m (Xmartinez moved page Review 592257080692 to Sierra et al 2022a) |
|||
| (20 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==1 INTRODUCTION== | ==1 INTRODUCTION== | ||
| − | Offshore renewable energy is a cornerstone of the clean energy transition in the EU. It consists of many different sources that are abundant, natural and clean, obtaining energy from wind, wave and tidal. This can be harnessed by modern technologies without emitting any greenhouse gases, (European Commission 2020). There is no doubt that the offshore renewable energy exploitation has a large potential to grow. | + | Offshore renewable energy is a cornerstone of the clean energy transition in the EU. It consists of many different sources that are abundant, natural and clean, obtaining energy from wind, wave and tidal. This can be harnessed by modern technologies without emitting any greenhouse gases, (European Commission 2020). There is no doubt that the offshore renewable energy exploitation has a large potential to grow. However, the open sea is a very aggressive environment, which may largely affect the maintenance costs of the installations and therefore the overall cost of offshore energy generation. The owners of offshore assets are aware of that and are paying a steep price. A massive amount of steel goes into those assets, and all this metal is subject to degradation, which explains why corrosion accounts for approximately 60% of offshore maintenance costs. In order to address this problem, the main objective of the EU H2020 952966 FIBREGY project, (EU 2023), is enabling the extensive use of FRP materials in the structure of the next generation of large Offshore Wind and Tidal Power (OWTP) platforms, due to the convenient immunity to corrosion and superior fatigue performance of these materials. Another innovative aspect that will be considered is the use of multifunctional FRP materials in the OWTP structure, by embedding sensors in the material for continuous SHM. |
| − | During FIBREGY project, a scale (1:50) of an FRP tower with an embedded SHM system will be tested. In this paper, a dynamic numerical analysis of this scaled structure is carried out. A | + | During FIBREGY project, a scale (1:50) of an FRP tower with an embedded SHM system will be tested. In this paper, a dynamic numerical analysis of this scaled structure is carried out. A FEM is made and analysed to obtain its dynamic behaviour, characterized by frequencies and modal shapes. Also, a model updating and optimization based damage detection method is proposed for this structure and tested using a numerical damaged scenario. |
==2 Numerical Model== | ==2 Numerical Model== | ||
<div id='img-1'> | <div id='img-1'> | ||
| − | 2.1 Geometry | + | ===2.1 Geometry=== |
The structure under study is a cone with the following geometric characteristics, showed in Fig. 1. The bottom face of the tower is fully fixed (displacement in x, y and z). | The structure under study is a cone with the following geometric characteristics, showed in Fig. 1. The bottom face of the tower is fully fixed (displacement in x, y and z). | ||
| − | * Height: <math display="inline">h = 1200 mm</math> | + | * Height: <math display="inline">h = 1200 \ mm</math> |
| − | * Bottom external diameter: <math display="inline">\Phi _b = 117 | + | * Bottom external diameter: <math display="inline">\Phi _b = 117 \ mm</math> |
| − | * Top external diameter: <math display="inline">\Phi _t = 84 | + | * Top external diameter: <math display="inline">\Phi _t = 84 \ mm</math> |
| − | * Thickness: <math display="inline">t = 4 | + | * Thickness: <math display="inline">t = 4 \ mm</math> |
The tower is divided into <math display="inline">10</math> sectors in its height (x axis) and in <math display="inline">6</math> layers evenly distributed in the thickness, in correspondence with the laminate that forms it, resulting in <math display="inline">60</math> volumes. | The tower is divided into <math display="inline">10</math> sectors in its height (x axis) and in <math display="inline">6</math> layers evenly distributed in the thickness, in correspondence with the laminate that forms it, resulting in <math display="inline">60</math> volumes. | ||
| Line 64: | Line 26: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | The FEM design is done with GiD,(CIMNE 2020), a pre and post processor for numerical simulations in science and engineering. The structure is discretized in <math display="inline">54\,096</math> nodes and <math display="inline">46\,080</math> hexahedra linear elements and is shown in Fig. 2. | + | The FEM design is done with GiD,(CIMNE 2020), a pre and post processor for numerical simulations in science and engineering. The structure is discretized in <math display="inline">54\,096</math> nodes and <math display="inline">46\,080</math> hexahedra linear elements and, as it is shown in Fig. 2. |
{| class="floating_imageSCP" style="text-align: center; border: 1px solid #BBB; margin: 1em auto; width: 100%;max-width: 100%;" | {| class="floating_imageSCP" style="text-align: center; border: 1px solid #BBB; margin: 1em auto; width: 100%;max-width: 100%;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 74: | Line 36: | ||
===2.2 Material=== | ===2.2 Material=== | ||
| − | The FRP used in the scaled tower is composed of a vinylester based resin with glass | + | The FRP used in the scaled tower is composed of a vinylester based resin with glass fibre reinforcement, with a <math display="inline">20 %</math> of fibre volume fraction. The main characteristics are listed in Tab 1. The composite has <math display="inline">6</math> layers of unidirectional fibres in the following orientations, from external to internal layer: [<math display="inline">0^{\circ } / 55^{\circ } / 0^{\circ } / {-55}^{\circ } / 0^{\circ } / 90^{\circ } </math>], angles from the axis of the tower, see Fig. 1. . |
{| class="floating_tableSCP wikitable" style="text-align: center; margin: 1em auto;min-width:50%;" | {| class="floating_tableSCP wikitable" style="text-align: center; margin: 1em auto;min-width:50%;" | ||
|+ style="font-size: 75%;" |<span id='table-1'></span>Table. 1 Materials properties | |+ style="font-size: 75%;" |<span id='table-1'></span>Table. 1 Materials properties | ||
| Line 102: | Line 64: | ||
===2.3 Numerical Analysis=== | ===2.3 Numerical Analysis=== | ||
| − | A dynamic analysis of the model is done using an | + | A dynamic analysis of the model is done using an in-house multi-physics FEM code, FEMUSS, developed by the International Centre for Numerical Methods in Engineering (CIMNE) and the Polytechnical University of Catalunya (UPC). The different orthotropic composite layers, are treated using the Serial-Parallel mixing theory, (Martinez, et al. 2008). |
===2.4 Damaged Case=== | ===2.4 Damaged Case=== | ||
| Line 110: | Line 72: | ||
==3 Dynamic behaviour== | ==3 Dynamic behaviour== | ||
| − | The embedded SHM system that is going to be used in tests allows up to <math display="inline">1\,000 Hz</math> of sampling rate. In consequence, the analysis is limited to <math display="inline">500 | + | The embedded SHM system that is going to be used in tests allows up to <math display="inline">1\,000 \ Hz</math> of sampling rate. In consequence, the analysis is limited to <math display="inline">500 \ Hz</math>, the half of the sampling rate value, corresponding to the Nyquist frequency. This value defines the bandwith by Fourier transform based analysis. |
In this range, <math display="inline">7</math> modes were found. The frequency values obtained in the analysis of the undamaged scenario and the described damaged reference case, are listed and compared in Tab. 2. Due to the rotational symmetry of the structure, modes 1-2, 3-4 and 6-7 have almost the same values between them, but not equal because the asymmetry in the fibre's orientation. These are flexural modes, while mode 5 is expansive, as is shown in Figs. 3 and 4. There, dark blue colour represents no displacement, red biggest displacement. | In this range, <math display="inline">7</math> modes were found. The frequency values obtained in the analysis of the undamaged scenario and the described damaged reference case, are listed and compared in Tab. 2. Due to the rotational symmetry of the structure, modes 1-2, 3-4 and 6-7 have almost the same values between them, but not equal because the asymmetry in the fibre's orientation. These are flexural modes, while mode 5 is expansive, as is shown in Figs. 3 and 4. There, dark blue colour represents no displacement, red biggest displacement. | ||
| Line 120: | Line 82: | ||
| Undamaged | | Undamaged | ||
| Damaged | | Damaged | ||
| − | | <math>\Delta _{rel} | + | | <math>\Delta _{rel}</math> |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 214: | Line 176: | ||
{| style="text-align: left; margin:auto;width: 100%;" | {| style="text-align: left; margin:auto;width: 100%;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | <math> | + | | style="text-align: center;" | <math>minimize \quad f\mathbf{(x)}, \quad \mathbf{x} = [x_1, x_2, \dots , x_n] </math> |
|} | |} | ||
| style="width: 5px;text-align: right;white-space: nowrap;" | (1) | | style="width: 5px;text-align: right;white-space: nowrap;" | (1) | ||
| Line 226: | Line 188: | ||
{| style="text-align: left; margin:auto;width: 100%;" | {| style="text-align: left; margin:auto;width: 100%;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | <math>lb_i \leq x_i \leq ub_i \quad for i = 1,2, \dots , n </math> | + | | style="text-align: center;" | <math>lb_i \leq x_i \leq ub_i \quad for \quad i = 1,2, \dots , n </math> |
|} | |} | ||
| style="width: 5px;text-align: right;white-space: nowrap;" | (2) | | style="width: 5px;text-align: right;white-space: nowrap;" | (2) | ||
| Line 233: | Line 195: | ||
There <math display="inline">lb</math> and <math display="inline">ub</math> represents the lower and upper bound limit, respectively. The global optimization is referred to find the set of <math display="inline">\mathbf{x}</math> that minimize <math display="inline">f\mathbf{(x)}</math> over the entire feasible region. The problem is harder as the dimension <math display="inline">n</math> increases and, in cases when the behaviour of the objective function is unknown, is not possible to be certain whether one has found the true global optimum. | There <math display="inline">lb</math> and <math display="inline">ub</math> represents the lower and upper bound limit, respectively. The global optimization is referred to find the set of <math display="inline">\mathbf{x}</math> that minimize <math display="inline">f\mathbf{(x)}</math> over the entire feasible region. The problem is harder as the dimension <math display="inline">n</math> increases and, in cases when the behaviour of the objective function is unknown, is not possible to be certain whether one has found the true global optimum. | ||
| − | Several global optimization algorithms were developed that are more or less efficient, depending on the behaviour of the problem. In this paper, the Multi Level Single Linkage (MLSL) algorithm for global optimization from the NLopt library, (Johnson 2020), is used for the damage detection problem. It consist of a sequence of local optimizations starting from random points, proposed by Rinnooy Kan & Timmer (1987a), (1987b). An alternative implementation is applied | + | Several global optimization algorithms were developed that are more or less efficient, depending on the behaviour of the problem. In this paper, the Multi Level Single Linkage (MLSL) algorithm for global optimization from the NLopt library, (Johnson 2020), is used for the damage detection problem. It consist of a sequence of local optimizations starting from random points, proposed by Rinnooy Kan & Timmer (1987a), (1987b). An alternative implementation is applied and it uses a Sobol low discrepancy sequence as starting points, instead of random numbers, providing more accurate results, practically and theoretically guaranteed. This application was presented by Kucherenko & Sytsko (2005). The local optimization is carried out by the derivative - free and bound - constrained BOBYQUA local optimizer. This algorithm was presented by Powell (2009). It consist of a quadratic approximation of the objective function, constructed iteratively. |
===4.2 Design variables=== | ===4.2 Design variables=== | ||
| Line 261: | Line 223: | ||
| <math>\mathbf{E}</math> [MPa] | | <math>\mathbf{E}</math> [MPa] | ||
|- style="border-top: 2px solid;" | |- style="border-top: 2px solid;" | ||
| − | | 0 | + | | <math>0 </math> |
| − | | | + | | <math>73\,100</math> |
| − | | | + | | <math>3\,350</math> |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 0.5 | + | | <math>0.5 </math> |
| − | | | + | | <math>36\,600</math> |
| − | | | + | | <math>1\,725</math> |
|- style="border-bottom: 2px solid;" | |- style="border-bottom: 2px solid;" | ||
| − | | 1 | + | | <math>1 </math> |
| − | | 100 | + | | <math>100</math> |
| − | | 100 | + | | <math>100</math> |
|} | |} | ||
| − | At first, a simpler scenario is evaluated, where are only <math display="inline">10</math> design variables. Each one of these represents the <math display="inline">3</math> layers with <math display="inline">0^{\circ }</math> fibre orientation of <math display="inline">1</math> zone in the structure | + | At first, a simpler scenario is evaluated, where are only <math display="inline">10</math> design variables. Each one of these represents the <math display="inline">3</math> layers with <math display="inline">0^{\circ }</math> fibre orientation of <math display="inline">1</math> zone in the structure, see Fig. 1. If, for example, the design variable <math display="inline">x_7 = 1</math>, it implies that the <math display="inline">3</math> layers <math display="inline">0^{\circ }</math> in zone <math display="inline">7</math> are damaged, so it's Young's modulus is equal to <math display="inline">100 MPa</math>. The damaged case, described in Section 2.4, is represented by the vector of Eq. 4.<span id="eq-4"></span> |
{| class="formulaSCP" style="width: 100%; text-align: left;" | {| class="formulaSCP" style="width: 100%; text-align: left;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 281: | Line 243: | ||
{| style="text-align: left; margin:auto;width: 100%;" | {| style="text-align: left; margin:auto;width: 100%;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | <math> | + | | style="text-align: center;" | <math>\mathbf{x} = [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0] </math> |
|} | |} | ||
| style="width: 5px;text-align: right;white-space: nowrap;" | (4) | | style="width: 5px;text-align: right;white-space: nowrap;" | (4) | ||
| Line 292: | Line 254: | ||
{| style="text-align: left; margin:auto;width: 100%;" | {| style="text-align: left; margin:auto;width: 100%;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | <math> | + | | style="text-align: center;" | <math>x_5 = 1.0, \quad x_{25} = 1.0, \quad x_{45} = 1.0 </math> |
|} | |} | ||
| style="width: 5px;text-align: right;white-space: nowrap;" | (5) | | style="width: 5px;text-align: right;white-space: nowrap;" | (5) | ||
| Line 307: | Line 269: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | In this paper Eigenfrequencies Method is used. The natural frequencies of the structure are very sensitive to the damage and it is easy to implement a monitoring system, thus is widely used. The variations in the frequencies and which mode is more or less affected depends on the position and severity of the damage. But it represents the global behavior of the structure, since doesn't use spatial information. The proposed objective function is Eq. 6.<span id="eq-6"></span> | + | In this paper the Eigenfrequencies Method is used. The natural frequencies of the structure are very sensitive to the damage and it is easy to implement a monitoring system, thus is widely used. The variations in the frequencies and which mode is more or less affected depends on the position and severity of the damage. But it represents the global behavior of the structure, since doesn't use spatial information. The proposed objective function is Eq. 6.<span id="eq-6"></span> |
{| class="formulaSCP" style="width: 100%; text-align: left;" | {| class="formulaSCP" style="width: 100%; text-align: left;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 344: | Line 306: | ||
In the first scenario, with <math display="inline">10</math> design variables as explained before, the optimization process is set up with a limit of <math display="inline">1\,000</math> evaluations. In that range, the algorithm found a minimum in the evaluation <math display="inline">255</math>, with an objective function value of <math display="inline">0.088</math>. The evolution of the objective function value is shown in Fig. 6. | In the first scenario, with <math display="inline">10</math> design variables as explained before, the optimization process is set up with a limit of <math display="inline">1\,000</math> evaluations. In that range, the algorithm found a minimum in the evaluation <math display="inline">255</math>, with an objective function value of <math display="inline">0.088</math>. The evolution of the objective function value is shown in Fig. 6. | ||
| − | The design variables | + | The design variables corresponding with the obtained minimum are listed in Eq. 9 and plotted in the histogram of Fig. 6. Except for minimal differences in zones <math display="inline">2</math> and <math display="inline">10</math> (less than <math display="inline">2 %</math>), the obtained structure and the damaged case are equal, so the damage is found.<span id="eq-9"></span> |
{| class="formulaSCP" style="width: 100%; text-align: left;" | {| class="formulaSCP" style="width: 100%; text-align: left;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 350: | Line 312: | ||
{| style="text-align: left; margin:auto;width: 100%;" | {| style="text-align: left; margin:auto;width: 100%;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="text-align: center;" | <math> | + | | style="text-align: center;" | <math>\mathbf{x}_{res} = [0.000, 0.020, 0.000, 0.000, 0.998, 0.000, 0.000, 0.000, 0.000, 0,019]</math> |
| style="width: 5px;text-align: right;white-space: nowrap;" | (9) | | style="width: 5px;text-align: right;white-space: nowrap;" | (9) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | In the <math display="inline">60</math> design variables scenario, the optimization is limited to <math display="inline">3\,500</math> evaluations. In this scenario the minimum value of the objective function was found in the evaluation <math display="inline">2\,801</math>, with an objective function value of <math display="inline">1.148</math>. The evolution of this function and the histogram representing the best sample found are shown in Fig. 7. | + | In the <math display="inline">60</math> design variables scenario, the optimization is limited to <math display="inline">3\,500</math> evaluations. In this scenario the minimum value of the objective function was found in the evaluation <math display="inline">2\,801</math>, with an objective function value of <math display="inline">1.148</math>. Although this value is bigger than the obtained before, is acceptable, due the problem is harder to solve. The evolution of this function and the histogram representing the best sample found are shown in Fig. 7. |
{| class="floating_imageSCP" style="text-align: center; border: 1px solid #BBB; margin: 1em auto; width: 100%;max-width: 100%;" | {| class="floating_imageSCP" style="text-align: center; border: 1px solid #BBB; margin: 1em auto; width: 100%;max-width: 100%;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 372: | Line 332: | ||
In this paper a numerical model of offshore windmill FRP tower is presented and its dynamic behaviour is characterized by its natural frequencies and modal shapes. A reference damaged case of the tower is analysed. The sensitivity to damage of the natural vibration frequencies of the structure has been verified. | In this paper a numerical model of offshore windmill FRP tower is presented and its dynamic behaviour is characterized by its natural frequencies and modal shapes. A reference damaged case of the tower is analysed. The sensitivity to damage of the natural vibration frequencies of the structure has been verified. | ||
| − | Also, a damage detection method is presented, based on optimization algorithms and model updating techniques. This method includes detection, localization and extension of the damage. Based on the comparison of the natural frequencies, <math display="inline">2</math> cases are evaluated with different space discretization. | + | Also, a damage detection method is presented, based on optimization algorithms and model updating techniques. This method includes detection, localization and extension of the damage. Based on the comparison of the natural frequencies, <math display="inline">2</math> cases are evaluated with different space discretization. One with the structure divided into <math display="inline">10</math> zones to apply damage, while in the second scenario into <math display="inline">60</math> zones. In both, satisfactory results were obtained. Its demonstrated that the proposed damage detection method could be used in SHM process for this kind of structures. These monitoring strategies periodically evaluates possibles structural damages, improving the operational safety of the structure and reducing its maintenance costs. |
==6 Acknowledgments== | ==6 Acknowledgments== | ||
| Line 389: | Line 349: | ||
Kucherenko, S. & Y. Sytsko (2005). Application of Deterministic Low-Discrepancy Sequences in Global Optimization. Computational Optimization and Applications 30, 297–318. | Kucherenko, S. & Y. Sytsko (2005). Application of Deterministic Low-Discrepancy Sequences in Global Optimization. Computational Optimization and Applications 30, 297–318. | ||
| − | Martinez, X., S. Oller, F. Rastellini, & A. Barbat (2008). A numerical procedure simulating RC structures reinforced with FRP using the serial/parallel mixing theory. Computers and | + | Martinez, X., S. Oller, F. Rastellini, & A. Barbat (2008). A numerical procedure simulating RC structures reinforced with FRP using the serial/parallel mixing theory. Computers and Structures 86, 1604–1618. |
| − | + | ||
| − | Structures 86, 1604–1618. | + | |
Powell, M. (2009). The BOBYQA Algorithm for Bound Constrained Optimization without Derivatives. Technical report, Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics. | Powell, M. (2009). The BOBYQA Algorithm for Bound Constrained Optimization without Derivatives. Technical report, Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics. | ||
Latest revision as of 13:30, 11 June 2022
1 INTRODUCTION
Offshore renewable energy is a cornerstone of the clean energy transition in the EU. It consists of many different sources that are abundant, natural and clean, obtaining energy from wind, wave and tidal. This can be harnessed by modern technologies without emitting any greenhouse gases, (European Commission 2020). There is no doubt that the offshore renewable energy exploitation has a large potential to grow. However, the open sea is a very aggressive environment, which may largely affect the maintenance costs of the installations and therefore the overall cost of offshore energy generation. The owners of offshore assets are aware of that and are paying a steep price. A massive amount of steel goes into those assets, and all this metal is subject to degradation, which explains why corrosion accounts for approximately 60% of offshore maintenance costs. In order to address this problem, the main objective of the EU H2020 952966 FIBREGY project, (EU 2023), is enabling the extensive use of FRP materials in the structure of the next generation of large Offshore Wind and Tidal Power (OWTP) platforms, due to the convenient immunity to corrosion and superior fatigue performance of these materials. Another innovative aspect that will be considered is the use of multifunctional FRP materials in the OWTP structure, by embedding sensors in the material for continuous SHM.
During FIBREGY project, a scale (1:50) of an FRP tower with an embedded SHM system will be tested. In this paper, a dynamic numerical analysis of this scaled structure is carried out. A FEM is made and analysed to obtain its dynamic behaviour, characterized by frequencies and modal shapes. Also, a model updating and optimization based damage detection method is proposed for this structure and tested using a numerical damaged scenario.
2 Numerical Model
2.1 Geometry
The structure under study is a cone with the following geometric characteristics, showed in Fig. 1. The bottom face of the tower is fully fixed (displacement in x, y and z).
- Height:
- Bottom external diameter:
- Top external diameter:
- Thickness:
The tower is divided into sectors in its height (x axis) and in layers evenly distributed in the thickness, in correspondence with the laminate that forms it, resulting in volumes.
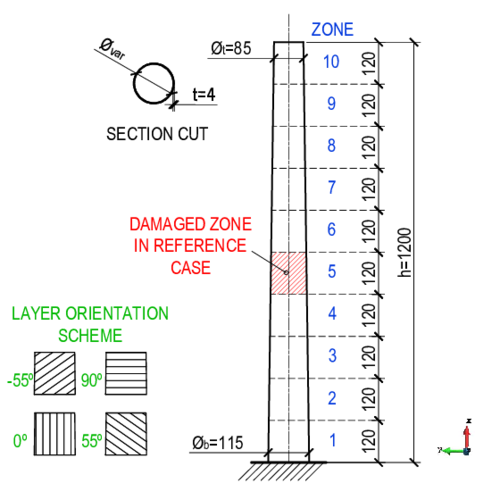
|
| Figure 1: Geometry of the analysed tower, dimensions in mm. |
The FEM design is done with GiD,(CIMNE 2020), a pre and post processor for numerical simulations in science and engineering. The structure is discretized in nodes and hexahedra linear elements and, as it is shown in Fig. 2.

|
| Figure 2: Numerical model discretization |
2.2 Material
The FRP used in the scaled tower is composed of a vinylester based resin with glass fibre reinforcement, with a of fibre volume fraction. The main characteristics are listed in Tab 1. The composite has layers of unidirectional fibres in the following orientations, from external to internal layer: [], angles from the axis of the tower, see Fig. 1. .
| Material | Young's Modulus | Poisson | Density |
| E (MPa) | |||
| Resin | |||
| Fibre |
2.3 Numerical Analysis
A dynamic analysis of the model is done using an in-house multi-physics FEM code, FEMUSS, developed by the International Centre for Numerical Methods in Engineering (CIMNE) and the Polytechnical University of Catalunya (UPC). The different orthotropic composite layers, are treated using the Serial-Parallel mixing theory, (Martinez, et al. 2008).
2.4 Damaged Case
A reference damaged tower is proposed to observe changes in the dynamic behaviour of the model and to use its modal frequencies as input data in the damage detection method. Numerically, the damaged is represented by a reduction of the Young's Modulus of both materials, fibre and resin, in layers , , and (zero degree fibre orientation layers of the laminate), to in the sector of the tower, as shown in Fig. 1.
3 Dynamic behaviour
The embedded SHM system that is going to be used in tests allows up to of sampling rate. In consequence, the analysis is limited to , the half of the sampling rate value, corresponding to the Nyquist frequency. This value defines the bandwith by Fourier transform based analysis.
In this range, modes were found. The frequency values obtained in the analysis of the undamaged scenario and the described damaged reference case, are listed and compared in Tab. 2. Due to the rotational symmetry of the structure, modes 1-2, 3-4 and 6-7 have almost the same values between them, but not equal because the asymmetry in the fibre's orientation. These are flexural modes, while mode 5 is expansive, as is shown in Figs. 3 and 4. There, dark blue colour represents no displacement, red biggest displacement.
| Mode | Main | Undamaged | Damaged | |
| Direction | Case | Case | ||
| 1 | Z | 43.16 | 37.97 | 12.02 |
| 2 | Y | 43.34 | 38.07 | 12.14 |
| 3 | Z | 209.12 | 177.76 | 14.99 |
| 4 | Y | 209.82 | 178.49 | 14.93 |
| 5 | - | 292.47 | 279.26 | 4.51 |
| 6 | Z | 488.72 | 470.05 | 3.81 |
| 7 | Y | 489.78 | 470.93 | 3.84 |
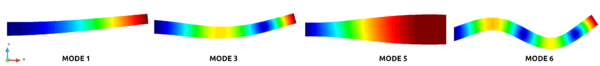
|
| Figure 3: Modal shapes of selected modes in undamaged tower. |
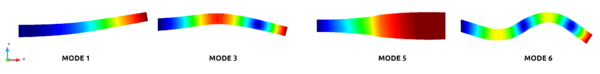
|
| Figure 4: Modal shapes of selected modes in reference damaged tower. |
The first modes are more affected for the damage, with changes in frequencies above , than the last 3 modes analysed. That is because the damage is located close to a nodal point of the modal shape in modes and and minimally affects the pressure stiffness, observed in mode .
From this analysis is concluded that the frequencies are sensitive to the damage and its location is related to the more affected modes. So, this parameter can be used in a damage detection method.
4 Damage detection
In this paper, structural damage is detected using changes in the natural frequencies. The method is a FEM updating based, that consist in modifying the mass, stiffness and damping parameters of the numerical model to match the behaviour in the model as in the test. To find it, an optimization algorithm is used, described in section 4.1. The problem is converted to a minimization of an objective function , where are the design variables, in this case the Young modulus of different volumes of the FEM. The basic scheme of the method is illustrated in Fig. 5, where is the vector of natural frequencies.
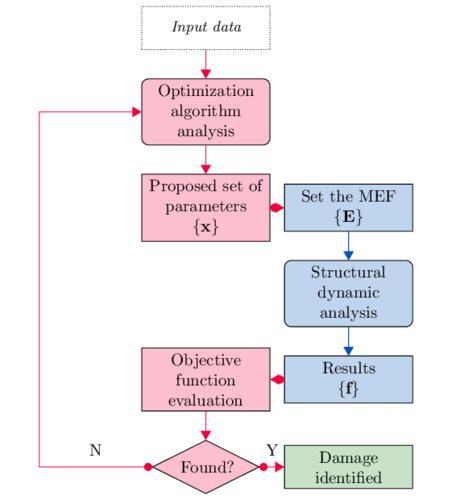
|
| Figure 5: Damage detection method scheme |
Several interfaces have been developed to couple the optimization algorithm with the structural analysis software. For example, to convert the proposed numerical design variables by the optimizer in an valid analysable FEM by FEMUSS, other to read the results of the dynamic analysis and evaluate the objective function.
4.1 Optimization
The general optimization problem can be formulated as solving the function:
|
|
(1) |
Where is the objective function, is the dimension of the problem and are the design variables. These may be subject to constraints in order to preserve physical sense.
|
|
(2) |
There and represents the lower and upper bound limit, respectively. The global optimization is referred to find the set of that minimize over the entire feasible region. The problem is harder as the dimension increases and, in cases when the behaviour of the objective function is unknown, is not possible to be certain whether one has found the true global optimum.
Several global optimization algorithms were developed that are more or less efficient, depending on the behaviour of the problem. In this paper, the Multi Level Single Linkage (MLSL) algorithm for global optimization from the NLopt library, (Johnson 2020), is used for the damage detection problem. It consist of a sequence of local optimizations starting from random points, proposed by Rinnooy Kan & Timmer (1987a), (1987b). An alternative implementation is applied and it uses a Sobol low discrepancy sequence as starting points, instead of random numbers, providing more accurate results, practically and theoretically guaranteed. This application was presented by Kucherenko & Sytsko (2005). The local optimization is carried out by the derivative - free and bound - constrained BOBYQUA local optimizer. This algorithm was presented by Powell (2009). It consist of a quadratic approximation of the objective function, constructed iteratively.
4.2 Design variables
In this numerical case, the design variables represent changes in the Young's modulus of the materials that are in the composite, fibre and resin. These variables can take any value between and .
|
|
(3) |
The zero value represents no damage, so the remains unalterable, with the values listed in Tab. 1. A value of one, represents fully damaged, to avoid convergence problems in the numerical analysis, the is reduced to for both, the resin and the fibre. Intermediate values are linearly interpolated, as shown in Tab. 3, with .
| Fibre | Resin | |
| [MPa] | [MPa] | |
At first, a simpler scenario is evaluated, where are only design variables. Each one of these represents the layers with fibre orientation of zone in the structure, see Fig. 1. If, for example, the design variable , it implies that the layers in zone are damaged, so it's Young's modulus is equal to . The damaged case, described in Section 2.4, is represented by the vector of Eq. 4.
|
|
(4) |
Another scenario is considered, with design variables. These are correlated with the material properties of each one of the volumes that the structure is divided. So, first variables represent the external layer, of fibre orientation, in the different zones. From to , the second layer, of fibre orientation, and so on for the following variables. The damaged case, described in Section 2.4, is represented by all values equal to , except the listed in Eq. 5.
|
|
(5) |
4.3 Objective function
The aim of the optimization process is to obtain the set of variables which minimize the objective function, Eq. 1. The success of the process depends on the correct behaviour of this function. This function must compare measurable values of a damaged structure (reference - ref), with the results of a proposed by the optimizer model of the structure (evaluation - ev).
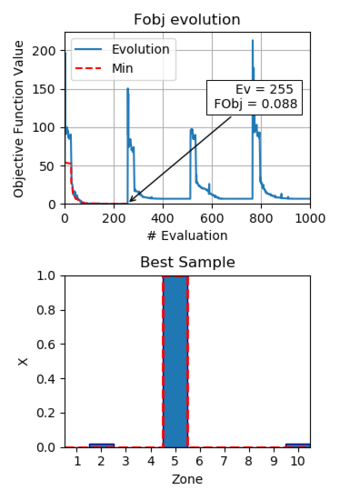
|
| Figure 6: Results optimization with design variables |
In this paper the Eigenfrequencies Method is used. The natural frequencies of the structure are very sensitive to the damage and it is easy to implement a monitoring system, thus is widely used. The variations in the frequencies and which mode is more or less affected depends on the position and severity of the damage. But it represents the global behavior of the structure, since doesn't use spatial information. The proposed objective function is Eq. 6.
|
|
(6) |
|
|
(7) |
|
|
(8) |
Where and are vectors of the first natural frequencies of the reference damaged structure and the results of the evaluation, respectively. This function is and is the global minimum when the vectors are equal, so the structure proposed and the damaged case matches.
4.4 Results
In the first scenario, with design variables as explained before, the optimization process is set up with a limit of evaluations. In that range, the algorithm found a minimum in the evaluation , with an objective function value of . The evolution of the objective function value is shown in Fig. 6.
The design variables corresponding with the obtained minimum are listed in Eq. 9 and plotted in the histogram of Fig. 6. Except for minimal differences in zones and (less than ), the obtained structure and the damaged case are equal, so the damage is found.
|
In the design variables scenario, the optimization is limited to evaluations. In this scenario the minimum value of the objective function was found in the evaluation , with an objective function value of . Although this value is bigger than the obtained before, is acceptable, due the problem is harder to solve. The evolution of this function and the histogram representing the best sample found are shown in Fig. 7.
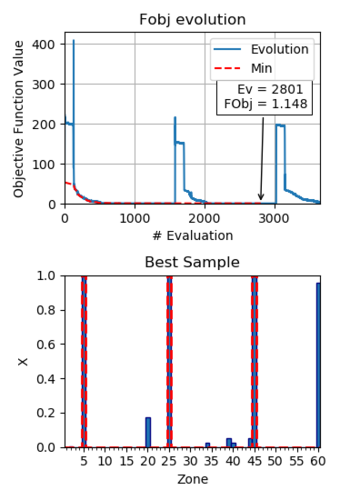
|
| Figure 7: Results optimization with design variables |
The damage in zones , and of the reference damaged case are well captured, but, there are also significant damage values in zones and , and respectively. The error in the remaining values is negligible, less than . To obtain better results, the optimization algorithm needs more evaluations, but the obtained results can be considered acceptable, considering the difficulty of the problem.
5 Conclusions
In this paper a numerical model of offshore windmill FRP tower is presented and its dynamic behaviour is characterized by its natural frequencies and modal shapes. A reference damaged case of the tower is analysed. The sensitivity to damage of the natural vibration frequencies of the structure has been verified.
Also, a damage detection method is presented, based on optimization algorithms and model updating techniques. This method includes detection, localization and extension of the damage. Based on the comparison of the natural frequencies, cases are evaluated with different space discretization. One with the structure divided into zones to apply damage, while in the second scenario into zones. In both, satisfactory results were obtained. Its demonstrated that the proposed damage detection method could be used in SHM process for this kind of structures. These monitoring strategies periodically evaluates possibles structural damages, improving the operational safety of the structure and reducing its maintenance costs.
6 Acknowledgments
The founding of FIBREGY, “Development, engineering, production and life-cycle management of improved FIBRE-based material solutions for structure and functional components of large offshore wind enerGY and tidal power platform” an H2020 project under agreement 952966 is gratefully acknowledged.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
CIMNE (2020, Sep. 30, 2020). GiD. https://www.gidhome.com.
EU (2021-2023). H2020 952966 FIBREGY - Development, engineering, production and life-cycle management of improved FIBRE-based material solutions for structure and functional components of large offshore wind enerGY and tidal power platform. https://fibregy.eu/.
European Commission (2020). An eu strategy to harness the potential of offshore renewable energy for a climate neutral future. Technical report, Commision to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the regiions. https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legalcontent/EN/TXT/?uri=COM:2020:741:FIN&qid=1605792629666.
Johnson, S. G. (2020, Sep. 30, 2020). NLopt - the NonLinear - optimization package. http://github.com/stevengj/nlopt.
Kucherenko, S. & Y. Sytsko (2005). Application of Deterministic Low-Discrepancy Sequences in Global Optimization. Computational Optimization and Applications 30, 297–318.
Martinez, X., S. Oller, F. Rastellini, & A. Barbat (2008). A numerical procedure simulating RC structures reinforced with FRP using the serial/parallel mixing theory. Computers and Structures 86, 1604–1618.
Powell, M. (2009). The BOBYQA Algorithm for Bound Constrained Optimization without Derivatives. Technical report, Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics.
Rinnooy Kan, A. H. G. & G. T. Timmer (1987a). Stochastic global optimization methods part I: Clustering methods. Mathematical Programming 39, 27–56.
Rinnooy Kan, A. H. G. & G. T. Timmer (1987b). Stochastic global optimization methods part II: Multi level methods. Mathematical Programming 39, 57–78.
Document information
Published on 16/10/22
Accepted on 11/06/22
Submitted on 20/05/22
Volume 07 - COMUNICACIONES MATCOMP21 (2022), Issue Núm. 2 - Aplicaciones Industriales - Caracterización, 2022
DOI: 10.23967/r.matcomp.2022.10.011
Licence: Other