" style="font-size: 75%;">'''Acronyms (alphabetical): '''AI (Artificial Intelligence); AF (Atrial Fibrillation); AL (Active Learning); ANFIS (adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system); API (Application Programming Interface); AR (Auto-Regressive Process); ARIMA (Auto-Regressive Integrated Moving Average); BTM (Biterm Topic Model); CDCP (Center for Disease Control and Prevention); CART (Classification And Regression Trees); CXR (Chest X-Ray); CMC (composite Monte-Carlo); CMM (Chinese Materia Medica); CNN (Convolutional Neural Networks); CT (computed tomography); ConvLSTM (Convolutional Long Short-Term Memory); CTree (Conditional Inference Tree); CUBIST (Cubist Regression); DCNN (Deep Convolution Neural Networks); DE (Differential Evolution); DL (deep learning); DT (Decision Trees); EA (Ensemble Algorithm); EBM (Ensemble Bagged Model) Trees); ELM (Extreme Learning Machine); FrMEMs (Fractional Multichannel Exponent Moments); FRI (Fuzzy Rule Induction); GA (Genetic Algorithm); GAN (Generative Adversarial Network); GBA (Gradient Boosting Algorithm); GPR(Gaussian Process Regression); GBM (Gradient Boosted Tree Models); GIWD (Generalized Inverse Weibull distribution); GHOST (Globally Harmonized Observational Surface Treatment); HCA (Hierarchical Clustering Algorithm); IoT (Internet of Things); k-NN (k-Nearest Neighbor); K-ELM (Kernel Extreme Learning Machine); LASSO (least absolute shrinkage and selection operator); LDA (Latent Dirichlet Allocation); LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory); LR (Linear Regression); LoR (Logistic Regression); LOS (Length of Stay); LSTM (Long /Short Term Memory); LR (Linear Regression); ML (Machine Learning); MLDSP (Machine Learning with Digital Signal Processing); MLP (Multilayer perceptron); MLP-ICA (MLP-imperialist competitive algorithm); MODE (Multi-objective Differential Evolution); MNB (Multinomial Naïve Bayes); NLP (Natural Language Processing); NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information); NN (Neural Network); PAC (Passive Aggressive Classifier); PCR (Principal Components Regression); PDR-NML (Partial Derivative Regression and Nonlinear Machine Learning); PLS-DA (Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis); PLSR (Partial Least Squares Regression); PNN+cf (Polynomial Neural Network with Corrective Feedback); PR (Polynomial Regression); RF (Random Forest); RFR (Random Forest Regression); RIDGE (Ridge Regression); RT (Regression Tree); SARIMA (Seasonal Auto-Regressive Integrated Moving Average); SEIRD (Susceptible, Exposed, Infected, Recovered, and Dead); SIR (Susceptible(P-Infected-Recovered epidemiological model); SLR (Simple Linear Regression); SMOM (Social Mimic Optimization Method); SNA (social network analysis); SUFMACS (SUperpixel based Fuzzy Memetic Advanced Cuckoo Search); SVM (Support Vector Machine); SVR (Support Vector Regression); STN (Spatial Transformer Network); SVC (Support Vector Classifier); SVR (Support Vector Regression); TClustVID (Clustered Based Proposed Classification and Topics modeling Approach); TCM (traditional Chinese medicine); TWC (Topological Weighted Centroid); USDA ERS (United States Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service); VGG (Visual Geometry Group based Neural Network); WHO (World Health Organization); VAR (Vector Autoregression); WSIDEA (Weighted Stochastic Data Envelopment Analysis); WSCC (Web of Science Core Collection); XGBoost (Extreme Gradient Boosting).</div> |
| + | |||
| + | |||
On the other hand, many works used ML techniques to analyze people’s feelings and emotions regarding the pandemic, even their impressions concerning the climate. Sentiment Analysis is an field of study that seeks useful information through the sentiments that people share on social media, such as Facebook and Twitter [40]. Sentiments can be classified as neutral, positive or negative. | On the other hand, many works used ML techniques to analyze people’s feelings and emotions regarding the pandemic, even their impressions concerning the climate. Sentiment Analysis is an field of study that seeks useful information through the sentiments that people share on social media, such as Facebook and Twitter [40]. Sentiments can be classified as neutral, positive or negative. | ||
| − | Gulati et al. [41], for example, presented a comparative analysis of seven ML classifiers, such as Linear Support Vector Classifier (SVC), Perceptron, Passive Aggressive Classifier (PAC), and Logistic Regression (LoR). They used more than 72,000 tweet datasets related to Covid-19 pandemic and achieved an accuracy score higher than 98%. Haupt et al. [42] used interdisciplinary approaches to big data, ML, content analysis, and social network analysis (SNA) to characterize the communicative behavior, conversation themes, and network structures of “Liberate protest” supporters and non-supporters. For this purpose, the authors used unsupervised ML techniques and social network analysis. Praveen et al. [43] | + | Gulati et al. [41], for example, presented a comparative analysis of seven ML classifiers, such as Linear Support Vector Classifier (SVC), Perceptron, Passive Aggressive Classifier (PAC), and Logistic Regression (LoR). They used more than 72,000 tweet datasets related to Covid-19 pandemic and achieved an accuracy score higher than 98%. Haupt et al. [42] used interdisciplinary approaches to big data, ML, content analysis, and social network analysis (SNA) to characterize the communicative behavior, conversation themes, and network structures of “Liberate protest” supporters and non-supporters. For this purpose, the authors used unsupervised ML techniques and social network analysis. Praveen et al. [43] conducted their study to analyze Indian citizens’ perceptions of what causes stress, anxiety, and trauma during Covid-19. For this purpose, the authors used ML techniques, more specifically, Natural Language Processing (NLP) in 840,000 tweets. Of the 117 articles analyzed, 13 were in this line of research and are listed in [[#tab-2|Table 2]]. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | {| style=" | + | <div class="center" style="font-size: 75%;">'''Table 2'''. Works (13) related to Covid-19 that used ML techniques and social network tools</div> |
| + | |||
| + | <div id='tab-2'></div> | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" style="margin: 1em auto 0.1em auto;border-collapse: collapse;font-size:85%;width:auto;" | ||
| + | |-style="text-align:center" | ||
| + | ! style="background-color: #d1e0df;text-align:left;"| Authors (year) !! style="background-color:#d1e0df;text-align:left;"| Focus of the paper !! style="background-color: #d1e0df;text-align:left;"| ML Techniques !! style="background-color: #d1e0df;text-align:left;"| Databases | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Abd-Alrazaq et al. (2020) [44] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Identify the topics related to Covid-19 posted by Twitter users |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|API; Tweepy Python library |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|February 2, 2020, to March 15, 2020 in public English language tweets |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Gulati et al. (2021) [41] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Classify sentiment based on tweets related to Covid-19 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Linear SVC; Perceptron; PAC; LoR |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|72,000 tweets |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Gupta et al. (2021) [45] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Quantify twitter users’ perceptions regarding the effect of weather and analyze how they evolved with respect to real-world events and time. |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|API |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|166,005 English tweets; from January 23 to June 22, 2020 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Haupt et al. (2021) [42] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Characterize communicative (tweets) behavior |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|ML techniques and SNA |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|API from Twitter | |
| − | + | ||
| − | | style=" | + | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Hou et al. (2021) [46] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Explore public attention on social media |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Text analysis; LDA |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Weibo (popular microblogging site in China) from December 27, 2019 to May 31, 2020 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Kabir & Madria (2021) [47] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Present tweets dataset on Covid-19 emotional responses (EMOCOV) |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|DL |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Data of 5,000 tweets |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Kyriazos et al. (2021) [48] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Model that differentiated the top 25% well-being scorers in early Covid-19 quarantine |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|CART; RF; CTREE |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Data (1,518) were collected in a web-link posted on webpages and Facebook accounts |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|S. Li et al. (2020) [49] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Explore Covid-19’s impacts on mental health |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|DL |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|17,865 active Weibo users | |
| − | + | ||
| − | | style=" | + | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Mackey et al. (2020) [50] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Characterize users’ conversations (tweets) associated with Covid-19 symptoms and experiences |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|BTM |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|4,492,954 tweets |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Praveen et al. (2021) [43] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Analyze Indian citizens’ perception of anxiety, stress and trauma during Covid-19 |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Natural language | |
| − | Covid-19 | + | | style="text-align: left;"|840,000 tweets |
| − | | style=" | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | | style=" | + | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Samuel et al. (2020) [51] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Identify public sentiment (tweets) associated with the pandemic |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Naïve Bayes; LR; LoR; k-NN |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|900,000 tweets |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Satu et al. (2021) [52] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Analyze Covid-19 public tweets to extract significant sentiments |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|TClustVID |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|IEEE data portal developed by Rabindra Lamsal |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Shah et al. (2021) [53] |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Analyze online physician rating (OPR) to identify emerging and fading topics and sentiment trends on physician websites | |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|NLP | |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|55,612 OPRs of 3,430 doctors | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | | style=" | + | |
| − | | style=" | + | |
| − | | style=" | + | |
|} | |} | ||
| − | Acronyms (alphabetical): See Table 1. | + | Acronyms (alphabetical): See [[#tab-1|Table 1]]. |
| + | |||
In turn, 44 of the 117 selected articles involved ML methods to predict a wide range of aspects, such as the number of patients who will be infected or intubated, the trends of the pandemic, the production of a real-time Covid-19 SEIRD (Susceptible, Exposed, Infected, Recovered, and Dead) model, and student performance. | In turn, 44 of the 117 selected articles involved ML methods to predict a wide range of aspects, such as the number of patients who will be infected or intubated, the trends of the pandemic, the production of a real-time Covid-19 SEIRD (Susceptible, Exposed, Infected, Recovered, and Dead) model, and student performance. | ||
| − | Amar et al. [54], for example, attempted to investigate the disease to eliminate its effects and, to this end, the authors examined a real database from Egypt, from February 15, 2020, to June 15, 2020. They predicted the number of patients that would be infected and estimated the final size of the pandemic. For this purpose, they applied several regression analysis models. Burdick et al. [55] attempted to predict patients’ need for ventilation to determine a better allocation of resources and prevent emergency intubations and their associated risks. The authors analyzed 197 patients, from five USA health systems between March 24 and May 4, 2020. The patients were enrolled in the REspirAtory Decompensation for the triage of the disease: a prospective studY (READY) clinical trial. Of the 117 articles analyzed, 44, including the two already mentioned above, were in this line of research and are listed in | + | Amar et al. [54], for example, attempted to investigate the disease to eliminate its effects and, to this end, the authors examined a real database from Egypt, from February 15, 2020, to June 15, 2020. They predicted the number of patients that would be infected and estimated the final size of the pandemic. For this purpose, they applied several regression analysis models. Burdick et al. [55] attempted to predict patients’ need for ventilation to determine a better allocation of resources and prevent emergency intubations and their associated risks. The authors analyzed 197 patients, from five USA health systems between March 24 and May 4, 2020. The patients were enrolled in the REspirAtory Decompensation for the triage of the disease: a prospective studY (READY) clinical trial. Of the 117 articles analyzed, 44, including the two already mentioned above, were in this line of research and are listed in [[#tab-3|Table 3]]. |
| + | |||
| − | <div class="center" style=" | + | <div class="center" style="font-size: 75%;">'''Table 3'''. Works (44) related to Covid-19 that directly used ML techniques for prediction</div> |
| − | '''Table 3 | + | |
| − | {| style=" | + | <div id='tab-3'></div> |
| + | {| class="wikitable" style="margin: 1em auto 0.1em auto;border-collapse: collapse;font-size:85%;width:auto;" | ||
| + | |-style="text-align:center" | ||
| + | ! style="background-color: #d1e0df;text-align:left;"| Authors (year) !! style="background-color:#d1e0df;text-align:left;"| Focus of the paper !! style="background-color: #d1e0df;text-align:left;"| ML Techniques !! style="background-color: #d1e0df;text-align:left;"| Databases | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Amar et al. (2020) [54] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Predict the number of patients that will be infected with Covid-19 in Egypt |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|LoR; Regression models |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Egyptian Ministry of Health; February 15, 2020, to June 15, 2020 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Ardabili et al. (2020) [56] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Predict the Covid-19 outbreak and the enforcement of relevant control measures |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|MLP; ANFIS |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Worldometers website for five countries |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Arvind et al. (2021) [57] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Predict future intubation among patients diagnosed with Covid-19 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|RF |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Data from 5 hospitals within an academic healthcare system (4,087 patients) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|ArunKumar et al. (2021) [58] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Forecast the epidemiological trends of the Covid-19 pandemic for top-16 countries |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Time series models; ARIMA; SARIMA | |
| − | Covid-19 | + | | style="text-align: left;"|John Hopkins University’s Covid-19 database |
| − | | style=" | + | |
| − | | style=" | + | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Aydin & Yurdakul (2020) [59] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Analyze the performance of countries to counter the Covid-19 outbreak |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|WSIDEA; k-means; HCA; RF; DT |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Data from 142 countries | |
| − | + | ||
| − | | style=" | + | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Ayyoubzadeh et al. (2020) [60] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Predict the incidence of Covid-19 in Iran |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|LR; LSTM models |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Google Trends website |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Ballı (2021) [61] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Identify the curve of the disease and forecast the epidemic trend |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|LR, MLP, RF and SVM |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Data from WHO (35 weeks) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Bloise & Tancioni (2021) [62] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Exploit the provincial variability of Covid-19 cases in Italy to select the territorial predictors for the pandemic |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|LASSO; Elastic net model |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Data from March 21, 2020 to June 3, 2020, in Italy |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Burdick et al. (2020) [55] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Predict the need for ventilation for Covid-19 patients |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|XGBoost; DT |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|197 patients were enrolled in the READY (REspirAtory Decompensation study) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Buscema et al. (2020) [63] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Analyze the evolution of the Covid-19 phenomenon |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|TWC algorithm |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Geospatial coordinates of latitude and longitude of the Italian locations where the events occurred. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Chakraborti et al. (2021) [64] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Perform the regression modelling and provide subsequent interpretation of most critical factors |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|RF; GBM |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Chatterjee et al. (2020) [65] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Analyze datasets to understand the trend of Covid-19 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Statistical and univariate time series |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Oxford University Database |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Chimmula & Zhang (2020) [66] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Forecast Covid-19 transmission |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Time series; DL; LSTM networks | |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Johns Hopkins university; Canadian health authority | |
| − | + | ||
| − | Covid-19 | + | |
| − | | style=" | + | |
| − | | style=" | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Cobre et al. (2021) [67] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Predict Covid-19 diagnosis and disease severity |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|ANN; DT; PLS-DA; KNN |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Kaggle platform 5,643 patient samples |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Ebinger et al. (2021) [68] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Predict the likelihood of prolonged LOS |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|3 ML models developed using DataRobot |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|966 patients | |
| − | + | ||
| − | | style=" | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Fong et al. (2020) [69] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Find a forecasting model (GROOWS) from a small dataset for Covid-19 cases |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|PNN+cf |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Archive of Chinese health authorities |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Gothai et al. (2021) [70] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Predict the growth and trend of Covid-19 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|LR; SVM; time series |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|172,479 documents from Johns Hopkins University Repository |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Jain et al. (2021) [71] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Predict Covid-19 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|SVM; Naïve Bayes; KNN; AdaBoost; GBoost; RF; ANN |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|B-cell dataset |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Kang et al. (2021) [72] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Predict severe Covid-19 cases |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|ANN |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|151 cases of a China center |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Kavadi et al. (2020) [73] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Global pandemic prediction of Covid-19 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|PDR-NML method |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Kaggle |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Khan et al. (2021) [74] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Predict the time after which the number of cases stops rising in India |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|DT; SVM; GPR |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW) on 10th June 2020 | |
| − | + | ||
| − | | style=" | + | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Lmater et al. (2021) [75] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Present an effective mathematical model for predicting the spread of the (Covid-19) pandemic. |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|SIDR model (susceptible, infected, diagnosed and recovered stages) |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Epidemiological data from 4 countries: Belgium; Morocco; Netherlands; Russia | |
| − | + | ||
| − | | style=" | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Malefors et al. (2021) [76] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Predict guest attendance during the pandemic (meal planning in Sweden) |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|RF; ANN |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Data from 18 primary school kitchens and 16 preschool kitchens |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Mojjada et al. (2020) [77] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Show the ability to predict the number of individuals who are affected by Covid-19. |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|LASSO; SVM; LR |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Git Hub, supplied by Johns Hopkins University |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Nemati et al. (2020) [78] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Predict patients’ period of stay in hospital |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|7 ML and statistical analysis techniques |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|1,182 hospitalized patients | |
| − | + | ||
| − | | style=" | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Ong et al. (2020) [79] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Predict Covid-19 vaccine candidates |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Vaxign reverse vaccinology tools | |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|ClinicalTrials.gov database and PubMed literature | |
| − | | style=" | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | | style=" | + | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Papastefanopoulos et al. (2020) [80] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Investigate the accuracy of six time series for coronavirus to forecast active cases per population |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Six time series |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Kaggle; population-by-country dataset |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Peng & Nagata (2020) [81] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Predict the number of Covid-19 cases for the 12 most affected countries |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|SVR |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|12 most affected countries |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Pinter et al. (2020) [82] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Predict the Covid-19 pandemic for Hungary |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Hybrid ML: ANFIS and MLP-ICA |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Worldometer for Hungary |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Pourhomayoun & Shakibi (2021) [83] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Determine the risk and predict the mortality risk of patients with Covid-19 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|SVM; ANN; RF; DT; LoR; KNN |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|2,670,000 Covid-19 patients from 146 countries |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Quintero et al. (2021) [84] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Predict the SEIRD variables based on a deep dependence on them |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|GA; AR; ARIMA |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|The National Institute of Health for Colombia and the National Administrative Department of Statistics |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Ribeiro et al. (2020) [85] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Develop short-term forecasting models to allow forecasting of the number of cases in the future |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|ARIMA; CUBIST; RF; RIDGE; SVR; SVR |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Cases in Brazil up to April, 19 of 2020; 10 datasets | |
| − | + | ||
| − | | style=" | + | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Santosh (2020) [86] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Develop AI-driven tools to identify Covid-19 outbreaks |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|AL |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Multitudinal and Multimodal data | |
| − | + | ||
| − | | style=" | + | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Shahid et al. (2021) [6] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Predict virus detection, spread prevention and medical assistance |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|survey of ML algorithms and models |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|--- |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|V. Singh et al. (2020) [87] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Produce a real-time SEIR model of confirmed, deceased, and recovered Covid-19 cases. |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|SVM; time series |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Johns Hopkins CSSE; data from January 22, 2020 to April 25, 2020 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Sujath et al. (2020) [88] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Predict the spread of Covid-2019 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|LR; MLP; VAR |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Kaggle; Indian database |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Tarik et al. (2021) [89] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Predict Moroccan student performance |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|RF; DT; LR |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Referral system |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Tuli et al. (2020) [90] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Analyze and predict the growth of the epidemic |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|GIWD in a cloud computing platform |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Our World in Data by Hannah Ritchie |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Wadhwa et al. (2021) [91] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Predict the extension of lockdown in order to eradicate Covid-19 from India. |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|LR |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Total number of cases, deaths, and recoveries all over India. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | | style=" | + | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|P. Wang et al. (2020) [92] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Predict epidemic trends |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|LoR | |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Johns Hopkins University, from January 22, 2020 to June 16, 2020. | |
| − | | style=" | + | |
| − | | style=" | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Yan et al. (2020) [93] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Identify crucial predictive biomarkers of Covid-19 mortality |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|XGBoost |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|485 patients |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Yadav et al. (2020) [94] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Solve 5 different tasks: I) Predict the spread of the disease; II) Analyze the growth rates; III) Predict how the pandemic will end; IV) Analyze the transmission rate; and V) Correlate the disease to the weather conditions. |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|SVR; SLR; PR |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Data from different countries |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Yeşilkanat (2020) [95] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Estimate the number of future cases for 190 countries in the world |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|RF | |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Johns Hopkins University Center for Systems Science; Engineering | |
| − | | style=" | + | |
| − | | style=" | + | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style=" text-align: left;"|Zivkovic et al. (2021) [96] |
| − | + | | style=" text-align: left;"|Predict the number of new coronavirus cases | |
| − | + | | style=" text-align: left;"|ANFIS; BASSI | |
| − | + | | style=" text-align: left;"|6 benchmark Functions | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | | style=" | + | |
| − | | style=" | + | |
| − | | style=" | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | Functions | + | |
|} | |} | ||
| − | Acronyms (alphabetical): See Table 1. | + | Acronyms (alphabetical): See [[#tab-1|Table 1]]. |
| − | |||
| − | + | Finally, the last 38 of the 117 selected articles that address general subjects involving ML techniques and Covid-19 are listed in [[#tab-4|Table 4]]. These include, for example, that of Di Castelnuovo et al. [97], who attempted to list those that aimed to identify the characteristics predisposing Covid-19 patients to in-hospital death. For this purpose, the authors used the data of 3,894 patients from 30 clinical centers distributed throughout Italy, who were hospitalized from February 19th to May 23rd, 2020. The authors used the RF technique to achieve their goal. They concluded that impaired renal function, elevated C-reactive protein, and advanced age were major predictors of in-hospital death. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | {| style=" | + | |
| + | <div class="center" style="font-size: 75%;">'''Table 4'''. Works (38) related to Covid-19 that used ML techniques involving general subjects</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div id='tab-4'></div> | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" style="margin: 1em auto 0.1em auto;border-collapse: collapse;font-size:85%;width:auto;" | ||
| + | |-style="text-align:center" | ||
| + | ! style="background-color: #d1e0df;text-align:left;"| Authors (year) !! style="background-color:#d1e0df;text-align:left;"| Focus of the paper !! style="background-color: #d1e0df;text-align:left;"| ML Techniques !! style="background-color: #d1e0df;text-align:left;"| Databases | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Alves et al. (2021) [98] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Present understandable solutions to deal with Covid-19 screening in routine blood tests |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|DT Explainer and criteria graphs |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|608 patients; public dataset from the Albert Einstein Hospital, São Paulo |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Baralić et al. (2020) [99] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Assess risks and benefits of Covid- 19 treatment with promising drug combinations: lopinavir/ritonavir and chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine+ azithromycin. |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|''in silico ''toxicogenomic data-mining approach |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Comparative Toxicogenomics Database | |
| − | + | ||
| − | | style=" | + | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Carrillo-Larco & Castillo-Cara (2020) [100] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Clustering countries which shared profiles of the pandemic |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|k-means; statistical techniques |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|155 countries; Johns Hopkins University and others |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Di Castelnuovo et al. (2020) [97] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Identify the characteristics predisposing Covid-19 patients to in-hospital death. |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|RF |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|3,894 patients hospitalized from a defined period (Italy) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Choudrie et al. (2021) [101] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Explore how ML techniques and experienced people process the online infodemic related to prevention and cure |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|DT; CNN | |
| − | to | + | | style="text-align: left;"|143 patients |
| − | | style=" | + | |
| − | | style=" | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Dandekar et al. (2020) [102] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Develop a globally applicable diagnostic Covid-19 model |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|SIR; NN |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|70 countries |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Doanvo et al. (2020) [15] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Identify knowledge research Covid-19 gaps in the literature |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|PCA |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|35,281 abstracts from CORD-19 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Fong et al. (2020) [103] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Gain stochastic insights into the pandemic development |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|CMC: DL; FRI |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Empirical data from the Chinese CDCP |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Godavarthi & Sowjanya (2021) [104] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Extract information from the scientific literature: text classification |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|KNN; MLP; XGBoost |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|CORD-19 dataset |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Hu et al. (2021) [105] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Detect the changes in air pollutants during Covid-19 lockdown |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|RF models |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Data from 35 sites in Beijing, from 2015 to 2020 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Jamshidi et al. (2020) [106] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Present a response to combat the virus through AI |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|GANs; LSTM; ELM |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|--- |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Kadioglu et al. (2021) [107] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Identify compounds against three targets of Covid-19 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Pharmaco strategy'' in silico'' |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Chemical libraries (FDA-approved drugs; natural compound datasets; ZINC database) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Khanday et al. (2020) [108] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Detect Covid-19 through clinical text data |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|LoR; MNB |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Data repository GitHub |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Kuo & Fu (2021) [109] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Analyze demographic and environmental impact and mobility during the pandemic period |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Elastic net model; PCR; PLSR; KNN; RT; RF; GBM; 2-layer ANN |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|New York Times; USDA ERA; gridMed; Google |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Lam et al. (2021) [110] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Present a ML system capable of identifying patients who could be treated with a corticosteroid or remdesivir |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|GBM |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|893 patients |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|M. Li et al. (2021) [16] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Detect novel critical factors associated with Covid-19 in 154 countries and in the 50 USA states |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|LoR; LASSO |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Johns Hopkins University |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Lip et al. (2021) [111] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Identify patients with Covid-19 who are at the highest risk of developing incident AF |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Inferential statistics and ML computations (LoR) |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Data from April 1, 2018 to Nov 30, 2020 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Loey et al. (2021) [112] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Develop a DL and classical ML for face detection |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|DL; DT; SVM; EA |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|3 datasets |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Lovrić et al. (2021) [113] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Analyze improvements in air quality during the Covid-19 lockdown |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|RFR |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Graz, Styria, Austria |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Magazzino et al. (2021) [114] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Analyze the relationship between Covid-19 deaths, economic growth and air pollution |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|DL |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|-- |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|McRae et al. (2020) [115] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Develop a decision support tool and rapid point-of-care platform to determine severity in patients with Covid-19 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Statistical learning algorithm |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|160 patients from Wuhan, China |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Malki et al. (2020) [116] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Verify the relationship between weather and Covid-19 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Regressor ML models |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Meteoblue website |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Mele & Magazzino (2021) [117] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Explore the relationship between pollution, economic growth and Covid-19 deaths in India |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Time Series approach; Stationarity and Toda-Yamamoto causality tests |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Indian data from January 29 to May 18, 2020 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Petetin et al. (2020) [118] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Use meteorological data to estimate the “business-as-usual” NO2 mixing ratios |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|GBM | |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|GHOST | |
| − | | style=" | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | | style=" | + | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Qiang et al. (2020) [119] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Evaluate the infection risk of Covid-19 for early warning through spike protein feature |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|RF models | |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|507 human origin viruses and 2,159 non-human-origin viruses | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | | style=" | + | |
| − | | style=" | + | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Radanliev et al. (2020) [120] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Investigate the scientific research response from the early stages of the pandemic |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Statistical methods |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|WSCC |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Randhawa et al. (2020) [121] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Use intrinsic genomic signatures to classify Covid-19 rapidly |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|MLDSP for genome analyses; DT |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Dataset of over 5,000 unique viral genomic sequences from the NCBI |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Shrock et al. (2020) [122] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Explore antiviral antibody responses across the human virome |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|XGBoost |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|232 coronavirus disease patients and 190 pre-Covid-19 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|X. Sun et al. (2020) [123] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Explore TCM formulae to investigate their compatibility with the CMM to understand their potential mechanisms for treatment of Covid-19 |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|TCM; CMM | |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Encyclopedia of Traditional Chinese Medicine database; BATMAN-TCM database | |
| − | | style=" | + | |
| − | | style=" | + | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|C. L. F. Sun et al. (2020) [124] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Identify risks and vectors of infection in nursing homes |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|GBA |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|1146 NHs in Massachusetts |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Swapnarekha et al. (2020) [125] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Present a state-of-the-art analysis using ML and DL methods in the diagnosis and prediction of Covid-19 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|ML; DL |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|January 23, 2020 to April, 21, 2020 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|S. Tiwari et al. (2020) [126] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Prepare Indian government and citizens to take control measures (SEIR) |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Time Series |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Kaggle (data available between January 22, 2020, and April 3, 2020, from India and China) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|A. Tiwari et al. (2021) [127] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Define a Covid-19 Vulnerability Index (C19VI) for identifying and mapping counties considered vulnerable |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|RF |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Johns Hopkins University; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Toğaçar et al. (2020) [128] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Detect Coronavirus |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|DL; SVM; SMOM |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|GitHub; Kaggle |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Vaishya et al. (2020) [129] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Revise the effectiveness of AI techniques for Covid-19 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|AI techniques |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|PubMed, Scopus and Google Scholar datasets |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|W.-C. Wang et al. (2021) [130] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Develop a system for monitoring global and local community outbreaks |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|k-means |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Johns Hopkins; data with daily infected, recovered and death cases |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Yacchirema & Chura (2021) [131] |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Implement a system based on IoT for saver mobility during the pandemic | |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|SVM; DT; LoR; RF; KNN (to detect the location of people) | |
| − | + | | style="text-align: left;"|From portable IoT devices | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | | style=" | + | |
| − | | style=" | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | (to detect the location of people) | + | |
| − | | style=" | + | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Yang et al. (2020) [132] |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|Demonstrate control measures impact the containment of the epidemic |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|SEIR model |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: left;"|2003 SARS data |
|} | |} | ||
| − | Acronyms (alphabetical): See Table 1. | + | Acronyms (alphabetical): See [[#tab-1|Table 1]]. |
| − | ==4.2 Bibliometric | + | ===4.2 Bibliometric literature review=== |
Of the 117 articles analyzed on the theme of the use of ML techniques in the study of Covid-19, 67 (57%) are from the year 2020, and the other 50 articles (43%) are from 2021, up to the month of June. | Of the 117 articles analyzed on the theme of the use of ML techniques in the study of Covid-19, 67 (57%) are from the year 2020, and the other 50 articles (43%) are from 2021, up to the month of June. | ||
| − | Furthermore, of the 117 articles, 10 were published in “Chaos, Solitons and Fractals” and eight in “Computers in Biology and Medicine”. The top 54% of journals with the highest number of publications are presented in | + | Furthermore, of the 117 articles, 10 were published in “Chaos, Solitons and Fractals” and eight in “Computers in Biology and Medicine”. The top 54% of journals with the highest number of publications are presented in [[#img-2|Figure 2]]. |
| − | <div | + | <div id='img-2'></div> |
| − | '''Figure 2 | + | {| style="text-align: center; border: 1px solid #BBB; margin: 1em auto; width: 70%;" |
| + | |- | ||
| + | |style="padding:10px;"| [[File:Steiner_et_al_2022a_2680_Figure_2.png|500px]] | ||
| + | |- style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;" | ||
| + | | colspan="1" style="padding:10px;"| '''Figure 2'''. Top 54% of journals in the selected papers | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | The two main ML techniques identified by the bibliometric analysis were Random Forest (RF) and Deep Learning (DL). The most used methods, employed in 61% of the publications, are presented in [[#img-3|Figure 3]]. | ||
| − | + | <div id='img-3'></div> | |
| − | + | {| style="text-align: center; border: 1px solid #BBB; margin: 1em auto; width: 60%;" | |
| − | <div | + | |- |
| − | '''Figure 3 | + | |style="padding:10px;"| [[File:Steiner_et_al_2022a_9166_Figure_3.png|500px]] |
| − | + | |- style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;" | |
| − | + | | colspan="1" style="padding:10px;"| '''Figure 3'''. Top 61% of publications with the most used methods | |
| − | + | |} | |
It is noticed the predominance of classical algorithms, such as RF, SVM, and DT, in addition to modern techniques, such as DL and CNN. This shows that classical methods still have space in current scientific research, even in new applications, as in the case of Covid-19. | It is noticed the predominance of classical algorithms, such as RF, SVM, and DT, in addition to modern techniques, such as DL and CNN. This shows that classical methods still have space in current scientific research, even in new applications, as in the case of Covid-19. | ||
| − | Finally, considering the nationality of the authors, the USA and India drew with 30 researchers each, followed by China, with 20 researchers. | + | Finally, considering the nationality of the authors, the USA and India drew with 30 researchers each, followed by China, with 20 researchers. [[#img-4|Figure 4]] shows 70% of the most frequent nationalities of the authors of the 117 articles. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | <div id='img-4'></div> | ||
| + | {| style="text-align: center; border: 1px solid #BBB; margin: 1em auto; width: 60%;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |style="padding:10px;"| [[File:Steiner_et_al_2022a_3203_Figure_4.png|500px]] | ||
| + | |- style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;" | ||
| + | | colspan="1" style="padding:10px;"| '''Figure 4'''. Top 70% of authors' nationality | ||
The first three positions, in relation to nationality, refer to the two countries with the highest number of cases of Covid-19 (USA and India) and the country where the virus was identified (China). | The first three positions, in relation to nationality, refer to the two countries with the highest number of cases of Covid-19 (USA and India) and the country where the virus was identified (China). | ||
| − | =5. Concluding Remarks= | + | ==5. Concluding Remarks== |
| − | The aim of the present study was to conduct a systematic and bibliometric review of the articles involving the protocol shown in | + | The aim of the present study was to conduct a systematic and bibliometric review of the articles involving the protocol shown in [[#img-2|Figure 2]] which, being the most frequently cited in the literature, set out to answer, among other questions, why certain patients are severely affected by the virus while others are asymptomatic. M. Li et al. [16], for example, commented that age, sex, temperature, humidity, social distancing, smoking, investments in health, level of urbanization and race can influence the severity of the disease. On the other hand, Di Castelnuovo et al. [97] concluded that impaired renal function, elevated C-reactive protein and advanced age were major predictors of in-hospital death. However, there are many patients who fit these specific conditions, but who present different degrees of aggravation of the disease. |
We firmly believe that the answer to this question is directly found in very recent studies that reveal a possible genetic predisposition to serious cases of Covid-19 [133,134,135]. Researchers discovered that more severe cases of the disease are associated with the low performance of molecules that identify the virus and are inherited from parents: class I human leukocyte antigen (HLA-I) molecules represent the group of molecules responsible for identifying and distinguishing everything that is in the body and what is not. Six HLA-I molecules, found on the surface of all cells, form a unique set for each individual, which is determined by the genes received from the parents [135]. In other words, it is very important to investigate whether there is a direct link between the seriousness of the disease and the performance of HLA-I in the identification of Sars-CoV-2. | We firmly believe that the answer to this question is directly found in very recent studies that reveal a possible genetic predisposition to serious cases of Covid-19 [133,134,135]. Researchers discovered that more severe cases of the disease are associated with the low performance of molecules that identify the virus and are inherited from parents: class I human leukocyte antigen (HLA-I) molecules represent the group of molecules responsible for identifying and distinguishing everything that is in the body and what is not. Six HLA-I molecules, found on the surface of all cells, form a unique set for each individual, which is determined by the genes received from the parents [135]. In other words, it is very important to investigate whether there is a direct link between the seriousness of the disease and the performance of HLA-I in the identification of Sars-CoV-2. | ||
Therefore, it would be very interesting and promising to analyze the genotype of patients who have suffered Covid-19 and healthy people, employing ML techniques and classifying patients, for instance, as serious, moderate, or mild cases. | Therefore, it would be very interesting and promising to analyze the genotype of patients who have suffered Covid-19 and healthy people, employing ML techniques and classifying patients, for instance, as serious, moderate, or mild cases. | ||
| − | + | <!--==Declaration of competing interest== | |
| − | ==Declaration of competing interest== | + | |
None. | None. | ||
| + | --> | ||
==Funding sources== | ==Funding sources== | ||
| Line 912: | Line 815: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| + | <div class="auto" style="text-align: left;width: auto; margin-left: auto; margin-right: auto;font-size: 85%;"> | ||
| − | [1] WHO. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. Retrieved from [https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019 https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019] 2021. | + | [1] WHO. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. Retrieved from [https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019 https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019], 2021. |
| − | [2] Piret J., Boivin G. Pandemics | + | [2] Piret J., Boivin G. Pandemics throughout history. Front. Microbiol., 15 January, 2021. |
| − | [3] Huremović D. Brief | + | [3] Huremović D. Brief history of pandemics (Pandemics Throughout History). Psychiatry of Pandemics, Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp. 7–35, 2019. |
[4] Carvalho T., Krammer F., Iwasaki A. The first 12 months of COVID-19: a timeline of immunological insights. Nat. Rev. Immunol., 21(4):245–256, 2021. | [4] Carvalho T., Krammer F., Iwasaki A. The first 12 months of COVID-19: a timeline of immunological insights. Nat. Rev. Immunol., 21(4):245–256, 2021. | ||
| − | [5] WHO. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Retrieved from [https://covid19.who.int/ https://covid19.who.int/] 2021. | + | [5] WHO. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Retrieved from [https://covid19.who.int/ https://covid19.who.int/], 2021. |
| − | [6] Shahid O., Nasajpour M., Pouriyeh S., et al. Machine learning research towards combating COVID-19: Virus detection, spread prevention, and medical assistance. J. Biomed. Inform., 117 | + | [6] Shahid O., Nasajpour M., Pouriyeh S., et al. Machine learning research towards combating COVID-19: Virus detection, spread prevention, and medical assistance. J. Biomed. Inform., 117:103751, 2021. |
| − | [7] Prabha B., Kaur S., Singh J., Nandankar P., Kumar Jain S., Pallathadka H. Intelligent predictions of Covid disease based on lung CT images using machine learning strategy. Mater. Today Proc., | + | [7] Prabha B., Kaur S., Singh J., Nandankar P., Kumar Jain S., Pallathadka H. Intelligent predictions of Covid disease based on lung CT images using machine learning strategy. Mater. Today Proc., Online July 2021. |
| − | [8] Haridy S., Maged A., Baker A.W., Shamsuzzaman M., Bashir H., Xie M. Monitoring scheme for early detection of coronavirus and other respiratory virus outbreaks. Comput. Ind. Eng., 156 | + | [8] Haridy S., Maged A., Baker A.W., Shamsuzzaman M., Bashir H., Xie M. Monitoring scheme for early detection of coronavirus and other respiratory virus outbreaks. Comput. Ind. Eng., 156:107235, 2021. |
[9] Waleed Salehi A., Baglat P., Gupta G. Review on machine and deep learning models for the detection and prediction of Coronavirus. Mater. Today Proc., 33:3896–3901, 2020. | [9] Waleed Salehi A., Baglat P., Gupta G. Review on machine and deep learning models for the detection and prediction of Coronavirus. Mater. Today Proc., 33:3896–3901, 2020. | ||
| − | [10] dos Santos B.S., Steiner M.T.A., Fenerich A.T., Lima R.H.P. Data mining and machine learning techniques applied to public health problems: A bibliometric analysis from 2009 to 2018. Comput. Ind. Eng., 138 | + | [10] dos Santos B.S., Steiner M.T.A., Fenerich A.T., Lima R.H.P. Data mining and machine learning techniques applied to public health problems: A bibliometric analysis from 2009 to 2018. Comput. Ind. Eng., 138:106120, 2019. |
[11] Carroll L.N., Au A.P., Detwiler L.T., Fu T., Painter I.S., Abernethy N.F. Visualization and analytics tools for infectious disease epidemiology: A systematic review. J. Biomed. Inform., 51:287–298, 2014. | [11] Carroll L.N., Au A.P., Detwiler L.T., Fu T., Painter I.S., Abernethy N.F. Visualization and analytics tools for infectious disease epidemiology: A systematic review. J. Biomed. Inform., 51:287–298, 2014. | ||
| − | [12] Dallora A.L., Eivazzadeh S., Mendes E., Berglund J., Anderberg P. Prognosis of | + | [12] Dallora A.L., Eivazzadeh S., Mendes E., Berglund J., Anderberg P. Prognosis of dementia employing machine learning and microsimulation techniques: A systematic literature review. Procedia Comput. Sci., 100:480–488, 2016. |
[13] Bellinger C., Mohomed Jabbar M.S., Zaïane O., Osornio-Vargas A. A systematic review of data mining and machine learning for air pollution epidemiology. BMC Public Health, 17(1):907, 2017. | [13] Bellinger C., Mohomed Jabbar M.S., Zaïane O., Osornio-Vargas A. A systematic review of data mining and machine learning for air pollution epidemiology. BMC Public Health, 17(1):907, 2017. | ||
| − | [14] Somasekar J., Pavan Kumar P., Sharma A., Ramesh G. Machine learning and image analysis applications in the fight against COVID-19 pandemic: Datasets, research directions, challenges and opportunities. Mater. Today Proc., | + | [14] Somasekar J., Pavan Kumar P., Sharma A., Ramesh G. Machine learning and image analysis applications in the fight against COVID-19 pandemic: Datasets, research directions, challenges and opportunities. Mater. Today Proc., 3–6, 2020. |
[15] Doanvo A., Qian X., Ramjee D., Piontkivska H., Desai A., Majumder M. Machine Learning Maps Research Needs in COVID-19 Literature. Patterns, 1(9):100123, 2020. | [15] Doanvo A., Qian X., Ramjee D., Piontkivska H., Desai A., Majumder M. Machine Learning Maps Research Needs in COVID-19 Literature. Patterns, 1(9):100123, 2020. | ||
| Line 945: | Line 849: | ||
[16] Li M., Zhang Z., Cao W., et al. Identifying novel factors associated with COVID-19 transmission and fatality using the machine learning approach. Sci. Total Environ., 764(639):142810, 2021. | [16] Li M., Zhang Z., Cao W., et al. Identifying novel factors associated with COVID-19 transmission and fatality using the machine learning approach. Sci. Total Environ., 764(639):142810, 2021. | ||
| − | [17] Snyder H. Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res., 104 | + | [17] Snyder H. Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res., 104:333–339, 2019. |
| − | [18] Xiao Y., Watson M. Guidance on | + | [18] Xiao Y., Watson M. Guidance on conducting a systematic literature review. J. Plan. Educ. Res., 39(1):93–112, 2019. |
| − | [19] Ardakani A.A., Kanafi A.R., Acharya U.R., Khadem N., Mohammadi A. Application of deep learning technique to manage COVID-19 in routine clinical practice using CT images: Results of 10 convolutional neural networks. Comput. Biol. Med., 121 | + | [19] Ardakani A.A., Kanafi A.R., Acharya U.R., Khadem N., Mohammadi A. Application of deep learning technique to manage COVID-19 in routine clinical practice using CT images: Results of 10 convolutional neural networks. Comput. Biol. Med., 121:103795, 2020. |
| − | [20] Cai W., Liu T., Xue X., et al. CT Quantification and | + | [20] Cai W., Liu T., Xue X., et al. CT Quantification and machine-learning models for assessment of disease severity and prognosis of COVID-19 patients. Acad. Radiol., 27(12):1665–1678, 2020. |
[21] Chowdhury M.E.H., Rahman T., Khandakar A., et al. Can AI Help in Screening Viral and COVID-19 Pneumonia? IEEE Access, 8:132665–132676, 2020. | [21] Chowdhury M.E.H., Rahman T., Khandakar A., et al. Can AI Help in Screening Viral and COVID-19 Pneumonia? IEEE Access, 8:132665–132676, 2020. | ||
| Line 961: | Line 865: | ||
[24] Brunese L., Martinelli F., Mercaldo F., Santone A. Machine learning for coronavirus covid-19 detection from chest x-rays. Procedia Comput. Sci., 176:2212–2221, 2020. | [24] Brunese L., Martinelli F., Mercaldo F., Santone A. Machine learning for coronavirus covid-19 detection from chest x-rays. Procedia Comput. Sci., 176:2212–2221, 2020. | ||
| − | [25] Chakraborty S., Mali K. SUFMACS: A machine learning-based robust image segmentation framework for COVID-19 radiological image interpretation. Expert Syst. Appl., 178 | + | [25] Chakraborty S., Mali K. SUFMACS: A machine learning-based robust image segmentation framework for COVID-19 radiological image interpretation. Expert Syst. Appl., 178:115069, 2021. |
[26] Elaziz M.A., Hosny K.M., Salah A., Darwish M.M., Lu S., Sahlol A.T. New machine learning method for image-based diagnosis of COVID-19. PLoS One, 15(6):e0235187, 2020. | [26] Elaziz M.A., Hosny K.M., Salah A., Darwish M.M., Lu S., Sahlol A.T. New machine learning method for image-based diagnosis of COVID-19. PLoS One, 15(6):e0235187, 2020. | ||
| − | [27] Vijay kumar J., Harshavardhan A., Bhukya H., Krishna Prasad A.V. Advanced machine learning-based analytics on COVID-19 data using generative adversarial networks. Mater. Today Proc. | + | [27] Vijay kumar J., Harshavardhan A., Bhukya H., Krishna Prasad A.V. Advanced machine learning-based analytics on COVID-19 data using generative adversarial networks. Mater. Today Proc., 2020. |
| − | [28] Loey M., Smarandache F., M. Khalifa N.E. Within the | + | [28] Loey M., Smarandache F., M. Khalifa N.E. Within the lack of chest COVID-19 X-ray dataset: A novel detection model based on GAN and deep transfer learning. Symmetry (Basel), 12(4):651, 2020. |
[29] Saha P., Sadi M.S., Islam M.M. EMCNet: Automated COVID-19 diagnosis from X-ray images using convolutional neural network and ensemble of machine learning classifiers. Informatics Med. Unlocked, 22:100505, 2021. | [29] Saha P., Sadi M.S., Islam M.M. EMCNet: Automated COVID-19 diagnosis from X-ray images using convolutional neural network and ensemble of machine learning classifiers. Informatics Med. Unlocked, 22:100505, 2021. | ||
| Line 973: | Line 877: | ||
[30] Saygılı A. A new approach for computer-aided detection of coronavirus (COVID-19) from CT and X-ray images using machine learning methods. Appl. Soft Comput., 105:107323, 2021. | [30] Saygılı A. A new approach for computer-aided detection of coronavirus (COVID-19) from CT and X-ray images using machine learning methods. Appl. Soft Comput., 105:107323, 2021. | ||
| − | [31] Sedik A., Iliyasu A.M., Abd El-Rahiem B., et al. Deploying | + | [31] Sedik A., Iliyasu A.M., Abd El-Rahiem B., et al. Deploying machine and deep learning models for efficient data-augmented detection of COVID-19 infections. Viruses, 12(7):769, 2020. |
| − | [32] Sethy P.K., Behera S.K., Ratha P.K., Biswas P. Detection of coronavirus | + | [32] Sethy P.K., Behera S.K., Ratha P.K., Biswas P. Detection of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) based on deep features and support vector machine. Int. J. Math. Eng. Manag. Sci., 5(4):643–651, 2020. |
[33] Shiri I., Sorouri M., Geramifar P., et al. Machine learning-based prognostic modeling using clinical data and quantitative radiomic features from chest CT images in COVID-19 patients. Comput. Biol. Med., 132:104304, 2021. | [33] Shiri I., Sorouri M., Geramifar P., et al. Machine learning-based prognostic modeling using clinical data and quantitative radiomic features from chest CT images in COVID-19 patients. Comput. Biol. Med., 132:104304, 2021. | ||
| Line 981: | Line 885: | ||
[34] Singh D., Kumar V., Vaishali, Kaur M. Classification of COVID-19 patients from chest CT images using multi-objective differential evolution–based convolutional neural networks. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis., 39(7):1379–1389, 2020. | [34] Singh D., Kumar V., Vaishali, Kaur M. Classification of COVID-19 patients from chest CT images using multi-objective differential evolution–based convolutional neural networks. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis., 39(7):1379–1389, 2020. | ||
| − | [35] Tamal M., Alshammari M., Alabdullah M., Hourani R., Alola H.A., Hegazi T.M. An integrated framework with machine learning and radiomics for accurate and rapid early diagnosis of COVID-19 from Chest X-ray. Expert Syst. Appl., 180 | + | [35] Tamal M., Alshammari M., Alabdullah M., Hourani R., Alola H.A., Hegazi T.M. An integrated framework with machine learning and radiomics for accurate and rapid early diagnosis of COVID-19 from Chest X-ray. Expert Syst. Appl., 180:115152, 2021. |
| − | [36] Tartaglione E., Barbano C.A., Berzovini C., Calandri M., Grangetto M. Unveiling COVID-19 from CHEST X-Ray with | + | [36] Tartaglione E., Barbano C.A., Berzovini C., Calandri M., Grangetto M. Unveiling COVID-19 from CHEST X-Ray with deep learning: A hurdles race with small data. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 17(18):6933, 2020. |
| − | [37] Wang X., Deng X., Fu Q., et al. A | + | [37] Wang X., Deng X., Fu Q., et al. A weakly-supervised framework for COVID-19 classification and lesion localization from chest CT. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging, 39(8):2615–2625, 2020. |
| − | [38] Waheed A., Goyal M., Gupta D., Khanna A., Al-Turjman F., Pinheiro P.R. CovidGAN: Data | + | [38] Waheed A., Goyal M., Gupta D., Khanna A., Al-Turjman F., Pinheiro P.R. CovidGAN: Data augmentation using auxiliary classifier GAN for improved Covid-19 detection. IEEE Access, 8:91916–91923, 2020. |
| − | [39] Wu Z., Li L., Jin R., et al. Texture feature-based machine learning classifier could assist in the diagnosis of COVID-19. Eur. J. Radiol., 137 | + | [39] Wu Z., Li L., Jin R., et al. Texture feature-based machine learning classifier could assist in the diagnosis of COVID-19. Eur. J. Radiol., 137:109602, 2021. |
| − | [40] Çalı S., Balaman Ş.Y. Improved decisions for marketing, supply and purchasing: Mining big data through an integration of sentiment analysis and intuitionistic fuzzy multi criteria assessment. Comput. Ind. Eng., 129 | + | [40] Çalı S., Balaman Ş.Y. Improved decisions for marketing, supply and purchasing: Mining big data through an integration of sentiment analysis and intuitionistic fuzzy multi criteria assessment. Comput. Ind. Eng., 129:315–332, 2019. |
| − | [41] Gulati K., Saravana Kumar S., Sarath Kumar Boddu R., Sarvakar K., Kumar Sharma D., Nomani M.Z.M. Comparative analysis of machine learning-based classification models using sentiment classification of tweets related to COVID-19 pandemic. Mater. Today Proc., | + | [41] Gulati K., Saravana Kumar S., Sarath Kumar Boddu R., Sarvakar K., Kumar Sharma D., Nomani M.Z.M. Comparative analysis of machine learning-based classification models using sentiment classification of tweets related to COVID-19 pandemic. Mater. Today Proc., 51(1):38-41, 2022. |
| − | [42] Haupt M.R., Jinich-Diamant A., Li J., Nali M., Mackey T.K. Characterizing twitter user topics and communication network dynamics of the “Liberate” movement during COVID-19 using unsupervised machine learning and social network analysis. Online Soc. Networks Media, 21 | + | [42] Haupt M.R., Jinich-Diamant A., Li J., Nali M., Mackey T.K. Characterizing twitter user topics and communication network dynamics of the “Liberate” movement during COVID-19 using unsupervised machine learning and social network analysis. Online Soc. Networks Media, 21:100114, 2021. |
[43] Praveen S.V., Ittamalla R., Deepak G. Analyzing Indian general public’s perspective on anxiety, stress and trauma during Covid-19 - A machine learning study of 840,000 tweets. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev., 15(3):667–671, 2021. | [43] Praveen S.V., Ittamalla R., Deepak G. Analyzing Indian general public’s perspective on anxiety, stress and trauma during Covid-19 - A machine learning study of 840,000 tweets. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev., 15(3):667–671, 2021. | ||
| − | [44] Abd-Alrazaq A., Alhuwail D., Househ M., Hamdi M., Shah Z. Top | + | [44] Abd-Alrazaq A., Alhuwail D., Househ M., Hamdi M., Shah Z. Top concerns of tweeters during the COVID-19 pandemic: Infoveillance study. J. Med. Internet Res., 22(4):e19016, 2020. |
| − | [45] Gupta M., Bansal A., Jain B., Rochelle J., Oak A., Jalali M.S. Whether the weather will help us weather the COVID-19 pandemic: Using machine learning to measure twitter users’ perceptions. Int. J. Med. Inform., 145 | + | [45] Gupta M., Bansal A., Jain B., Rochelle J., Oak A., Jalali M.S. Whether the weather will help us weather the COVID-19 pandemic: Using machine learning to measure twitter users’ perceptions. Int. J. Med. Inform., 145:104340, 2021. |
| − | [46] Hou K., Hou T., Cai L. Public attention about COVID-19 on social media: An investigation based on data mining and text analysis. Pers. Individ. Dif., 175 | + | [46] Hou K., Hou T., Cai L. Public attention about COVID-19 on social media: An investigation based on data mining and text analysis. Pers. Individ. Dif., 175:110701, 2021. |
| − | [47] Kabir M.Y., Madria S. EMOCOV: Machine learning for emotion detection, analysis and visualization using COVID-19 tweets. Online Soc. Networks Media, 23 | + | [47] Kabir M.Y., Madria S. EMOCOV: Machine learning for emotion detection, analysis and visualization using COVID-19 tweets. Online Soc. Networks Media, 23:100135, 2021. |
| − | [48] Kyriazos T., Galanakis M., Karakasidou E., Stalikas A. Early COVID-19 quarantine: A machine learning approach to model what differentiated the top 25% well-being scorers. Pers. Individ. Dif., 181 | + | [48] Kyriazos T., Galanakis M., Karakasidou E., Stalikas A. Early COVID-19 quarantine: A machine learning approach to model what differentiated the top 25% well-being scorers. Pers. Individ. Dif., 181:110980, 2021. |
| − | [49] Li S., Wang Y., Xue J., Zhao N., Zhu T. The | + | [49] Li S., Wang Y., Xue J., Zhao N., Zhu T. The impact of COVID-19 epidemic declaration on psychological consequences: A study on active weibo users. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 17(6):2032, 2020. |
| − | [50] Mackey T., Purushothaman V., Li J., et al. Machine | + | [50] Mackey T., Purushothaman V., Li J., et al. Machine learning to detect self-reporting of symptoms, testing access, and recovery associated with COVID-19 on twitter: Retrospective big data infoveillance study. JMIR Public Heal. Surveill., 6(2):e19509, 2020. |
| − | [51] Samuel J., Ali G.G.M.N., Rahman M.M., Esawi E., Samuel Y. COVID-19 | + | [51] Samuel J., Ali G.G.M.N., Rahman M.M., Esawi E., Samuel Y. COVID-19 public sentiment insights and machine learning for tweets classification. Information, 11(6):314, 2020. |
[52] Satu M.S., Khan M.I., Mahmud M., et al. TClustVID: A novel machine learning classification model to investigate topics and sentiment in COVID-19 tweets. Knowledge-Based Syst., 226:107126, 2021. | [52] Satu M.S., Khan M.I., Mahmud M., et al. TClustVID: A novel machine learning classification model to investigate topics and sentiment in COVID-19 tweets. Knowledge-Based Syst., 226:107126, 2021. | ||
| − | [53] Shah A.M., Yan X., Qayyum A., Naqvi R.A., Shah S.J. Mining topic and sentiment dynamics in physician rating websites during the early wave of the COVID-19 pandemic: Machine learning approach. Int. J. Med. Inform., 149 | + | [53] Shah A.M., Yan X., Qayyum A., Naqvi R.A., Shah S.J. Mining topic and sentiment dynamics in physician rating websites during the early wave of the COVID-19 pandemic: Machine learning approach. Int. J. Med. Inform., 149:104434, 2021. |
[54] Amar L.A., Taha A.A., Mohamed M.Y. Prediction of the final size for COVID-19 epidemic using machine learning: A case study of Egypt. Infect. Dis. Model., 5:622–634, 2020. | [54] Amar L.A., Taha A.A., Mohamed M.Y. Prediction of the final size for COVID-19 epidemic using machine learning: A case study of Egypt. Infect. Dis. Model., 5:622–634, 2020. | ||
| Line 1,023: | Line 927: | ||
[55] Burdick H., Lam C., Mataraso S., et al. Prediction of respiratory decompensation in Covid-19 patients using machine learning: The READY trial. Comput. Biol. Med., 124:103949, 2020. | [55] Burdick H., Lam C., Mataraso S., et al. Prediction of respiratory decompensation in Covid-19 patients using machine learning: The READY trial. Comput. Biol. Med., 124:103949, 2020. | ||
| − | [56] Ardabili S.F., Mosavi A., Ghamisi P., et al. COVID-19 | + | [56] Ardabili S.F., Mosavi A., Ghamisi P., et al. COVID-19 outbreak prediction with machine learning. Algorithms, 13(10):249, 2020. |
[57] Arvind V., Kim J.S., Cho B.H., Geng E., Cho S.K. Development of a machine learning algorithm to predict intubation among hospitalized patients with COVID-19. J. Crit. Care, 62:25–30, 2021. | [57] Arvind V., Kim J.S., Cho B.H., Geng E., Cho S.K. Development of a machine learning algorithm to predict intubation among hospitalized patients with COVID-19. J. Crit. Care, 62:25–30, 2021. | ||
| − | [58] ArunKumar K.E., Kalaga D. V., Sai Kumar C.M., Chilkoor G., Kawaji M., Brenza T.M. Forecasting the dynamics of cumulative COVID-19 cases (confirmed, recovered and deaths) for top-16 countries using statistical machine learning models: Auto-Regressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) and Seasonal Auto-Regressive Integrated Moving Averag. Appl. Soft Comput., 103 | + | [58] ArunKumar K.E., Kalaga D. V., Sai Kumar C.M., Chilkoor G., Kawaji M., Brenza T.M. Forecasting the dynamics of cumulative COVID-19 cases (confirmed, recovered and deaths) for top-16 countries using statistical machine learning models: Auto-Regressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) and Seasonal Auto-Regressive Integrated Moving Averag. Appl. Soft Comput., 103:107161, 2021. |
[59] Aydin N., Yurdakul G. Assessing countries’ performances against COVID-19 via WSIDEA and machine learning algorithms. Appl. Soft Comput., 97:106792, 2020. | [59] Aydin N., Yurdakul G. Assessing countries’ performances against COVID-19 via WSIDEA and machine learning algorithms. Appl. Soft Comput., 97:106792, 2020. | ||
| − | [60] Ayyoubzadeh S.M., Ayyoubzadeh S.M., Zahedi H., Ahmadi M., R Niakan Kalhori S. Predicting COVID-19 | + | [60] Ayyoubzadeh S.M., Ayyoubzadeh S.M., Zahedi H., Ahmadi M., R Niakan Kalhori S. Predicting COVID-19 incidence through analysis of Google trends data in Iran: Data mining and deep learning pilot study. JMIR Public Heal. Surveill., 6(2):e18828, 2020. |
[61] Ballı S. Data analysis of Covid-19 pandemic and short-term cumulative case forecasting using machine learning time series methods. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 142:110512, 2021. | [61] Ballı S. Data analysis of Covid-19 pandemic and short-term cumulative case forecasting using machine learning time series methods. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 142:110512, 2021. | ||
| Line 1,041: | Line 945: | ||
[64] Chakraborti S., Maiti A., Pramanik S., et al. Evaluating the plausible application of advanced machine learnings in exploring determinant factors of present pandemic: A case for continent specific COVID-19 analysis. Sci. Total Environ., 765:142723, 2021. | [64] Chakraborti S., Maiti A., Pramanik S., et al. Evaluating the plausible application of advanced machine learnings in exploring determinant factors of present pandemic: A case for continent specific COVID-19 analysis. Sci. Total Environ., 765:142723, 2021. | ||
| − | [65] Chatterjee A., Gerdes M.W., Martinez S.G. Statistical | + | [65] Chatterjee A., Gerdes M.W., Martinez S.G. Statistical explorations and univariate timeseries analysis on COVID-19 datasets to understand the trend of disease spreading and death. Sensors, 20(11):3089, 2020. |
[66] Chimmula V.K.R., Zhang L. Time series forecasting of COVID-19 transmission in Canada using LSTM networks. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 135:109864, 2020. | [66] Chimmula V.K.R., Zhang L. Time series forecasting of COVID-19 transmission in Canada using LSTM networks. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 135:109864, 2020. | ||
| Line 1,047: | Line 951: | ||
[67] Cobre A. de F., Stremel D.P., Noleto G.R., et al. Diagnosis and prediction of COVID-19 severity: can biochemical tests and machine learning be used as prognostic indicators? Comput. Biol. Med., 134:104531, 2021. | [67] Cobre A. de F., Stremel D.P., Noleto G.R., et al. Diagnosis and prediction of COVID-19 severity: can biochemical tests and machine learning be used as prognostic indicators? Comput. Biol. Med., 134:104531, 2021. | ||
| − | [68] Ebinger J., Wells M., Ouyang D., et al. A | + | [68] Ebinger J., Wells M., Ouyang D., et al. A machine learning algorithm predicts duration of hospitalization in COVID-19 patients. Intell. Med., 5:100035, 2021. |
| − | [69] Fong S.J., Li G., Dey N., Crespo R.G., Herrera-Viedma E. Finding an | + | [69] Fong S.J., Li G., Dey N., Crespo R.G., Herrera-Viedma E. Finding an accurate early forecasting model from small dataset: A case of 2019-nCoV novel coronavirus outbreak. Int. J. Interact. Multimed. Artif. Intell., 6(1):132, 2020. |
| − | [70] Gothai E., Thamilselvan R., Rajalaxmi R.R., Sadana R.M., Ragavi A., Sakthivel R. Prediction of COVID-19 growth and trend using machine learning approach. Mater. Today Proc., | + | [70] Gothai E., Thamilselvan R., Rajalaxmi R.R., Sadana R.M., Ragavi A., Sakthivel R. Prediction of COVID-19 growth and trend using machine learning approach. Mater. Today Proc., April 2021. |
[71] Jain N., Jhunthra S., Garg H., et al. Prediction modelling of COVID using machine learning methods from B-cell dataset. Results Phys., 21:103813, 2021. | [71] Jain N., Jhunthra S., Garg H., et al. Prediction modelling of COVID using machine learning methods from B-cell dataset. Results Phys., 21:103813, 2021. | ||
| − | [72] Kang J., Chen T., Luo H., Luo Y., Du G., Jiming-Yang M. Machine learning predictive model for severe COVID-19. Infect. Genet. Evol., 90 | + | [72] Kang J., Chen T., Luo H., Luo Y., Du G., Jiming-Yang M. Machine learning predictive model for severe COVID-19. Infect. Genet. Evol., 90:104737, 2021. |
| − | [73] Kavadi D.P., Patan R., Ramachandran M., Gandomi A.H. Partial derivative | + | [73] Kavadi D.P., Patan R., Ramachandran M., Gandomi A.H. Partial derivative nonlinear global pandemic machine learning prediction of COVID 19. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 139:110056, 2020. |
[74] Khan F.M., Kumar A., Puppala H., Kumar G., Gupta R. Projecting the criticality of COVID-19 transmission in India using GIS and machine learning methods. J. Saf. Sci. Resil., 2(2):50–62, 2021. | [74] Khan F.M., Kumar A., Puppala H., Kumar G., Gupta R. Projecting the criticality of COVID-19 transmission in India using GIS and machine learning methods. J. Saf. Sci. Resil., 2(2):50–62, 2021. | ||
| Line 1,063: | Line 967: | ||
[75] Lmater M.A., Eddabbah M., Elmoussaoui T., Boussaa S. Modelization of Covid-19 pandemic spreading: A machine learning forecasting with relaxation scenarios of countermeasures. J. Infect. Public Health, 14(4):468–473, 2021. | [75] Lmater M.A., Eddabbah M., Elmoussaoui T., Boussaa S. Modelization of Covid-19 pandemic spreading: A machine learning forecasting with relaxation scenarios of countermeasures. J. Infect. Public Health, 14(4):468–473, 2021. | ||
| − | [76] Malefors C., Secondi L., Marchetti S., Eriksson M. Food waste reduction and economic savings in times of crisis: The potential of machine learning methods to plan guest attendance in Swedish public catering during the Covid-19 pandemic. Socioecon. Plann. Sci., | + | [76] Malefors C., Secondi L., Marchetti S., Eriksson M. Food waste reduction and economic savings in times of crisis: The potential of machine learning methods to plan guest attendance in Swedish public catering during the Covid-19 pandemic. Socioecon. Plann. Sci., 82(A):101041, 2022. |
| − | [77] Mojjada R.K., Yadav A., Prabhu A.V., Natarajan Y. Machine learning models for covid-19 future forecasting. Mater. Today Proc., | + | [77] Mojjada R.K., Yadav A., Prabhu A.V., Natarajan Y. Machine learning models for covid-19 future forecasting. Mater. Today Proc., December 2020. |
| − | [78] Nemati M., Ansary J., Nemati N. Machine- | + | [78] Nemati M., Ansary J., Nemati N. Machine-learning approaches in COVID-19 survival analysis and discharge-time likelihood prediction using clinical data. Patterns, 1(5):100074, 2020. |
| − | [79] Ong E., Wong M.U., Huffman A., He Y. COVID-19 | + | [79] Ong E., Wong M.U., Huffman A., He Y. COVID-19 coronavirus vaccine design using reverse vaccinology and machine learning. Front. Immunol., 11(July):1581, 2020. |
| − | [80] Papastefanopoulos V., Linardatos P., Kotsiantis S. COVID-19: A | + | [80] Papastefanopoulos V., Linardatos P., Kotsiantis S. COVID-19: A comparison of time series methods to forecast percentage of active cases per population. Appl. Sci., 10(11):3880, 2020. |
[81] Peng Y., Nagata M.H. An empirical overview of nonlinearity and overfitting in machine learning using COVID-19 data. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 139:110055, 2020. | [81] Peng Y., Nagata M.H. An empirical overview of nonlinearity and overfitting in machine learning using COVID-19 data. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 139:110055, 2020. | ||
| − | [82] Pinter G., Felde I., Mosavi A., Ghamisi P., Gloaguen R. COVID-19 | + | [82] Pinter G., Felde I., Mosavi A., Ghamisi P., Gloaguen R. COVID-19 pandemic prediction for Hungary; A hybrid machine learning approach. SSRN Electron. J., 8(6):890, 2020. |
| − | [83] Pourhomayoun M., Shakibi M. Predicting mortality risk in patients with COVID-19 using machine learning to help medical decision-making. Smart Heal., 20 | + | [83] Pourhomayoun M., Shakibi M. Predicting mortality risk in patients with COVID-19 using machine learning to help medical decision-making. Smart Heal., 20:100178, 2021. |
| − | [84] Quintero Y., Ardila D., Camargo E., Rivas F., Aguilar J. Machine learning models for the prediction of the SEIRD variables for the COVID-19 pandemic based on a deep dependence analysis of variables. Comput. Biol. Med., 134 | + | [84] Quintero Y., Ardila D., Camargo E., Rivas F., Aguilar J. Machine learning models for the prediction of the SEIRD variables for the COVID-19 pandemic based on a deep dependence analysis of variables. Comput. Biol. Med., 134:104500, 2021. |
[85] Ribeiro M.H.D.M., da Silva R.G., Mariani V.C., Coelho L. dos S. Short-term forecasting COVID-19 cumulative confirmed cases: Perspectives for Brazil. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 135:109853, 2020. | [85] Ribeiro M.H.D.M., da Silva R.G., Mariani V.C., Coelho L. dos S. Short-term forecasting COVID-19 cumulative confirmed cases: Perspectives for Brazil. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 135:109853, 2020. | ||
| − | [86] Santosh K.C. AI- | + | [86] Santosh K.C. AI-driven tools for coronavirus outbreak: Need of active learning and cross-population train/test models on multitudinal/multimodal data. J. Med. Syst., 44(5):93, 2020. |
[87] Singh V., Poonia R.C., Kumar S., et al. Prediction of COVID-19 corona virus pandemic based on time series data using support vector machine. J. Discret. Math. Sci. Cryptogr., 23(8):1583–1597, 2020. | [87] Singh V., Poonia R.C., Kumar S., et al. Prediction of COVID-19 corona virus pandemic based on time series data using support vector machine. J. Discret. Math. Sci. Cryptogr., 23(8):1583–1597, 2020. | ||
| Line 1,089: | Line 993: | ||
[88] Sujath R., Chatterjee J.M., Hassanien A.E. A machine learning forecasting model for COVID-19 pandemic in India. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess., 34(7):959–972, 2020. | [88] Sujath R., Chatterjee J.M., Hassanien A.E. A machine learning forecasting model for COVID-19 pandemic in India. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess., 34(7):959–972, 2020. | ||
| − | [89] Tarik A., Aissa H., Yousef F. Artificial | + | [89] Tarik A., Aissa H., Yousef F. Artificial intelligence and machine learning to predict student performance during the COVID-19. Procedia Comput. Sci., 184:835–840, 2021. |
[90] Tuli S., Tuli S., Tuli R., Gill S.S. Predicting the growth and trend of COVID-19 pandemic using machine learning and cloud computing. Internet of Things, 11:100222, 2020. | [90] Tuli S., Tuli S., Tuli R., Gill S.S. Predicting the growth and trend of COVID-19 pandemic using machine learning and cloud computing. Internet of Things, 11:100222, 2020. | ||
| Line 1,103: | Line 1,007: | ||
[95] Yeşilkanat C.M. Spatio-temporal estimation of the daily cases of COVID-19 in worldwide using random forest machine learning algorithm. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 140:110210, 2020. | [95] Yeşilkanat C.M. Spatio-temporal estimation of the daily cases of COVID-19 in worldwide using random forest machine learning algorithm. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 140:110210, 2020. | ||
| − | [96] Zivkovic M., Bacanin N., Venkatachalam K., et al. COVID-19 cases prediction by using hybrid machine learning and beetle antennae search approach. Sustain. Cities Soc., 66 | + | [96] Zivkovic M., Bacanin N., Venkatachalam K., et al. COVID-19 cases prediction by using hybrid machine learning and beetle antennae search approach. Sustain. Cities Soc., 66:102669, 2021. |
[97] Di Castelnuovo A., Bonaccio M., Costanzo S., et al. Common cardiovascular risk factors and in-hospital mortality in 3,894 patients with COVID-19: survival analysis and machine learning-based findings from the multicentre Italian CORIST Study. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis., 30(11):1899–1913, 2020. | [97] Di Castelnuovo A., Bonaccio M., Costanzo S., et al. Common cardiovascular risk factors and in-hospital mortality in 3,894 patients with COVID-19: survival analysis and machine learning-based findings from the multicentre Italian CORIST Study. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis., 30(11):1899–1913, 2020. | ||
| − | [98] Alves M.A., Castro G.Z., Oliveira B.A.S., et al. Explaining machine learning based diagnosis of COVID-19 from routine blood tests with decision trees and criteria graphs. Comput. Biol. Med., 132 | + | [98] Alves M.A., Castro G.Z., Oliveira B.A.S., et al. Explaining machine learning based diagnosis of COVID-19 from routine blood tests with decision trees and criteria graphs. Comput. Biol. Med., 132:104335, 2021. |
| − | [99] Baralić K., Jorgovanović D., Živančević K., et al. Safety assessment of drug combinations used in COVID-19 treatment: in silico toxicogenomic data-mining approach. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 406 | + | [99] Baralić K., Jorgovanović D., Živančević K., et al. Safety assessment of drug combinations used in COVID-19 treatment: in silico toxicogenomic data-mining approach. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 406:115237, 2020. |
[100] Carrillo-Larco R.M., Castillo-Cara M. Using country-level variables to classify countries according to the number of confirmed COVID-19 cases: An unsupervised machine learning approach. Wellcome Open Res., 5:56, 2020. | [100] Carrillo-Larco R.M., Castillo-Cara M. Using country-level variables to classify countries according to the number of confirmed COVID-19 cases: An unsupervised machine learning approach. Wellcome Open Res., 5:56, 2020. | ||
| − | [101] Choudrie J., Banerjee S., Kotecha K., Walambe R., Karende H., Ameta J. Machine learning techniques and older adults processing of online information and misinformation: A covid 19 study. Comput. Human Behav., 119 | + | [101] Choudrie J., Banerjee S., Kotecha K., Walambe R., Karende H., Ameta J. Machine learning techniques and older adults processing of online information and misinformation: A covid 19 study. Comput. Human Behav., 119:106716, 2021. |
| − | [102] Dandekar R., Rackauckas C., Barbastathis G. A | + | [102] Dandekar R., Rackauckas C., Barbastathis G. A machine learning-aided global diagnostic and comparative tool to assess effect of quarantine control in COVID-19 spread. Patterns, 1(9):100145, 2020. |
| − | [103] Fong S.J., Li G., Dey N., Crespo R.G., Herrera-Viedma E. Composite Monte Carlo decision making under high uncertainty of novel coronavirus epidemic using hybridized deep learning and fuzzy rule induction. Appl. Soft Comput., 93 | + | [103] Fong S.J., Li G., Dey N., Crespo R.G., Herrera-Viedma E. Composite Monte Carlo decision making under high uncertainty of novel coronavirus epidemic using hybridized deep learning and fuzzy rule induction. Appl. Soft Comput., 93:106282, 2020. |
| − | [104] Godavarthi D., Sowjanya M. Classification of covid related articles using machine learning. Mater. Today Proc., | + | [104] Godavarthi D., Sowjanya M. Classification of covid related articles using machine learning. Mater. Today Proc., February 2021. |
[105] Hu J., Pan Y., He Y., et al. Changes in air pollutants during the COVID-19 lockdown in Beijing: Insights from a machine-learning technique and implications for future control policy. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett., 14(4):100060, 2021. | [105] Hu J., Pan Y., He Y., et al. Changes in air pollutants during the COVID-19 lockdown in Beijing: Insights from a machine-learning technique and implications for future control policy. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett., 14(4):100060, 2021. | ||
| − | [106] Jamshidi M., Lalbakhsh A., Talla J., et al. Artificial | + | [106] Jamshidi M., Lalbakhsh A., Talla J., et al. Artificial intelligence and COVID-19: deep learning approaches for diagnosis and treatment. IEEE Access, 8:109581–109595, 2020. |
| − | [107] Kadioglu O., Saeed M., Greten H.J., Efferth T. Identification of novel compounds against three targets of SARS CoV-2 coronavirus by combined virtual screening and supervised machine learning. Comput. Biol. Med., 133 | + | [107] Kadioglu O., Saeed M., Greten H.J., Efferth T. Identification of novel compounds against three targets of SARS CoV-2 coronavirus by combined virtual screening and supervised machine learning. Comput. Biol. Med., 133:104359, 2021. |
[108] Khanday A.M.U.D., Rabani S.T., Khan Q.R., Rouf N., Mohi Ud Din M. Machine learning based approaches for detecting COVID-19 using clinical text data. Int. J. Inf. Technol., 12(3):731–739, 2020. | [108] Khanday A.M.U.D., Rabani S.T., Khan Q.R., Rouf N., Mohi Ud Din M. Machine learning based approaches for detecting COVID-19 using clinical text data. Int. J. Inf. Technol., 12(3):731–739, 2020. | ||
| Line 1,131: | Line 1,035: | ||
[109] Kuo C.-P., Fu J.S. Evaluating the impact of mobility on COVID-19 pandemic with machine learning hybrid predictions. Sci. Total Environ., 758:144151, 2021. | [109] Kuo C.-P., Fu J.S. Evaluating the impact of mobility on COVID-19 pandemic with machine learning hybrid predictions. Sci. Total Environ., 758:144151, 2021. | ||
| − | [110] Lam C., Siefkas A., Zelin N.S., et al. Machine | + | [110] Lam C., Siefkas A., Zelin N.S., et al. Machine learning as a precision-medicine approach to prescribing COVID-19 pharmacotherapy with remdesivir or corticosteroids. Clin. Ther., 43(5):871-885, 2021. |
| − | [111] Lip G.Y.H., Genaidy A., Tran G., Marroquin P., Estes C. Incident atrial fibrillation and its risk prediction in patients developing COVID-19: A machine learning based algorithm approach. Eur. J. Intern. Med., | + | [111] Lip G.Y.H., Genaidy A., Tran G., Marroquin P., Estes C. Incident atrial fibrillation and its risk prediction in patients developing COVID-19: A machine learning based algorithm approach. Eur. J. Intern. Med., 91:53-58, 2021. |
| − | [112] Loey M., Manogaran G., Taha M.H.N., Khalifa N.E.M. A hybrid deep transfer learning model with machine learning methods for face mask detection in the era of the COVID-19 pandemic. Measurement, 167 | + | [112] Loey M., Manogaran G., Taha M.H.N., Khalifa N.E.M. A hybrid deep transfer learning model with machine learning methods for face mask detection in the era of the COVID-19 pandemic. Measurement, 167:108288, 2021. |
[113] Lovrić M., Pavlović K., Vuković M., Grange S.K., Haberl M., Kern R. Understanding the true effects of the COVID-19 lockdown on air pollution by means of machine learning. Environ. Pollut., 274:115900, 2021. | [113] Lovrić M., Pavlović K., Vuković M., Grange S.K., Haberl M., Kern R. Understanding the true effects of the COVID-19 lockdown on air pollution by means of machine learning. Environ. Pollut., 274:115900, 2021. | ||
| − | [114] Magazzino C., Mele M., Sarkodie S.A. The nexus between COVID-19 deaths, air pollution and economic growth in New York state: Evidence from Deep Machine Learning. J. Environ. Manage., 286 | + | [114] Magazzino C., Mele M., Sarkodie S.A. The nexus between COVID-19 deaths, air pollution and economic growth in New York state: Evidence from Deep Machine Learning. J. Environ. Manage., 286:112241, 2021. |
[115] McRae M.P., Simmons G.W., Christodoulides N.J., et al. Clinical decision support tool and rapid point-of-care platform for determining disease severity in patients with COVID-19. Lab Chip, 20(12):2075–2085, 2020. | [115] McRae M.P., Simmons G.W., Christodoulides N.J., et al. Clinical decision support tool and rapid point-of-care platform for determining disease severity in patients with COVID-19. Lab Chip, 20(12):2075–2085, 2020. | ||
| Line 1,155: | Line 1,059: | ||
[121] Randhawa G.S., Soltysiak M.P.M., El Roz H., de Souza C.P.E., Hill K.A., Kari L. Machine learning using intrinsic genomic signatures for rapid classification of novel pathogens: COVID-19 case study. PLoS One, 15(4):e0232391, 2020. | [121] Randhawa G.S., Soltysiak M.P.M., El Roz H., de Souza C.P.E., Hill K.A., Kari L. Machine learning using intrinsic genomic signatures for rapid classification of novel pathogens: COVID-19 case study. PLoS One, 15(4):e0232391, 2020. | ||
| − | [122] Shrock E., Fujimura E., Kula T., et al. Viral epitope profiling of COVID-19 patients reveals cross-reactivity and correlates of severity. Science | + | [122] Shrock E., Fujimura E., Kula T., et al. Viral epitope profiling of COVID-19 patients reveals cross-reactivity and correlates of severity. Science, 370(6520):eabd4250, 2020. |
| − | [123] Sun X., Jiang J., Wang Y., Liu S. Exploring the potential therapeutic effect of traditional Chinese medicine on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) through a combination of data mining and network pharmacology analysis. Eur. J. Integr. Med., 40 | + | [123] Sun X., Jiang J., Wang Y., Liu S. Exploring the potential therapeutic effect of traditional Chinese medicine on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) through a combination of data mining and network pharmacology analysis. Eur. J. Integr. Med., 40:101242, 2020. |
| − | [124] Sun C.L.F., Zuccarelli E., Zerhouni E.G.A., et al. Predicting | + | [124] Sun C.L.F., Zuccarelli E., Zerhouni E.G.A., et al. Predicting coronavirus disease 2019 infection risk and related risk drivers in nursing homes: A machine learning approach. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc., 21(11):1533-1538.e6, 2020. |
[125] Swapnarekha H., Behera H.S., Nayak J., Naik B. Role of intelligent computing in COVID-19 prognosis: A state-of-the-art review. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 138:109947, 2020. | [125] Swapnarekha H., Behera H.S., Nayak J., Naik B. Role of intelligent computing in COVID-19 prognosis: A state-of-the-art review. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 138:109947, 2020. | ||
| − | [126] Tiwari S., Kumar S., Guleria K. Outbreak | + | [126] Tiwari S., Kumar S., Guleria K. Outbreak trends of coronavirus disease–2019 in India: A prediction. Disaster Med. Public Health Prep., 14(5):e33–e38, 2020. |
[127] Tiwari A., Dadhania A. V., Ragunathrao V.A.B., Oliveira E.R.A. Using machine learning to develop a novel COVID-19 Vulnerability Index (C19VI). Sci. Total Environ., 773:145650, 2021. | [127] Tiwari A., Dadhania A. V., Ragunathrao V.A.B., Oliveira E.R.A. Using machine learning to develop a novel COVID-19 Vulnerability Index (C19VI). Sci. Total Environ., 773:145650, 2021. | ||
| − | [128] Toğaçar M., Ergen B., Cömert Z. COVID-19 detection using deep learning models to exploit Social Mimic Optimization and structured chest X-ray images using fuzzy color and stacking approaches. Comput. Biol. Med., 121 | + | [128] Toğaçar M., Ergen B., Cömert Z. COVID-19 detection using deep learning models to exploit Social Mimic Optimization and structured chest X-ray images using fuzzy color and stacking approaches. Comput. Biol. Med., 121:103805, 2020. |
[129] Vaishya R., Javaid M., Khan I.H., Haleem A. Artificial Intelligence (AI) applications for COVID-19 pandemic. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev., 14(4):337–339, 2020. | [129] Vaishya R., Javaid M., Khan I.H., Haleem A. Artificial Intelligence (AI) applications for COVID-19 pandemic. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev., 14(4):337–339, 2020. | ||
| − | [130] Wang W.-C., Lin T.-Y., Chiu S.Y.-H., et al. Classification of community-acquired outbreaks for the global transmission of COVID-19: Machine learning and statistical model analysis. J. Formos. Med. Assoc., 120 | + | [130] Wang W.-C., Lin T.-Y., Chiu S.Y.-H., et al. Classification of community-acquired outbreaks for the global transmission of COVID-19: Machine learning and statistical model analysis. J. Formos. Med. Assoc., 120:S26–S37, 2021. |
[131] Yacchirema D., Chura A. SafeMobility: An IoT- based System for safer mobility using machine learning in the age of COVID-19. Procedia Comput. Sci., 184:524–531, 2021. | [131] Yacchirema D., Chura A. SafeMobility: An IoT- based System for safer mobility using machine learning in the age of COVID-19. Procedia Comput. Sci., 184:524–531, 2021. | ||
| Line 1,177: | Line 1,081: | ||
[132] Yang Z., Zeng Z., Wang K., et al. Modified SEIR and AI prediction of the epidemics trend of COVID-19 in China under public health interventions. J. Thorac. Dis., 12(3):165–174, 2020. | [132] Yang Z., Zeng Z., Wang K., et al. Modified SEIR and AI prediction of the epidemics trend of COVID-19 in China under public health interventions. J. Thorac. Dis., 12(3):165–174, 2020. | ||
| − | [133] | + | [133] COVID-19 Host Genetics Initiative. Mapping the human genetic architecture of COVID-19. Nature, 600:472–477, 2021. |
[134] Pairo-Castineira E., Clohisey S., Klaric L., et al. Genetic mechanisms of critical illness in COVID-19. Nature, 591(7848):92–98, 2021. | [134] Pairo-Castineira E., Clohisey S., Klaric L., et al. Genetic mechanisms of critical illness in COVID-19. Nature, 591(7848):92–98, 2021. | ||
| − | [135] Shkurnikov M., Nersisyan S., Jankevic T., et al. Association of HLA | + | [135] Shkurnikov M., Nersisyan S., Jankevic T., et al. Association of HLA class I genotypes with severity of coronavirus disease-19. Front. Immunol., 12:641900, 2021. |
Latest revision as of 12:33, 15 December 2022
Abstract
During the pandemic caused by the Coronavirus (Covid-19), Machine Learning (ML) techniques can be used, among other alternatives, to detect the virus in its early stages, which would aid a fast recovery and help to ease the pressure on healthcare systems. In this study, we present a Systematic Literature Review (SLR) and a Bibliometric Analysis of ML technique applications in the Covid-19 pandemic, from January 2020 to June 2021, identifying possible unexplored gaps. In the SLR, the 117 most cited papers published during the period were analyzed and divided into four categories: 22 articles that analyzed the problem of the disease using ML techniques in an X-Ray (XR) analysis and Computed Tomography (CT) of the lungs of infected patients; 13 articles that studied the problem by addressing social network tools using ML techniques; 44 articles directly used ML techniques in forecasting problems; and 38 articles that applied ML techniques for general issues regarding the disease. The gap identified in the literature had to do with the use of ML techniques when analyzing the relationship between the human genotype and susceptibility to Covid-19 or the severity of the infection, a subject that has begun to be explored in the scientific community.
Keywords: Machine learning, coronavirus pandemic, systematic literature review, bibliometric analysis, genetic predisposition
1. Introduction
According to the World Health Organization [1], pandemic is a term used for a determined disease that rapidly spreads through diverse regions (at the continental or world level) through sustained contamination. In this respect, the gravity of the disease is not a determining factor, but rather its contagiousness and geographical proliferation.
In the last 30 years, the number of virus outbreaks has grown, proliferating diseases that affect the world. However, historical reports of pandemics stretch back to long before the twenty-first century and have been a concern of the human race for over two thousand years [2]. The main concerns include the Plague of Justinian, which occurred around 541 A.D., caused by the bacterium responsible for the Black Death of 1343, which reached its peak in 1353, also called the bubonic plague. Russian Flu, which was first reported in 1580, was the first to be documented beginning in 1889. Spanish Flu, first recorded in 1918, caused the death of 20 to 50 million people around the world [3].
Even with their biological, social, temporal, and geographical differences, pandemics usually share similar consequences, such as social chaos, changes in behavior and the spread of false information. Looking back to the past, there is an increasingly clear need to invest in and appreciate scientific research, studies, and healthcare professionals. After all, even with such a long history of pandemics, we still have to make considerable advances to ensure that this type of phenomenon does not once again have such a terribly fatal impact on humanity.
On 31 December 2019, representatives from the WHO in China were formally informed of the outbreak of a new Coronavirus disease (Covid-19), caused by the virus SARS-CoV-2, in the city of Wuhan, China [4]. The following months were marked around the world by this event that had been hitherto deemed as being of little importance. The aforementioned date marked the official beginning of the chronology of the disease that, a few weeks later, would be declared a pandemic by the WHO. Coronavirus disease is an inflammation disease, which causes respiratory ailments with reactions like a cold, fever and cough, and in progressively serious cases can result in the patient’s death. National health authorities are constantly striving to stem the spread of the virus by emphasizing the importance of wearing masks, social distancing, and hygiene.
By June 2021, over four million people had died of coronavirus, businesses had declared bankruptcy and life as it had been known changed radically. The three most affected countries so far (June 30th) were the United States (599,089 deaths), Brazil (514,092 deaths) and India (398,454 deaths) [5]. Amid so much terrible news, since late 2020, another form of counting has emerged to share attention with the victims of Covid-19, this time more optimistic: the number of people who have been given one of the vaccines now available.
With the advances in computer algorithms and Artificial Intelligence (AI), more specifically, Machine Learning (ML) techniques, the detection of this type of virus in the early stages will aid a fast recovery and help to ease the pressure on healthcare systems [6]. Covid-19 is highly contagious and spreads rapidly worldwide. Therefore, early detection is very important. Any technological tool that can provide rapid detection of a Covid-19 infection with high accuracy can be very useful to medical professionals. Covid-19 images, using techniques such as computed tomography (CT) and X-rays (XR), are very similar to other lung infections, making it difficult for medical professionals to distinguish Covid-19. Therefore, computer aided diagnostic solutions are being developed to facilitate the identification of positive Covid-19 cases [7].
The aim of this paper is to present a systematic review and a bibliometric analysis of the literature on the applications of ML techniques to a broader scope of problems related to the Covid-19. More specifically, this paper aims to: (i) analyze the number of papers with the greatest impact published from January 2020 to June 2021 due to the growing interest of the researchers in this theme; (ii) identify the journals with the highest number of papers; (iii) determine the focus of the papers; (iv) identify which ML techniques are used most by researchers; (v) identify which countries and databases were targeted by these studies; (vi) analyze which Covid-19 problems are more frequently addressed; and finally, (vii) identify the existing gaps that could yet be explored to gain a better understanding of why certain patients are so severely affected by the virus, while others are asymptomatic.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 presents the theoretical background of ML applied to the Covid-19 disease. Section 3 discusses the methodological procedures, including the research terms and the flowchart used in the systematic literature review. Section 4 presents and discusses the results, i.e., the survey conducted with the researched articles. Finally, Section 5 concludes the paper and suggests directions for future research in this field.
2. Theoretical background: ML techniques for the Covid-19 disease
The Covid-19 pandemic has become the most devastating disease of the twenty-first century and has spread to all the 216 countries in the world. Despite the availability of modern and sophisticated medical treatment, the disease is spreading through more outbreaks.
According to the WHO, the number of confirmed Covid-19 cases up to 26 July 2021 was 194,080,019, with this number including 4,162,304 deaths. Up to this date, 3,694,984,437 doses of vaccines had been administered [5]. There have been many studies seeking solutions to a wide range of problems and monitoring these numbers [8]. Among these studies, those that involve the use of ML techniques should be highlighted [9].
ML techniques have been extensively used by many researchers to address health problems, of which the work of dos Santos et al. [10] should be highlighted. These researchers conducted a bibliometric analysis from 2009 to 2018 on this issue. Among the other researchers were Carroll et al. [11], who conducted a systematic review of the tools used by public health professionals with emphasis on social network analysis and geographical information systems from 1980 to 2013. Dallora et al. [12], on the other hand, conducted a systematic review regarding the application of ML techniques to the prognosis of dementia. Furthermore, Bellinger et al. [13] conducted a systematic review of the application of ML techniques to the epidemiology of air pollution.
The analysis of patients’ lung images using ML techniques, conducted by Somasekar et al. [14], has seen great progress in many directions in the field of health to provide support for subsequent medical diagnoses. The authors proposed three directions for research in the struggle against the pandemic using ML techniques: classification of X-ray images of the thorax (CXR); predicting the patient’s risk based on his characteristics (including comorbidities, initial symptoms, and vital signs for the prognosis of the disease); and forecasting the propagation of the disease and the fatality rate.
On the other hand, Shahid et al. [6], presented an analysis of the role that ML has played so far in combating the virus, mainly the aspects of triage, prediction and vaccines. The authors presented a wide-ranging study of ML techniques that can be used for this purpose. Doanvo et al. [15] reflected on the fact that since August 2020, thousands of publications involving Covid-19 have been produced. The authors commented, up to the time of their research, that these works were mainly clinical in nature, from modeling or based in the field, contrasting with studies conducted in laboratories. Furthermore, the modeling of topics indicates that publications on Covid-19 have focused on public health, notifications of an outbreak, clinical treatment, and coronavirus tests.
In their analysis, M. Li et al. [16] concluded that economic inequality increases the risk of Covid-19 transmission, considering, for instance, the per capita availability of hospital beds. Increased intake of vegetables, edible oil, protein, vitamin D and vitamin K may be associated with lower risks, while a greater alcohol intake may increase the risk of Covid-19. They also commented that age, gender, temperature, humidity, social distancing, smoking, investments in health, level of urbanization and race can influence the severity of the disease.
The present study differs from other works in that it does not focus on a single type of application, but to all the situations widely cited in the literature and seeking answers to why certain patients are so severely affected by the virus, while others are asymptomatic when affected by it.
3. Methodology
This study was based on the methodology proposed by Snyder [17] and Xiao and Watson [18] to delineate the flow of information and procedures necessary to conduct this literature review. The review was guided by the research questions presented in Section 1. The initial search criteria adopted are (“Data Mining” OR “Machine Learning”) AND (“Covid” OR “Coronavirus”).
The search was limited to original articles published in peer-reviewed journals form January 2020 to June 2021, and only in English. Three scientific databases were used: ScienceDirect; Scopus; and Web of Science. Figure 1 shows the systematic literature review flowchart.
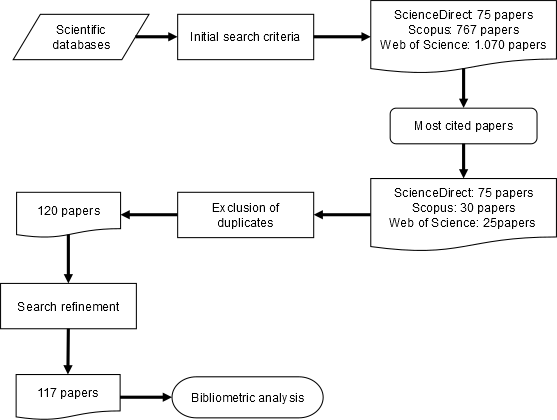
|
| Figure 1. Systematic literature review flowchart |
Based on the initial search criteria, 1,912 articles were identified in the three scientific databases. The most frequently cited articles were then selected, resulting in a total of 130 articles, of which 10 were duplicates and three did not fit the initial search profile (the first lay outside the predefined time interval, the second was an article from the field of pharmaceutics, and the third was not an original article, but a report). These 13 articles were removed in the exclusion of duplicates and search refinement stages, leaving a total of 117 original articles whose contents were analyzed.
4. Results and discussion
The results of the study conducted in accordance with the methodology presented in Section 3 are presented here, with the 117 most cited articles from the ScienceDirect, Scopus and Web of Science databases. The systematic review of the articles is presented in Section 4.1 and the bibliometric review in Section 4.2.
4.1. Systematic literature review
Of the 117 articles analyzed, 22 are studies that used X-rays (XR) and Computed Tomography (CT) of the lungs of patients affected by Covid-19 so that, through ML techniques, they could be differentiated from other lung ailments, predicting their level of severity, and determining which measures should be taken, among other alternatives, as shown in Table 1.
Researchers Ardakani et al. [19], for example, suggested a rapid and valid method for Covid-19 diagnosis based on AI techniques. They used 1,020 CT slices from 108 patients with laboratory proven Covid-19 (Covid-19 group) and 86 patients with other atypical and viral pneumonia diseases (non-Covid-19 group). The authors used 10 known Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and concluded that a computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) approach based on CT images has promising potential to distinguish Covid-19 infections from other atypical and viral pneumonia diseases. Their study showed that ResNet-101 can be considered a promising model to characterize and diagnose Covid-19 infections. This model does not involve substantial costs and can be used as an adjuvant method during CT imaging in radiology departments.
Another example is the work of Cai et al. [20], who analyzed the CT quantification of Covid-19 pneumonia and how are the impacts on the assessment of disease severity through the prediction, using Random Forest Regression (RFR), of clinical outcomes in the management of Covid-19 patients. Meanwhile, the work of Chowdhury et al. [21], proposed a robust technique for automatic detection of Covid-19 pneumonia from digital chest X-ray images applying pre-trained Deep Learning (DL) algorithms while maximizing the detection accuracy. A public database was created by the authors combining several public databases and also by collecting images from recently published papers.
Table 1 provides an overview of this research niche involving ML and XR/CT. The first column contains the authors, while the second presents the focus of the study. The third column identifies the ML technique that was employed, and the fourth column shows the databases that were used.
| Authors (year) | Focus of the paper | ML Techniques | Databases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anastasopoulos et al. (2020) [22] | Implement an automated software to solve the substantial increase in chest CT admissions | DL | GitHub platform with Covid-19 chest CT dataset |
| Ardakani et al. (2020) [19] | Develop a rapid and valid method for Covid-19 diagnosis | 10 Convolutional NN | 108 patients |
| Bharati et al. (2020) [23] | Detect lung diseases from X-ray images through VGG Data STN with CNN (VDSNet) | DL; VGG; STN; CNN | Kaggle repository |
| Brunese et al. (2020) [24] | Detect Covid-19 from chest X-rays | Supervised ML techniques | 85 chest X-rays |
| Cai et al. (2020) [20] | Analyze CT quantification | RFR | 99 patients from Zhejiang |
| Chakraborty & Mali (2021) [25] | Efficiently Interpret and segment Covid-19 radiological images. | SUFMACS | 250 CT images; 250 X-Ray images |
| Chowdhury et al. (2020) [21] | Detect Covid-19 pneumonia from digital X-ray images | DL | Kaggle databases |
| Elaziz et al. (2020) [26] | Classify chest x-ray images into 2 classes: Covid-19 patient or non-Covid-19 person | New FrMEMs; modified Manta-Ray Foraging Optimization based on DE | GitHub; Qatar University; University of Dhaka |
| Vijay kumar et al. (2020) [27] | Use the analytics of key points from images of Covid-19 for diagnosis and predictions | GANs; DL | 16 benchmark datasets |
| Loey et al. (2020) [28] | Detect coronavirus in chest X-ray images | GAN; DL | 307 images |
| Saha et al. (2021) [29] | Identify Covid-19 patients by evaluating chest X-ray images through an automated detection scheme (EMCNet) | DL; RF; SVM; DT; AdaBoost | Github repository (400 chest X-ray images) |
| Saygılı (2021) [30] | Achieve rapid and accurate detection of Covid-19 from CT and X-ray images | k-NN; SVM; Bag of Tree; K-ELM | 3 public Covid-19 data sets |
| Sedik et al. (2020) [31] | Present two data-augmentation models to enhance learnability of Covid-19 detection | CNN: ConvLSTM-based on DL | 2 datasets consisting of X-ray and CT images |
| Sethy et al. (2020) [32] | Detect coronavirus infected patients using X-ray images | Deep feature; SVM | GitHub repositor (University of Montreal; 381 images) |
| Shiri et al. (2021) [33] | Predict Covid-19 patients using clinical data and lung/lesion radiomic features extracted from chest CT images | XGBoost | 152 patients |
| D. Singh et al. (2020) [34] | Classify Covid-19 patients from chest CT images | MODE; ANN; ANFIS; CNN | --- |
| Somasekar et al. (2020) [14] | Open 3 research directions in the fight against the pandemic: CXR image classification; patient risk prediction; and forecasting of disease | DCNN | --- |
| Tamal et al. (2021) [35] | Detect Covid-19 early and rapidly from CXR | SVM; k-NN; EBM Trees | 378 images |
| Tartaglione et al. (2020) [36] | Provide which information to expect through CXR images | DL to Covid classification of CXR images | Hospitals in Northern Italy |
| X. Wang et al. (2020) [37] | Develop a DL using 3D CT for Covid-19 classification and lesion localization | DL | 540 patients |
| Waheed et al. (2020) [38] | Generate synthetic chest X-ray images | DL: CNNs | 3 publicly accessible datasets |
| Wu et al. (2021) [39] | Improve Covid-19 diagnosis using CT | RF | Youan Hospital, Beijing. |
On the other hand, many works used ML techniques to analyze people’s feelings and emotions regarding the pandemic, even their impressions concerning the climate. Sentiment Analysis is an field of study that seeks useful information through the sentiments that people share on social media, such as Facebook and Twitter [40]. Sentiments can be classified as neutral, positive or negative.
Gulati et al. [41], for example, presented a comparative analysis of seven ML classifiers, such as Linear Support Vector Classifier (SVC), Perceptron, Passive Aggressive Classifier (PAC), and Logistic Regression (LoR). They used more than 72,000 tweet datasets related to Covid-19 pandemic and achieved an accuracy score higher than 98%. Haupt et al. [42] used interdisciplinary approaches to big data, ML, content analysis, and social network analysis (SNA) to characterize the communicative behavior, conversation themes, and network structures of “Liberate protest” supporters and non-supporters. For this purpose, the authors used unsupervised ML techniques and social network analysis. Praveen et al. [43] conducted their study to analyze Indian citizens’ perceptions of what causes stress, anxiety, and trauma during Covid-19. For this purpose, the authors used ML techniques, more specifically, Natural Language Processing (NLP) in 840,000 tweets. Of the 117 articles analyzed, 13 were in this line of research and are listed in Table 2.
| Authors (year) | Focus of the paper | ML Techniques | Databases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abd-Alrazaq et al. (2020) [44] | Identify the topics related to Covid-19 posted by Twitter users | API; Tweepy Python library | February 2, 2020, to March 15, 2020 in public English language tweets |
| Gulati et al. (2021) [41] | Classify sentiment based on tweets related to Covid-19 | Linear SVC; Perceptron; PAC; LoR | 72,000 tweets |
| Gupta et al. (2021) [45] | Quantify twitter users’ perceptions regarding the effect of weather and analyze how they evolved with respect to real-world events and time. | API | 166,005 English tweets; from January 23 to June 22, 2020 |
| Haupt et al. (2021) [42] | Characterize communicative (tweets) behavior | ML techniques and SNA | API from Twitter |
| Hou et al. (2021) [46] | Explore public attention on social media | Text analysis; LDA | Weibo (popular microblogging site in China) from December 27, 2019 to May 31, 2020 |
| Kabir & Madria (2021) [47] | Present tweets dataset on Covid-19 emotional responses (EMOCOV) | DL | Data of 5,000 tweets |
| Kyriazos et al. (2021) [48] | Model that differentiated the top 25% well-being scorers in early Covid-19 quarantine | CART; RF; CTREE | Data (1,518) were collected in a web-link posted on webpages and Facebook accounts |
| S. Li et al. (2020) [49] | Explore Covid-19’s impacts on mental health | DL | 17,865 active Weibo users |
| Mackey et al. (2020) [50] | Characterize users’ conversations (tweets) associated with Covid-19 symptoms and experiences | BTM | 4,492,954 tweets |
| Praveen et al. (2021) [43] | Analyze Indian citizens’ perception of anxiety, stress and trauma during Covid-19 | Natural language | 840,000 tweets |
| Samuel et al. (2020) [51] | Identify public sentiment (tweets) associated with the pandemic | Naïve Bayes; LR; LoR; k-NN | 900,000 tweets |
| Satu et al. (2021) [52] | Analyze Covid-19 public tweets to extract significant sentiments | TClustVID | IEEE data portal developed by Rabindra Lamsal |
| Shah et al. (2021) [53] | Analyze online physician rating (OPR) to identify emerging and fading topics and sentiment trends on physician websites | NLP | 55,612 OPRs of 3,430 doctors |
Acronyms (alphabetical): See Table 1.
In turn, 44 of the 117 selected articles involved ML methods to predict a wide range of aspects, such as the number of patients who will be infected or intubated, the trends of the pandemic, the production of a real-time Covid-19 SEIRD (Susceptible, Exposed, Infected, Recovered, and Dead) model, and student performance.
Amar et al. [54], for example, attempted to investigate the disease to eliminate its effects and, to this end, the authors examined a real database from Egypt, from February 15, 2020, to June 15, 2020. They predicted the number of patients that would be infected and estimated the final size of the pandemic. For this purpose, they applied several regression analysis models. Burdick et al. [55] attempted to predict patients’ need for ventilation to determine a better allocation of resources and prevent emergency intubations and their associated risks. The authors analyzed 197 patients, from five USA health systems between March 24 and May 4, 2020. The patients were enrolled in the REspirAtory Decompensation for the triage of the disease: a prospective studY (READY) clinical trial. Of the 117 articles analyzed, 44, including the two already mentioned above, were in this line of research and are listed in Table 3.
| Authors (year) | Focus of the paper | ML Techniques | Databases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amar et al. (2020) [54] | Predict the number of patients that will be infected with Covid-19 in Egypt | LoR; Regression models | Egyptian Ministry of Health; February 15, 2020, to June 15, 2020 |
| Ardabili et al. (2020) [56] | Predict the Covid-19 outbreak and the enforcement of relevant control measures | MLP; ANFIS | Worldometers website for five countries |
| Arvind et al. (2021) [57] | Predict future intubation among patients diagnosed with Covid-19 | RF | Data from 5 hospitals within an academic healthcare system (4,087 patients) |
| ArunKumar et al. (2021) [58] | Forecast the epidemiological trends of the Covid-19 pandemic for top-16 countries | Time series models; ARIMA; SARIMA | John Hopkins University’s Covid-19 database |
| Aydin & Yurdakul (2020) [59] | Analyze the performance of countries to counter the Covid-19 outbreak | WSIDEA; k-means; HCA; RF; DT | Data from 142 countries |
| Ayyoubzadeh et al. (2020) [60] | Predict the incidence of Covid-19 in Iran | LR; LSTM models | Google Trends website |
| Ballı (2021) [61] | Identify the curve of the disease and forecast the epidemic trend | LR, MLP, RF and SVM | Data from WHO (35 weeks) |
| Bloise & Tancioni (2021) [62] | Exploit the provincial variability of Covid-19 cases in Italy to select the territorial predictors for the pandemic | LASSO; Elastic net model | Data from March 21, 2020 to June 3, 2020, in Italy |
| Burdick et al. (2020) [55] | Predict the need for ventilation for Covid-19 patients | XGBoost; DT | 197 patients were enrolled in the READY (REspirAtory Decompensation study) |
| Buscema et al. (2020) [63] | Analyze the evolution of the Covid-19 phenomenon | TWC algorithm | Geospatial coordinates of latitude and longitude of the Italian locations where the events occurred. |
| Chakraborti et al. (2021) [64] | Perform the regression modelling and provide subsequent interpretation of most critical factors | RF; GBM | European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) |
| Chatterjee et al. (2020) [65] | Analyze datasets to understand the trend of Covid-19 | Statistical and univariate time series | Oxford University Database |
| Chimmula & Zhang (2020) [66] | Forecast Covid-19 transmission | Time series; DL; LSTM networks | Johns Hopkins university; Canadian health authority |
| Cobre et al. (2021) [67] | Predict Covid-19 diagnosis and disease severity | ANN; DT; PLS-DA; KNN | Kaggle platform 5,643 patient samples |
| Ebinger et al. (2021) [68] | Predict the likelihood of prolonged LOS | 3 ML models developed using DataRobot | 966 patients |
| Fong et al. (2020) [69] | Find a forecasting model (GROOWS) from a small dataset for Covid-19 cases | PNN+cf | Archive of Chinese health authorities |
| Gothai et al. (2021) [70] | Predict the growth and trend of Covid-19 | LR; SVM; time series | 172,479 documents from Johns Hopkins University Repository |
| Jain et al. (2021) [71] | Predict Covid-19 | SVM; Naïve Bayes; KNN; AdaBoost; GBoost; RF; ANN | B-cell dataset |
| Kang et al. (2021) [72] | Predict severe Covid-19 cases | ANN | 151 cases of a China center |
| Kavadi et al. (2020) [73] | Global pandemic prediction of Covid-19 | PDR-NML method | Kaggle |
| Khan et al. (2021) [74] | Predict the time after which the number of cases stops rising in India | DT; SVM; GPR | Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW) on 10th June 2020 |
| Lmater et al. (2021) [75] | Present an effective mathematical model for predicting the spread of the (Covid-19) pandemic. | SIDR model (susceptible, infected, diagnosed and recovered stages) | Epidemiological data from 4 countries: Belgium; Morocco; Netherlands; Russia |
| Malefors et al. (2021) [76] | Predict guest attendance during the pandemic (meal planning in Sweden) | RF; ANN | Data from 18 primary school kitchens and 16 preschool kitchens |
| Mojjada et al. (2020) [77] | Show the ability to predict the number of individuals who are affected by Covid-19. | LASSO; SVM; LR | Git Hub, supplied by Johns Hopkins University |
| Nemati et al. (2020) [78] | Predict patients’ period of stay in hospital | 7 ML and statistical analysis techniques | 1,182 hospitalized patients |
| Ong et al. (2020) [79] | Predict Covid-19 vaccine candidates | Vaxign reverse vaccinology tools | ClinicalTrials.gov database and PubMed literature |
| Papastefanopoulos et al. (2020) [80] | Investigate the accuracy of six time series for coronavirus to forecast active cases per population | Six time series | Kaggle; population-by-country dataset |
| Peng & Nagata (2020) [81] | Predict the number of Covid-19 cases for the 12 most affected countries | SVR | 12 most affected countries |
| Pinter et al. (2020) [82] | Predict the Covid-19 pandemic for Hungary | Hybrid ML: ANFIS and MLP-ICA | Worldometer for Hungary |
| Pourhomayoun & Shakibi (2021) [83] | Determine the risk and predict the mortality risk of patients with Covid-19 | SVM; ANN; RF; DT; LoR; KNN | 2,670,000 Covid-19 patients from 146 countries |
| Quintero et al. (2021) [84] | Predict the SEIRD variables based on a deep dependence on them | GA; AR; ARIMA | The National Institute of Health for Colombia and the National Administrative Department of Statistics |
| Ribeiro et al. (2020) [85] | Develop short-term forecasting models to allow forecasting of the number of cases in the future | ARIMA; CUBIST; RF; RIDGE; SVR; SVR | Cases in Brazil up to April, 19 of 2020; 10 datasets |
| Santosh (2020) [86] | Develop AI-driven tools to identify Covid-19 outbreaks | AL | Multitudinal and Multimodal data |
| Shahid et al. (2021) [6] | Predict virus detection, spread prevention and medical assistance | survey of ML algorithms and models | --- |
| V. Singh et al. (2020) [87] | Produce a real-time SEIR model of confirmed, deceased, and recovered Covid-19 cases. | SVM; time series | Johns Hopkins CSSE; data from January 22, 2020 to April 25, 2020 |
| Sujath et al. (2020) [88] | Predict the spread of Covid-2019 | LR; MLP; VAR | Kaggle; Indian database |
| Tarik et al. (2021) [89] | Predict Moroccan student performance | RF; DT; LR | Referral system |
| Tuli et al. (2020) [90] | Analyze and predict the growth of the epidemic | GIWD in a cloud computing platform | Our World in Data by Hannah Ritchie |
| Wadhwa et al. (2021) [91] | Predict the extension of lockdown in order to eradicate Covid-19 from India. | LR | Total number of cases, deaths, and recoveries all over India. |
| P. Wang et al. (2020) [92] | Predict epidemic trends | LoR | Johns Hopkins University, from January 22, 2020 to June 16, 2020. |
| Yan et al. (2020) [93] | Identify crucial predictive biomarkers of Covid-19 mortality | XGBoost | 485 patients |
| Yadav et al. (2020) [94] | Solve 5 different tasks: I) Predict the spread of the disease; II) Analyze the growth rates; III) Predict how the pandemic will end; IV) Analyze the transmission rate; and V) Correlate the disease to the weather conditions. | SVR; SLR; PR | Data from different countries |
| Yeşilkanat (2020) [95] | Estimate the number of future cases for 190 countries in the world | RF | Johns Hopkins University Center for Systems Science; Engineering |
| Zivkovic et al. (2021) [96] | Predict the number of new coronavirus cases | ANFIS; BASSI | 6 benchmark Functions |
Acronyms (alphabetical): See Table 1.
Finally, the last 38 of the 117 selected articles that address general subjects involving ML techniques and Covid-19 are listed in Table 4. These include, for example, that of Di Castelnuovo et al. [97], who attempted to list those that aimed to identify the characteristics predisposing Covid-19 patients to in-hospital death. For this purpose, the authors used the data of 3,894 patients from 30 clinical centers distributed throughout Italy, who were hospitalized from February 19th to May 23rd, 2020. The authors used the RF technique to achieve their goal. They concluded that impaired renal function, elevated C-reactive protein, and advanced age were major predictors of in-hospital death.
| Authors (year) | Focus of the paper | ML Techniques | Databases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alves et al. (2021) [98] | Present understandable solutions to deal with Covid-19 screening in routine blood tests | DT Explainer and criteria graphs | 608 patients; public dataset from the Albert Einstein Hospital, São Paulo |
| Baralić et al. (2020) [99] | Assess risks and benefits of Covid- 19 treatment with promising drug combinations: lopinavir/ritonavir and chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine+ azithromycin. | in silico toxicogenomic data-mining approach | Comparative Toxicogenomics Database |
| Carrillo-Larco & Castillo-Cara (2020) [100] | Clustering countries which shared profiles of the pandemic | k-means; statistical techniques | 155 countries; Johns Hopkins University and others |
| Di Castelnuovo et al. (2020) [97] | Identify the characteristics predisposing Covid-19 patients to in-hospital death. | RF | 3,894 patients hospitalized from a defined period (Italy) |
| Choudrie et al. (2021) [101] | Explore how ML techniques and experienced people process the online infodemic related to prevention and cure | DT; CNN | 143 patients |
| Dandekar et al. (2020) [102] | Develop a globally applicable diagnostic Covid-19 model | SIR; NN | 70 countries |
| Doanvo et al. (2020) [15] | Identify knowledge research Covid-19 gaps in the literature | PCA | 35,281 abstracts from CORD-19 |
| Fong et al. (2020) [103] | Gain stochastic insights into the pandemic development | CMC: DL; FRI | Empirical data from the Chinese CDCP |
| Godavarthi & Sowjanya (2021) [104] | Extract information from the scientific literature: text classification | KNN; MLP; XGBoost | CORD-19 dataset |
| Hu et al. (2021) [105] | Detect the changes in air pollutants during Covid-19 lockdown | RF models | Data from 35 sites in Beijing, from 2015 to 2020 |
| Jamshidi et al. (2020) [106] | Present a response to combat the virus through AI | GANs; LSTM; ELM | --- |
| Kadioglu et al. (2021) [107] | Identify compounds against three targets of Covid-19 | Pharmaco strategy in silico | Chemical libraries (FDA-approved drugs; natural compound datasets; ZINC database) |
| Khanday et al. (2020) [108] | Detect Covid-19 through clinical text data | LoR; MNB | Data repository GitHub |
| Kuo & Fu (2021) [109] | Analyze demographic and environmental impact and mobility during the pandemic period | Elastic net model; PCR; PLSR; KNN; RT; RF; GBM; 2-layer ANN | New York Times; USDA ERA; gridMed; Google |
| Lam et al. (2021) [110] | Present a ML system capable of identifying patients who could be treated with a corticosteroid or remdesivir | GBM | 893 patients |
| M. Li et al. (2021) [16] | Detect novel critical factors associated with Covid-19 in 154 countries and in the 50 USA states | LoR; LASSO | Johns Hopkins University |
| Lip et al. (2021) [111] | Identify patients with Covid-19 who are at the highest risk of developing incident AF | Inferential statistics and ML computations (LoR) | Data from April 1, 2018 to Nov 30, 2020 |
| Loey et al. (2021) [112] | Develop a DL and classical ML for face detection | DL; DT; SVM; EA | 3 datasets |
| Lovrić et al. (2021) [113] | Analyze improvements in air quality during the Covid-19 lockdown | RFR | Graz, Styria, Austria |
| Magazzino et al. (2021) [114] | Analyze the relationship between Covid-19 deaths, economic growth and air pollution | DL | -- |
| McRae et al. (2020) [115] | Develop a decision support tool and rapid point-of-care platform to determine severity in patients with Covid-19 | Statistical learning algorithm | 160 patients from Wuhan, China |
| Malki et al. (2020) [116] | Verify the relationship between weather and Covid-19 | Regressor ML models | Meteoblue website |
| Mele & Magazzino (2021) [117] | Explore the relationship between pollution, economic growth and Covid-19 deaths in India | Time Series approach; Stationarity and Toda-Yamamoto causality tests | Indian data from January 29 to May 18, 2020 |
| Petetin et al. (2020) [118] | Use meteorological data to estimate the “business-as-usual” NO2 mixing ratios | GBM | GHOST |
| Qiang et al. (2020) [119] | Evaluate the infection risk of Covid-19 for early warning through spike protein feature | RF models | 507 human origin viruses and 2,159 non-human-origin viruses |
| Radanliev et al. (2020) [120] | Investigate the scientific research response from the early stages of the pandemic | Statistical methods | WSCC |
| Randhawa et al. (2020) [121] | Use intrinsic genomic signatures to classify Covid-19 rapidly | MLDSP for genome analyses; DT | Dataset of over 5,000 unique viral genomic sequences from the NCBI |
| Shrock et al. (2020) [122] | Explore antiviral antibody responses across the human virome | XGBoost | 232 coronavirus disease patients and 190 pre-Covid-19 |
| X. Sun et al. (2020) [123] | Explore TCM formulae to investigate their compatibility with the CMM to understand their potential mechanisms for treatment of Covid-19 | TCM; CMM | Encyclopedia of Traditional Chinese Medicine database; BATMAN-TCM database |
| C. L. F. Sun et al. (2020) [124] | Identify risks and vectors of infection in nursing homes | GBA | 1146 NHs in Massachusetts |
| Swapnarekha et al. (2020) [125] | Present a state-of-the-art analysis using ML and DL methods in the diagnosis and prediction of Covid-19 | ML; DL | January 23, 2020 to April, 21, 2020 |
| S. Tiwari et al. (2020) [126] | Prepare Indian government and citizens to take control measures (SEIR) | Time Series | Kaggle (data available between January 22, 2020, and April 3, 2020, from India and China) |
| A. Tiwari et al. (2021) [127] | Define a Covid-19 Vulnerability Index (C19VI) for identifying and mapping counties considered vulnerable | RF | Johns Hopkins University; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |
| Toğaçar et al. (2020) [128] | Detect Coronavirus | DL; SVM; SMOM | GitHub; Kaggle |
| Vaishya et al. (2020) [129] | Revise the effectiveness of AI techniques for Covid-19 | AI techniques | PubMed, Scopus and Google Scholar datasets |
| W.-C. Wang et al. (2021) [130] | Develop a system for monitoring global and local community outbreaks | k-means | Johns Hopkins; data with daily infected, recovered and death cases |
| Yacchirema & Chura (2021) [131] | Implement a system based on IoT for saver mobility during the pandemic | SVM; DT; LoR; RF; KNN (to detect the location of people) | From portable IoT devices |
| Yang et al. (2020) [132] | Demonstrate control measures impact the containment of the epidemic | SEIR model | 2003 SARS data |
Acronyms (alphabetical): See Table 1.
4.2 Bibliometric literature review
Of the 117 articles analyzed on the theme of the use of ML techniques in the study of Covid-19, 67 (57%) are from the year 2020, and the other 50 articles (43%) are from 2021, up to the month of June.
Furthermore, of the 117 articles, 10 were published in “Chaos, Solitons and Fractals” and eight in “Computers in Biology and Medicine”. The top 54% of journals with the highest number of publications are presented in Figure 2.
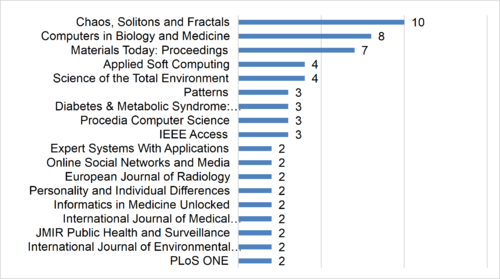
|
| Figure 2. Top 54% of journals in the selected papers |
The two main ML techniques identified by the bibliometric analysis were Random Forest (RF) and Deep Learning (DL). The most used methods, employed in 61% of the publications, are presented in Figure 3.
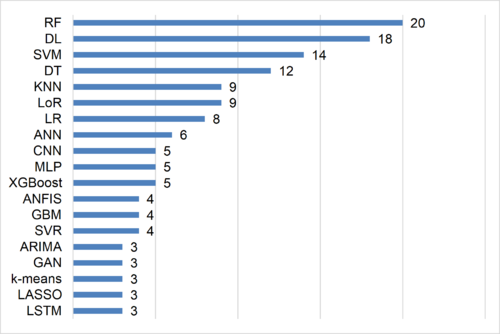
|
| Figure 3. Top 61% of publications with the most used methods |
It is noticed the predominance of classical algorithms, such as RF, SVM, and DT, in addition to modern techniques, such as DL and CNN. This shows that classical methods still have space in current scientific research, even in new applications, as in the case of Covid-19.
Finally, considering the nationality of the authors, the USA and India drew with 30 researchers each, followed by China, with 20 researchers. Figure 4 shows 70% of the most frequent nationalities of the authors of the 117 articles.
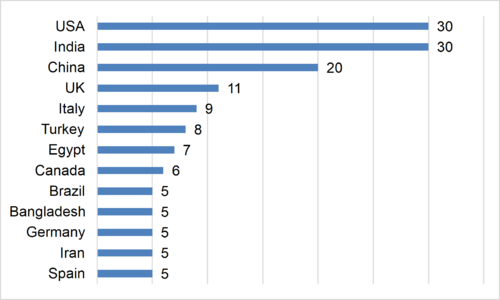
|
| Figure 4. Top 70% of authors' nationality
The first three positions, in relation to nationality, refer to the two countries with the highest number of cases of Covid-19 (USA and India) and the country where the virus was identified (China). 5. Concluding RemarksThe aim of the present study was to conduct a systematic and bibliometric review of the articles involving the protocol shown in Figure 2 which, being the most frequently cited in the literature, set out to answer, among other questions, why certain patients are severely affected by the virus while others are asymptomatic. M. Li et al. [16], for example, commented that age, sex, temperature, humidity, social distancing, smoking, investments in health, level of urbanization and race can influence the severity of the disease. On the other hand, Di Castelnuovo et al. [97] concluded that impaired renal function, elevated C-reactive protein and advanced age were major predictors of in-hospital death. However, there are many patients who fit these specific conditions, but who present different degrees of aggravation of the disease. We firmly believe that the answer to this question is directly found in very recent studies that reveal a possible genetic predisposition to serious cases of Covid-19 [133,134,135]. Researchers discovered that more severe cases of the disease are associated with the low performance of molecules that identify the virus and are inherited from parents: class I human leukocyte antigen (HLA-I) molecules represent the group of molecules responsible for identifying and distinguishing everything that is in the body and what is not. Six HLA-I molecules, found on the surface of all cells, form a unique set for each individual, which is determined by the genes received from the parents [135]. In other words, it is very important to investigate whether there is a direct link between the seriousness of the disease and the performance of HLA-I in the identification of Sars-CoV-2. Therefore, it would be very interesting and promising to analyze the genotype of patients who have suffered Covid-19 and healthy people, employing ML techniques and classifying patients, for instance, as serious, moderate, or mild cases. Funding sourcesThis research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. It is part of a larger set of projects that have been funded by the Brazilian Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES) and the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) for the research funding. References[1] WHO. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019, 2021. [2] Piret J., Boivin G. Pandemics throughout history. Front. Microbiol., 15 January, 2021. [3] Huremović D. Brief history of pandemics (Pandemics Throughout History). Psychiatry of Pandemics, Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp. 7–35, 2019. [4] Carvalho T., Krammer F., Iwasaki A. The first 12 months of COVID-19: a timeline of immunological insights. Nat. Rev. Immunol., 21(4):245–256, 2021. [5] WHO. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Retrieved from https://covid19.who.int/, 2021. [6] Shahid O., Nasajpour M., Pouriyeh S., et al. Machine learning research towards combating COVID-19: Virus detection, spread prevention, and medical assistance. J. Biomed. Inform., 117:103751, 2021. [7] Prabha B., Kaur S., Singh J., Nandankar P., Kumar Jain S., Pallathadka H. Intelligent predictions of Covid disease based on lung CT images using machine learning strategy. Mater. Today Proc., Online July 2021. [8] Haridy S., Maged A., Baker A.W., Shamsuzzaman M., Bashir H., Xie M. Monitoring scheme for early detection of coronavirus and other respiratory virus outbreaks. Comput. Ind. Eng., 156:107235, 2021. [9] Waleed Salehi A., Baglat P., Gupta G. Review on machine and deep learning models for the detection and prediction of Coronavirus. Mater. Today Proc., 33:3896–3901, 2020. [10] dos Santos B.S., Steiner M.T.A., Fenerich A.T., Lima R.H.P. Data mining and machine learning techniques applied to public health problems: A bibliometric analysis from 2009 to 2018. Comput. Ind. Eng., 138:106120, 2019. [11] Carroll L.N., Au A.P., Detwiler L.T., Fu T., Painter I.S., Abernethy N.F. Visualization and analytics tools for infectious disease epidemiology: A systematic review. J. Biomed. Inform., 51:287–298, 2014. [12] Dallora A.L., Eivazzadeh S., Mendes E., Berglund J., Anderberg P. Prognosis of dementia employing machine learning and microsimulation techniques: A systematic literature review. Procedia Comput. Sci., 100:480–488, 2016. [13] Bellinger C., Mohomed Jabbar M.S., Zaïane O., Osornio-Vargas A. A systematic review of data mining and machine learning for air pollution epidemiology. BMC Public Health, 17(1):907, 2017. [14] Somasekar J., Pavan Kumar P., Sharma A., Ramesh G. Machine learning and image analysis applications in the fight against COVID-19 pandemic: Datasets, research directions, challenges and opportunities. Mater. Today Proc., 3–6, 2020. [15] Doanvo A., Qian X., Ramjee D., Piontkivska H., Desai A., Majumder M. Machine Learning Maps Research Needs in COVID-19 Literature. Patterns, 1(9):100123, 2020. [16] Li M., Zhang Z., Cao W., et al. Identifying novel factors associated with COVID-19 transmission and fatality using the machine learning approach. Sci. Total Environ., 764(639):142810, 2021. [17] Snyder H. Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res., 104:333–339, 2019. [18] Xiao Y., Watson M. Guidance on conducting a systematic literature review. J. Plan. Educ. Res., 39(1):93–112, 2019. [19] Ardakani A.A., Kanafi A.R., Acharya U.R., Khadem N., Mohammadi A. Application of deep learning technique to manage COVID-19 in routine clinical practice using CT images: Results of 10 convolutional neural networks. Comput. Biol. Med., 121:103795, 2020. [20] Cai W., Liu T., Xue X., et al. CT Quantification and machine-learning models for assessment of disease severity and prognosis of COVID-19 patients. Acad. Radiol., 27(12):1665–1678, 2020. [21] Chowdhury M.E.H., Rahman T., Khandakar A., et al. Can AI Help in Screening Viral and COVID-19 Pneumonia? IEEE Access, 8:132665–132676, 2020. [22] Anastasopoulos C., Weikert T., Yang S., et al. Development and clinical implementation of tailored image analysis tools for COVID-19 in the midst of the pandemic: The synergetic effect of an open, clinically embedded software development platform and machine learning. Eur. J. Radiol., 131:109233, 2020. [23] Bharati S., Podder P., Mondal M.R.H. Hybrid deep learning for detecting lung diseases from X-ray images. Informatics Med. Unlocked, 20:100391, 2020. [24] Brunese L., Martinelli F., Mercaldo F., Santone A. Machine learning for coronavirus covid-19 detection from chest x-rays. Procedia Comput. Sci., 176:2212–2221, 2020. [25] Chakraborty S., Mali K. SUFMACS: A machine learning-based robust image segmentation framework for COVID-19 radiological image interpretation. Expert Syst. Appl., 178:115069, 2021. [26] Elaziz M.A., Hosny K.M., Salah A., Darwish M.M., Lu S., Sahlol A.T. New machine learning method for image-based diagnosis of COVID-19. PLoS One, 15(6):e0235187, 2020. [27] Vijay kumar J., Harshavardhan A., Bhukya H., Krishna Prasad A.V. Advanced machine learning-based analytics on COVID-19 data using generative adversarial networks. Mater. Today Proc., 2020. [28] Loey M., Smarandache F., M. Khalifa N.E. Within the lack of chest COVID-19 X-ray dataset: A novel detection model based on GAN and deep transfer learning. Symmetry (Basel), 12(4):651, 2020. [29] Saha P., Sadi M.S., Islam M.M. EMCNet: Automated COVID-19 diagnosis from X-ray images using convolutional neural network and ensemble of machine learning classifiers. Informatics Med. Unlocked, 22:100505, 2021. [30] Saygılı A. A new approach for computer-aided detection of coronavirus (COVID-19) from CT and X-ray images using machine learning methods. Appl. Soft Comput., 105:107323, 2021. [31] Sedik A., Iliyasu A.M., Abd El-Rahiem B., et al. Deploying machine and deep learning models for efficient data-augmented detection of COVID-19 infections. Viruses, 12(7):769, 2020. [32] Sethy P.K., Behera S.K., Ratha P.K., Biswas P. Detection of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) based on deep features and support vector machine. Int. J. Math. Eng. Manag. Sci., 5(4):643–651, 2020. [33] Shiri I., Sorouri M., Geramifar P., et al. Machine learning-based prognostic modeling using clinical data and quantitative radiomic features from chest CT images in COVID-19 patients. Comput. Biol. Med., 132:104304, 2021. [34] Singh D., Kumar V., Vaishali, Kaur M. Classification of COVID-19 patients from chest CT images using multi-objective differential evolution–based convolutional neural networks. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis., 39(7):1379–1389, 2020. [35] Tamal M., Alshammari M., Alabdullah M., Hourani R., Alola H.A., Hegazi T.M. An integrated framework with machine learning and radiomics for accurate and rapid early diagnosis of COVID-19 from Chest X-ray. Expert Syst. Appl., 180:115152, 2021. [36] Tartaglione E., Barbano C.A., Berzovini C., Calandri M., Grangetto M. Unveiling COVID-19 from CHEST X-Ray with deep learning: A hurdles race with small data. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 17(18):6933, 2020. [37] Wang X., Deng X., Fu Q., et al. A weakly-supervised framework for COVID-19 classification and lesion localization from chest CT. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging, 39(8):2615–2625, 2020. [38] Waheed A., Goyal M., Gupta D., Khanna A., Al-Turjman F., Pinheiro P.R. CovidGAN: Data augmentation using auxiliary classifier GAN for improved Covid-19 detection. IEEE Access, 8:91916–91923, 2020. [39] Wu Z., Li L., Jin R., et al. Texture feature-based machine learning classifier could assist in the diagnosis of COVID-19. Eur. J. Radiol., 137:109602, 2021. [40] Çalı S., Balaman Ş.Y. Improved decisions for marketing, supply and purchasing: Mining big data through an integration of sentiment analysis and intuitionistic fuzzy multi criteria assessment. Comput. Ind. Eng., 129:315–332, 2019. [41] Gulati K., Saravana Kumar S., Sarath Kumar Boddu R., Sarvakar K., Kumar Sharma D., Nomani M.Z.M. Comparative analysis of machine learning-based classification models using sentiment classification of tweets related to COVID-19 pandemic. Mater. Today Proc., 51(1):38-41, 2022. [42] Haupt M.R., Jinich-Diamant A., Li J., Nali M., Mackey T.K. Characterizing twitter user topics and communication network dynamics of the “Liberate” movement during COVID-19 using unsupervised machine learning and social network analysis. Online Soc. Networks Media, 21:100114, 2021. [43] Praveen S.V., Ittamalla R., Deepak G. Analyzing Indian general public’s perspective on anxiety, stress and trauma during Covid-19 - A machine learning study of 840,000 tweets. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev., 15(3):667–671, 2021. [44] Abd-Alrazaq A., Alhuwail D., Househ M., Hamdi M., Shah Z. Top concerns of tweeters during the COVID-19 pandemic: Infoveillance study. J. Med. Internet Res., 22(4):e19016, 2020. [45] Gupta M., Bansal A., Jain B., Rochelle J., Oak A., Jalali M.S. Whether the weather will help us weather the COVID-19 pandemic: Using machine learning to measure twitter users’ perceptions. Int. J. Med. Inform., 145:104340, 2021. [46] Hou K., Hou T., Cai L. Public attention about COVID-19 on social media: An investigation based on data mining and text analysis. Pers. Individ. Dif., 175:110701, 2021. [47] Kabir M.Y., Madria S. EMOCOV: Machine learning for emotion detection, analysis and visualization using COVID-19 tweets. Online Soc. Networks Media, 23:100135, 2021. [48] Kyriazos T., Galanakis M., Karakasidou E., Stalikas A. Early COVID-19 quarantine: A machine learning approach to model what differentiated the top 25% well-being scorers. Pers. Individ. Dif., 181:110980, 2021. [49] Li S., Wang Y., Xue J., Zhao N., Zhu T. The impact of COVID-19 epidemic declaration on psychological consequences: A study on active weibo users. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 17(6):2032, 2020. [50] Mackey T., Purushothaman V., Li J., et al. Machine learning to detect self-reporting of symptoms, testing access, and recovery associated with COVID-19 on twitter: Retrospective big data infoveillance study. JMIR Public Heal. Surveill., 6(2):e19509, 2020. [51] Samuel J., Ali G.G.M.N., Rahman M.M., Esawi E., Samuel Y. COVID-19 public sentiment insights and machine learning for tweets classification. Information, 11(6):314, 2020. [52] Satu M.S., Khan M.I., Mahmud M., et al. TClustVID: A novel machine learning classification model to investigate topics and sentiment in COVID-19 tweets. Knowledge-Based Syst., 226:107126, 2021. [53] Shah A.M., Yan X., Qayyum A., Naqvi R.A., Shah S.J. Mining topic and sentiment dynamics in physician rating websites during the early wave of the COVID-19 pandemic: Machine learning approach. Int. J. Med. Inform., 149:104434, 2021. [54] Amar L.A., Taha A.A., Mohamed M.Y. Prediction of the final size for COVID-19 epidemic using machine learning: A case study of Egypt. Infect. Dis. Model., 5:622–634, 2020. [55] Burdick H., Lam C., Mataraso S., et al. Prediction of respiratory decompensation in Covid-19 patients using machine learning: The READY trial. Comput. Biol. Med., 124:103949, 2020. [56] Ardabili S.F., Mosavi A., Ghamisi P., et al. COVID-19 outbreak prediction with machine learning. Algorithms, 13(10):249, 2020. [57] Arvind V., Kim J.S., Cho B.H., Geng E., Cho S.K. Development of a machine learning algorithm to predict intubation among hospitalized patients with COVID-19. J. Crit. Care, 62:25–30, 2021. [58] ArunKumar K.E., Kalaga D. V., Sai Kumar C.M., Chilkoor G., Kawaji M., Brenza T.M. Forecasting the dynamics of cumulative COVID-19 cases (confirmed, recovered and deaths) for top-16 countries using statistical machine learning models: Auto-Regressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) and Seasonal Auto-Regressive Integrated Moving Averag. Appl. Soft Comput., 103:107161, 2021. [59] Aydin N., Yurdakul G. Assessing countries’ performances against COVID-19 via WSIDEA and machine learning algorithms. Appl. Soft Comput., 97:106792, 2020. [60] Ayyoubzadeh S.M., Ayyoubzadeh S.M., Zahedi H., Ahmadi M., R Niakan Kalhori S. Predicting COVID-19 incidence through analysis of Google trends data in Iran: Data mining and deep learning pilot study. JMIR Public Heal. Surveill., 6(2):e18828, 2020. [61] Ballı S. Data analysis of Covid-19 pandemic and short-term cumulative case forecasting using machine learning time series methods. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 142:110512, 2021. [62] Bloise F., Tancioni M. Predicting the spread of COVID-19 in Italy using machine learning: Do socio-economic factors matter? Struct. Chang. Econ. Dyn., 56:310–329, 2021. [63] Buscema P.M., Della Torre F., Breda M., Massini G., Grossi E. COVID-19 in Italy and extreme data mining. Phys. A Stat. Mech. its Appl., 557:124991, 2020. [64] Chakraborti S., Maiti A., Pramanik S., et al. Evaluating the plausible application of advanced machine learnings in exploring determinant factors of present pandemic: A case for continent specific COVID-19 analysis. Sci. Total Environ., 765:142723, 2021. [65] Chatterjee A., Gerdes M.W., Martinez S.G. Statistical explorations and univariate timeseries analysis on COVID-19 datasets to understand the trend of disease spreading and death. Sensors, 20(11):3089, 2020. [66] Chimmula V.K.R., Zhang L. Time series forecasting of COVID-19 transmission in Canada using LSTM networks. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 135:109864, 2020. [67] Cobre A. de F., Stremel D.P., Noleto G.R., et al. Diagnosis and prediction of COVID-19 severity: can biochemical tests and machine learning be used as prognostic indicators? Comput. Biol. Med., 134:104531, 2021. [68] Ebinger J., Wells M., Ouyang D., et al. A machine learning algorithm predicts duration of hospitalization in COVID-19 patients. Intell. Med., 5:100035, 2021. [69] Fong S.J., Li G., Dey N., Crespo R.G., Herrera-Viedma E. Finding an accurate early forecasting model from small dataset: A case of 2019-nCoV novel coronavirus outbreak. Int. J. Interact. Multimed. Artif. Intell., 6(1):132, 2020. [70] Gothai E., Thamilselvan R., Rajalaxmi R.R., Sadana R.M., Ragavi A., Sakthivel R. Prediction of COVID-19 growth and trend using machine learning approach. Mater. Today Proc., April 2021. [71] Jain N., Jhunthra S., Garg H., et al. Prediction modelling of COVID using machine learning methods from B-cell dataset. Results Phys., 21:103813, 2021. [72] Kang J., Chen T., Luo H., Luo Y., Du G., Jiming-Yang M. Machine learning predictive model for severe COVID-19. Infect. Genet. Evol., 90:104737, 2021. [73] Kavadi D.P., Patan R., Ramachandran M., Gandomi A.H. Partial derivative nonlinear global pandemic machine learning prediction of COVID 19. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 139:110056, 2020. [74] Khan F.M., Kumar A., Puppala H., Kumar G., Gupta R. Projecting the criticality of COVID-19 transmission in India using GIS and machine learning methods. J. Saf. Sci. Resil., 2(2):50–62, 2021. [75] Lmater M.A., Eddabbah M., Elmoussaoui T., Boussaa S. Modelization of Covid-19 pandemic spreading: A machine learning forecasting with relaxation scenarios of countermeasures. J. Infect. Public Health, 14(4):468–473, 2021. [76] Malefors C., Secondi L., Marchetti S., Eriksson M. Food waste reduction and economic savings in times of crisis: The potential of machine learning methods to plan guest attendance in Swedish public catering during the Covid-19 pandemic. Socioecon. Plann. Sci., 82(A):101041, 2022. [77] Mojjada R.K., Yadav A., Prabhu A.V., Natarajan Y. Machine learning models for covid-19 future forecasting. Mater. Today Proc., December 2020. [78] Nemati M., Ansary J., Nemati N. Machine-learning approaches in COVID-19 survival analysis and discharge-time likelihood prediction using clinical data. Patterns, 1(5):100074, 2020. [79] Ong E., Wong M.U., Huffman A., He Y. COVID-19 coronavirus vaccine design using reverse vaccinology and machine learning. Front. Immunol., 11(July):1581, 2020. [80] Papastefanopoulos V., Linardatos P., Kotsiantis S. COVID-19: A comparison of time series methods to forecast percentage of active cases per population. Appl. Sci., 10(11):3880, 2020. [81] Peng Y., Nagata M.H. An empirical overview of nonlinearity and overfitting in machine learning using COVID-19 data. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 139:110055, 2020. [82] Pinter G., Felde I., Mosavi A., Ghamisi P., Gloaguen R. COVID-19 pandemic prediction for Hungary; A hybrid machine learning approach. SSRN Electron. J., 8(6):890, 2020. [83] Pourhomayoun M., Shakibi M. Predicting mortality risk in patients with COVID-19 using machine learning to help medical decision-making. Smart Heal., 20:100178, 2021. [84] Quintero Y., Ardila D., Camargo E., Rivas F., Aguilar J. Machine learning models for the prediction of the SEIRD variables for the COVID-19 pandemic based on a deep dependence analysis of variables. Comput. Biol. Med., 134:104500, 2021. [85] Ribeiro M.H.D.M., da Silva R.G., Mariani V.C., Coelho L. dos S. Short-term forecasting COVID-19 cumulative confirmed cases: Perspectives for Brazil. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 135:109853, 2020. [86] Santosh K.C. AI-driven tools for coronavirus outbreak: Need of active learning and cross-population train/test models on multitudinal/multimodal data. J. Med. Syst., 44(5):93, 2020. [87] Singh V., Poonia R.C., Kumar S., et al. Prediction of COVID-19 corona virus pandemic based on time series data using support vector machine. J. Discret. Math. Sci. Cryptogr., 23(8):1583–1597, 2020. [88] Sujath R., Chatterjee J.M., Hassanien A.E. A machine learning forecasting model for COVID-19 pandemic in India. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess., 34(7):959–972, 2020. [89] Tarik A., Aissa H., Yousef F. Artificial intelligence and machine learning to predict student performance during the COVID-19. Procedia Comput. Sci., 184:835–840, 2021. [90] Tuli S., Tuli S., Tuli R., Gill S.S. Predicting the growth and trend of COVID-19 pandemic using machine learning and cloud computing. Internet of Things, 11:100222, 2020. [91] Wadhwa P., Aishwarya, Tripathi A., Singh P., Diwakar M., Kumar N. Predicting the time period of extension of lockdown due to increase in rate of COVID-19 cases in India using machine learning. Mater. Today Proc., 37(Part 2):2617–2622, 2021. [92] Wang P., Zheng X., Li J., Zhu B. Prediction of epidemic trends in COVID-19 with logistic model and machine learning technics. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 139:110058, 2020. [93] Yan L., Zhang H.-T., Goncalves J., et al. An interpretable mortality prediction model for COVID-19 patients. Nat. Mach. Intell., 2(5):283–288, 2020. [94] Yadav M., Perumal M., Srinivas M. Analysis on novel coronavirus (COVID-19) using machine learning methods. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 139:110050, 2020. [95] Yeşilkanat C.M. Spatio-temporal estimation of the daily cases of COVID-19 in worldwide using random forest machine learning algorithm. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 140:110210, 2020. [96] Zivkovic M., Bacanin N., Venkatachalam K., et al. COVID-19 cases prediction by using hybrid machine learning and beetle antennae search approach. Sustain. Cities Soc., 66:102669, 2021. [97] Di Castelnuovo A., Bonaccio M., Costanzo S., et al. Common cardiovascular risk factors and in-hospital mortality in 3,894 patients with COVID-19: survival analysis and machine learning-based findings from the multicentre Italian CORIST Study. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis., 30(11):1899–1913, 2020. [98] Alves M.A., Castro G.Z., Oliveira B.A.S., et al. Explaining machine learning based diagnosis of COVID-19 from routine blood tests with decision trees and criteria graphs. Comput. Biol. Med., 132:104335, 2021. [99] Baralić K., Jorgovanović D., Živančević K., et al. Safety assessment of drug combinations used in COVID-19 treatment: in silico toxicogenomic data-mining approach. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 406:115237, 2020. [100] Carrillo-Larco R.M., Castillo-Cara M. Using country-level variables to classify countries according to the number of confirmed COVID-19 cases: An unsupervised machine learning approach. Wellcome Open Res., 5:56, 2020. [101] Choudrie J., Banerjee S., Kotecha K., Walambe R., Karende H., Ameta J. Machine learning techniques and older adults processing of online information and misinformation: A covid 19 study. Comput. Human Behav., 119:106716, 2021. [102] Dandekar R., Rackauckas C., Barbastathis G. A machine learning-aided global diagnostic and comparative tool to assess effect of quarantine control in COVID-19 spread. Patterns, 1(9):100145, 2020. [103] Fong S.J., Li G., Dey N., Crespo R.G., Herrera-Viedma E. Composite Monte Carlo decision making under high uncertainty of novel coronavirus epidemic using hybridized deep learning and fuzzy rule induction. Appl. Soft Comput., 93:106282, 2020. [104] Godavarthi D., Sowjanya M. Classification of covid related articles using machine learning. Mater. Today Proc., February 2021. [105] Hu J., Pan Y., He Y., et al. Changes in air pollutants during the COVID-19 lockdown in Beijing: Insights from a machine-learning technique and implications for future control policy. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett., 14(4):100060, 2021. [106] Jamshidi M., Lalbakhsh A., Talla J., et al. Artificial intelligence and COVID-19: deep learning approaches for diagnosis and treatment. IEEE Access, 8:109581–109595, 2020. [107] Kadioglu O., Saeed M., Greten H.J., Efferth T. Identification of novel compounds against three targets of SARS CoV-2 coronavirus by combined virtual screening and supervised machine learning. Comput. Biol. Med., 133:104359, 2021. [108] Khanday A.M.U.D., Rabani S.T., Khan Q.R., Rouf N., Mohi Ud Din M. Machine learning based approaches for detecting COVID-19 using clinical text data. Int. J. Inf. Technol., 12(3):731–739, 2020. [109] Kuo C.-P., Fu J.S. Evaluating the impact of mobility on COVID-19 pandemic with machine learning hybrid predictions. Sci. Total Environ., 758:144151, 2021. [110] Lam C., Siefkas A., Zelin N.S., et al. Machine learning as a precision-medicine approach to prescribing COVID-19 pharmacotherapy with remdesivir or corticosteroids. Clin. Ther., 43(5):871-885, 2021. [111] Lip G.Y.H., Genaidy A., Tran G., Marroquin P., Estes C. Incident atrial fibrillation and its risk prediction in patients developing COVID-19: A machine learning based algorithm approach. Eur. J. Intern. Med., 91:53-58, 2021. [112] Loey M., Manogaran G., Taha M.H.N., Khalifa N.E.M. A hybrid deep transfer learning model with machine learning methods for face mask detection in the era of the COVID-19 pandemic. Measurement, 167:108288, 2021. [113] Lovrić M., Pavlović K., Vuković M., Grange S.K., Haberl M., Kern R. Understanding the true effects of the COVID-19 lockdown on air pollution by means of machine learning. Environ. Pollut., 274:115900, 2021. [114] Magazzino C., Mele M., Sarkodie S.A. The nexus between COVID-19 deaths, air pollution and economic growth in New York state: Evidence from Deep Machine Learning. J. Environ. Manage., 286:112241, 2021. [115] McRae M.P., Simmons G.W., Christodoulides N.J., et al. Clinical decision support tool and rapid point-of-care platform for determining disease severity in patients with COVID-19. Lab Chip, 20(12):2075–2085, 2020. [116] Malki Z., Atlam E.-S., Hassanien A.E., Dagnew G., Elhosseini M.A., Gad I. Association between weather data and COVID-19 pandemic predicting mortality rate: Machine learning approaches. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 138:110137, 2020. [117] Mele M., Magazzino C. Pollution, economic growth, and COVID-19 deaths in India: a machine learning evidence. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., 28(3):2669–2677, 2021. [118] Petetin H., Bowdalo D., Soret A., et al. Meteorology-normalized impact of the COVID-19 lockdown upon NO<sub>2</sub> pollution in Spain. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 20(18):11119–11141, 2020. [119] Qiang X.-L., Xu P., Fang G., Liu W.-B., Kou Z. Using the spike protein feature to predict infection risk and monitor the evolutionary dynamic of coronavirus. Infect. Dis. Poverty, 9(1):33, 2020. [120] Radanliev P., De Roure D., Walton R. Data mining and analysis of scientific research data records on Covid-19 mortality, immunity, and vaccine development - In the first wave of the Covid-19 pandemic. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev., 14(5):1121–1132, 2020. [121] Randhawa G.S., Soltysiak M.P.M., El Roz H., de Souza C.P.E., Hill K.A., Kari L. Machine learning using intrinsic genomic signatures for rapid classification of novel pathogens: COVID-19 case study. PLoS One, 15(4):e0232391, 2020. [122] Shrock E., Fujimura E., Kula T., et al. Viral epitope profiling of COVID-19 patients reveals cross-reactivity and correlates of severity. Science, 370(6520):eabd4250, 2020. [123] Sun X., Jiang J., Wang Y., Liu S. Exploring the potential therapeutic effect of traditional Chinese medicine on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) through a combination of data mining and network pharmacology analysis. Eur. J. Integr. Med., 40:101242, 2020. [124] Sun C.L.F., Zuccarelli E., Zerhouni E.G.A., et al. Predicting coronavirus disease 2019 infection risk and related risk drivers in nursing homes: A machine learning approach. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc., 21(11):1533-1538.e6, 2020. [125] Swapnarekha H., Behera H.S., Nayak J., Naik B. Role of intelligent computing in COVID-19 prognosis: A state-of-the-art review. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 138:109947, 2020. [126] Tiwari S., Kumar S., Guleria K. Outbreak trends of coronavirus disease–2019 in India: A prediction. Disaster Med. Public Health Prep., 14(5):e33–e38, 2020. [127] Tiwari A., Dadhania A. V., Ragunathrao V.A.B., Oliveira E.R.A. Using machine learning to develop a novel COVID-19 Vulnerability Index (C19VI). Sci. Total Environ., 773:145650, 2021. [128] Toğaçar M., Ergen B., Cömert Z. COVID-19 detection using deep learning models to exploit Social Mimic Optimization and structured chest X-ray images using fuzzy color and stacking approaches. Comput. Biol. Med., 121:103805, 2020. [129] Vaishya R., Javaid M., Khan I.H., Haleem A. Artificial Intelligence (AI) applications for COVID-19 pandemic. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev., 14(4):337–339, 2020. [130] Wang W.-C., Lin T.-Y., Chiu S.Y.-H., et al. Classification of community-acquired outbreaks for the global transmission of COVID-19: Machine learning and statistical model analysis. J. Formos. Med. Assoc., 120:S26–S37, 2021. [131] Yacchirema D., Chura A. SafeMobility: An IoT- based System for safer mobility using machine learning in the age of COVID-19. Procedia Comput. Sci., 184:524–531, 2021. [132] Yang Z., Zeng Z., Wang K., et al. Modified SEIR and AI prediction of the epidemics trend of COVID-19 in China under public health interventions. J. Thorac. Dis., 12(3):165–174, 2020. [133] COVID-19 Host Genetics Initiative. Mapping the human genetic architecture of COVID-19. Nature, 600:472–477, 2021. [134] Pairo-Castineira E., Clohisey S., Klaric L., et al. Genetic mechanisms of critical illness in COVID-19. Nature, 591(7848):92–98, 2021. [135] Shkurnikov M., Nersisyan S., Jankevic T., et al. Association of HLA class I genotypes with severity of coronavirus disease-19. Front. Immunol., 12:641900, 2021. |
Document information
Published on 09/09/22
Accepted on 26/08/22
Submitted on 20/03/22
Volume 38, Issue 3, 2022
DOI: 10.23967/j.rimni.2022.09.001
Licence: CC BY-NC-SA license