(→3. Methodology) |
(→4. Validity) |
||
| (22 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
One of the most common methods of strengthening concrete structures is the use of composite fibers such as FRP. These fibers have found a special place in structural retrofitting methods due to a number of specific ability including lightness and ease of performance. Reinforced concrete structures have long been considered by design engineers for the possibility of retrofitting high strength composite steel structures. In this study, twenty-two steel beam models were modeled by ANSYS software. Variable parameters studied in the modeled steel beams can be referred to the number, orientation and thickness of composite layers. | One of the most common methods of strengthening concrete structures is the use of composite fibers such as FRP. These fibers have found a special place in structural retrofitting methods due to a number of specific ability including lightness and ease of performance. Reinforced concrete structures have long been considered by design engineers for the possibility of retrofitting high strength composite steel structures. In this study, twenty-two steel beam models were modeled by ANSYS software. Variable parameters studied in the modeled steel beams can be referred to the number, orientation and thickness of composite layers. | ||
| − | '''Keywords:''' Steel beams, CFRP, unidirectional and bi-directional, bending stress | + | '''Keywords:''' Steel beams, CFRP, unidirectional and bi-directional, bending stress |
==1. Introduction== | ==1. Introduction== | ||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
==2. Materials properties== | ==2. Materials properties== | ||
| − | ===2.1 | + | ===2.1 Steel beam=== |
In this research, steel beams with geometrical and technical properties as shown in [[#img-2|Figure 2]] and in [[#tab-1|Table 1]] are used as follows. | In this research, steel beams with geometrical and technical properties as shown in [[#img-2|Figure 2]] and in [[#tab-1|Table 1]] are used as follows. | ||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="margin: 1em auto 0.1em auto;border-collapse: collapse;font-size:85%;width:auto;" | {| class="wikitable" style="margin: 1em auto 0.1em auto;border-collapse: collapse;font-size:85%;width:auto;" | ||
|-style="text-align:center" | |-style="text-align:center" | ||
| − | + | ! l !! h !! b !! t !! E !! F<sub>y</sub> !! F<sub>u</sub> !!ɣ !! S<sub>X</sub> !! I<sub>X</sub> !! g | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="text-align: center;"|600 | | style="text-align: center;"|600 | ||
| Line 90: | Line 80: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | ===2.2 Composite fibers=== | |
| − | ===2.2 | + | |
In this study, based on the information available in Journal 345 of deputy of planning and strategic oversight of the President [11] and research by Reddy [12], the high-strength carbon composite properties available in [[#tab-2|Table 2]] are used as follows. | In this study, based on the information available in Journal 345 of deputy of planning and strategic oversight of the President [11] and research by Reddy [12], the high-strength carbon composite properties available in [[#tab-2|Table 2]] are used as follows. | ||
| Line 100: | Line 89: | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="margin: 1em auto 0.1em auto;border-collapse: collapse;font-size:85%;width:auto;" | {| class="wikitable" style="margin: 1em auto 0.1em auto;border-collapse: collapse;font-size:85%;width:auto;" | ||
|-style="text-align:center" | |-style="text-align:center" | ||
| − | + | ! '''E''' !! '''ƃ''' !! '''Ɣ''' !! '''µ''' | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|1.4e6 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|5430 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|1.9e-3 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|0.2 |
|} | |} | ||
| Line 115: | Line 101: | ||
In this research, the results of bending stresses are investigated using the relation between theory and software modeling. | In this research, the results of bending stresses are investigated using the relation between theory and software modeling. | ||
| − | ===3.1 | + | ===3.1 Theory relationship=== |
In one study, Benati et al. [13] compute bearing capacity enhancements of steel beams reinforced by FRP-prestressed fiber. In this study, steel beams with conventional IPE sections were reinforced with FRP polymeric composite strips, which eventually bearing capacity of mentioned sections were investigated in two plastic and elastic states. Equation (1) indicates the flexural stresses caused by gravity loads in the presence of composite fibers in the beams: | In one study, Benati et al. [13] compute bearing capacity enhancements of steel beams reinforced by FRP-prestressed fiber. In this study, steel beams with conventional IPE sections were reinforced with FRP polymeric composite strips, which eventually bearing capacity of mentioned sections were investigated in two plastic and elastic states. Equation (1) indicates the flexural stresses caused by gravity loads in the presence of composite fibers in the beams: | ||
| Line 143: | Line 129: | ||
{| style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;margin:auto;width: 100%;" | {| style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;margin:auto;width: 100%;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | <math>{g}_{2}=min\left| \begin{matrix}\frac{1}{8}\ast \left( {g}_{1}+{g}_{2}\right) \ast (2L{)}^{2}\leq 0.33\ast Fy\ast Sx\\\frac{5}{384}\ast \left( \frac{{g}_{1}+{g}_{2}}{E\ast I}\right) \ast (2L{)}^{4}\leq \frac{1}{800}\ast (2L)\end{matrix}\right.</math> | + | | <math>{g}_{2}=min\left| \begin{matrix}\displaystyle\frac{1}{8}\ast \left( {g}_{1}+{g}_{2}\right) \ast (2L{)}^{2}\leq 0.33\ast Fy\ast Sx\\ \displaystyle\frac{5}{384}\ast \left( \displaystyle\frac{{g}_{1}+{g}_{2}}{E\ast I}\right) \ast (2L{)}^{4}\leq \displaystyle\frac{1}{800}\ast (2L)\end{matrix}\right.</math> |
|} | |} | ||
| style="text-align: right;vertical-align: center;width: 5px;text-align: right;white-space: nowrap;"|(3) | | style="text-align: right;vertical-align: center;width: 5px;text-align: right;white-space: nowrap;"|(3) | ||
| Line 150: | Line 136: | ||
It is noteworthy that in the aforementioned relationships, <math>A_f</math> is steel beam compression wing area, <math>A_{cfrp}</math> is cross-sectional area of composite sheet, <math>F_{fk}</math> is tensile stress value due to composite fibers, and <math display="inline">{\gamma}_{f}</math> is the relationship coefficient value as shown in Eq.(2). | It is noteworthy that in the aforementioned relationships, <math>A_f</math> is steel beam compression wing area, <math>A_{cfrp}</math> is cross-sectional area of composite sheet, <math>F_{fk}</math> is tensile stress value due to composite fibers, and <math display="inline">{\gamma}_{f}</math> is the relationship coefficient value as shown in Eq.(2). | ||
| − | ==3.2 | + | ===3.2 Software modeling=== |
| − | + | Today, with the advent of computer science, the accuracy of specialized software computing has increased dramatically. ANSYS software is one of the good soft wares that is used in engineering analysis such as structure and mechanics. | |
| − | + | This software is finite element software that aims at analyzing the modeling. In this software, the basis of solving equations is to split the model into smaller elements. These types of elements can be structural, thermal, or other, depending on the number of degrees of freedom and the type of analysis method. One of the methods of analysis in this software is static nonlinear analysis. There are various ways to analyze nonlinear equations in this method, including Newton-Raphson iterative method. The basis of using a nonlinear static method is that the software gradually increases the amount of load until the structure reaches a failure and instability boundary and it is noteworthy that the convergence of the solutions obtained by this method is activated by automatic time step algorithm. | |
| − | =4. Validity= | + | ==4. Validity== |
| − | + | To evaluate the validity of the software model used in this study, the stress values obtained by software for steel beam model with unidirectional carbon fiber with 1mm thickness are compared with theoretical relationship in Section 3 that is described in equations (4) to (6): | |
| − | {| style="width: 100%; | + | {| class="formulaSCP" style="width: 100%; text-align: left;" |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | |
| + | {| style="text-align: center; margin:auto;width: 100%;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | style="text-align: center;" |<math>g_2 =\min\left| \begin{matrix}\displaystyle\frac{1}{8}\ast \left( 0.361+{g}_{2}\right) \ast (2\ast 600{)}^{2}<0.33\ast 2400\ast 429\\\displaystyle\frac{5}{384}\ast \left( \frac{0.361+{g}_{2}}{2\ast {10}^{6}\ast 5790}\right) \ast (2\ast 600{)}^{4}\leq \displaystyle\frac{1}{800}\ast \left( 2\ast 600\right) \quad \quad \quad \end{matrix}\right.\rightarrow {g}_{2}= 0.282</math> |
| + | |} | ||
| + | | style="width: 5px;text-align: right;white-space: nowrap;" |(4) | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="formulaSCP" style="width: 100%; text-align: left;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | |
| + | {| style="text-align: center; margin:auto;width: 100%;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | style="text-align: center;" | <math display="inline">p=0.5\ast \displaystyle\frac{5430}{1.1}\ast 13.5\ast 0.1=3331.05</math> |
| + | |} | ||
| + | | style="width: 5px;text-align: right;white-space: nowrap;" |(5) | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | {| class="formulaSCP" style="width: 100%; text-align: left;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | {| style="text-align: center; margin:auto;width: 100%;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="text-align: center;" | <math>{\sigma }^{\mp }=\frac{-3332.05}{\left( 13.5\ast 1.02\right) }\mp \frac{\left( 0.361+0.282\right) \ast {600}^{2}-3332.05\ast 27}{429}\ast 0.5</math> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | | style="width: 5px;text-align: right;white-space: nowrap;" |(6) | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | {| class="formulaSCP" style="width: 100%; text-align: left;" | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | |
| − | | | + | {| style="text-align: center; margin:auto;width: 100%;" |
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | style="text-align: center;" | <math>{\sigma }^{\mp }=-241.98\mp 164.94=\left| \begin{matrix}-77.04\, \, O.K.\\+406.92\quad N.G\end{matrix}\right.</math> |
| − | | | + | |} |
| − | | | + | |
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | In this section and slight difference in [[#tab-3|Table 3]] shows the validity of the software analysis. | |
| − | == | + | <div class="center" style="font-size: 75%;">'''Table 3'''. Validation of software modeling results</div> |
| − | < | + | <div id='tab-3'></div> |
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" style="margin: 1em auto 0.1em auto;border-collapse: collapse;font-size:85%;width:auto;" | |
| − | {| style=" | + | |-style="text-align:center" |
| + | ! Theory bending stress !! Software bending stress !! Changing ratio | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|77.04 |
| − | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|77 | |
| − | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|0.5% | |
|} | |} | ||
| + | ==5. Results and discussion== | ||
| − | + | ===5.1 Numerical results of reinforced steel beam by one to three unidirectional CFRP composite layers=== | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | The specimens modeled in software with the results extracted from the presence of one to three unidirectional composite layers are described in [[#tab-4|Table 4]], as shown in the results, the highest and the lowest increase in bending stress compared to the first model (one unidirectional composite layer with 1mm thickness) is equal to 155% and 45% respectively. As shown in [[#img-3|Figures 3]] and [[#img-4|4]], increasing the thickness of composite fibers in unidirectional state decreases the flexural stress values due to the gravity loading of reinforced steel beams. | |
| − | | | + | |
| + | <div class="center" style="font-size: 75%;">'''Table 4'''. Numerical results of reinforced steel beam by one to three unidirectional CFRP composite layers</div> | ||
| − | <div | + | <div id='tab-1'></div> |
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" style="margin: 1em auto 0.1em auto;border-collapse: collapse;font-size:85%;width:auto;" | |
| − | + | |-style="text-align:center" | |
| − | {| style=" | + | ! '''Models NO''' !! '''Layers NO''' !! '''Layer Thickness''' !! '''Angle Degree''' !! '''Bending Stress'''!! '''Increasing Ratio''' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|1 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|1 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|0.1 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|0 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|77 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|0 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|2 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|1 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|0.125 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|0 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|126 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|63% |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|3 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|1 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|0.15 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|0 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|168 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|118% |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|4 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|1 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|0.2 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|0 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|196 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|155% |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|5 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|1 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|0.3 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|0 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|168 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|118% |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|6 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|1 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|0.5 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|0 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|133 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|73% |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|7 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|2 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|0.1 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|0,0 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|140 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|82% |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|8 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|2 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|0.15 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|0,0 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|182 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|136% |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|9 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|2 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|0.1 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|90,0 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|77 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|0% |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|10 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|3 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|0.15 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|90,0 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|112 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|45% |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|11 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|3 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|0.1 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|0,0,0 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|182 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|136% |
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <div id='img-3'></div> | ||
| + | {| style="text-align: center; border: 1px solid #BBB; margin: 1em auto; width: auto;max-width: auto;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |style="padding:10px;"| [[Image:Review_684227244602-chart1.svg|354px]] |
| − | + | |- style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;" | |
| − | | | + | | colspan="1" style="padding:10px;"| '''Figure 3'''. The Results of bending stress in reinforced steel beam by unidirectional composite layer due to increased layer thickness |
| − | + | ||
| − | | | + | |
| − | + | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | < | + | <div id='img-4'></div> |
| + | {| style="text-align: center; border: 1px solid #BBB; margin: 1em auto; width: auto;max-width: auto;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |style="padding:10px;"| [[Image:Review_684227244602-chart2.svg|354px]] | ||
| + | |- style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;" | ||
| + | | colspan="1" style="padding:10px;"| '''Figure 4'''. Numerical results of reinforced steel beam by one to three unidirectional CFRP composite layers | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | ===5.2 Numerical results of reinforced steel beam with one to three layers of bi-directional CFRP composite=== | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | The characteristics of the modeled samples in software along with the results obtained from the presence of one to three bi-directional composite layers are presented in [[#tab-5|Table 5]]. The results showed that the highest and lowest increase in bending stress compared to the first model (one unidirectional composite layer with 1mm thickness) is equal 73% and 7% respectively. As illustrated in [[#img-5|Figure 5]], the use of bidirectional fiber in reducing bending stress values is effective than the corresponding bending fibers. As shown in [[#img-6|Figures 6]], changing the angle of the composite fibers improve the flexural stress values only in unidirectional fiber mode. | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="center" style="font-size: 75%;">'''Table 5'''. The numerical results of reinforced steel beam by one to three bi-directional CFRP composite layers</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div id='tab-5'></div> | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" style="margin: 1em auto 0.1em auto;border-collapse: collapse;font-size:85%;width:auto;" | ||
| + | |-style="text-align:center" | ||
| + | ! '''Models NO'''!! '''Layers NO''' !! '''Layer Thickness''' !! '''Angle Degree''' !!'''Bending Stress''' !! '''Increasing Ratio''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|1 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|1 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|0.1 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|0 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|105 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|0 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|2 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|1 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|0.125 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|0 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|31.5 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|-70% |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|3 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|1 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|0.15 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|0 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|77 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|-27% |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|4 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|1 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|0.2 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|0 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|133 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|27% |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|5 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|1 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|0.3 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|0 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|175 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;"|67% |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|6 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|1 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|0.5 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|0 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|182 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|73% |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|7 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|2 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|0.1 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|0,0 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|91 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|-13% |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|8 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|2 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|0.15 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|0,0 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|133 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|27% |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|9 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|2 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|0.1 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|90,0 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|91 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|-13% |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|10 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|3 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|0.15 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|90,0 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|133 |
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|27% |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style=" | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|11 |
| − | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|3 | |
| − | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|0.1 | |
| − | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|0,0,0 | |
| − | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|112 | |
| − | + | | style="text-align: center;vertical-align: top;"|7% | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | | style=" | + | |
| − | | style=" | + | |
| − | | style=" | + | |
| − | | style=" | + | |
| − | | style=" | + | |
|} | |} | ||
| − | {| style=" | + | <div id='img-5'></div> |
| + | {| style="text-align: center; border: 1px solid #BBB; margin: 1em auto; width: auto;max-width: auto;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |style="padding:10px;"| [[Image:Review_684227244602-chart3.svg|354px]] |
| − | + | |- style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;" | |
| − | Figure 5 | + | | colspan="1" style="padding:10px;"| '''Figure 5'''. The effect of number of layers direction on bending stress values of steel beams reinforced by composite fiber |
|} | |} | ||
| − | {| style=" | + | <div id='img-6'></div> |
| + | {| style="text-align: center; border: 1px solid #BBB; margin: 1em auto; width: auto;max-width: auto;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |style="padding:10px;"| [[Image:Review_684227244602-chart4.svg|354px]] |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="padding:10px;"|[[Image:Review_684227244602-chart5.svg|354px]] | ||
| + | |- style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;" | ||
| + | | colspan="1" style="padding:10px;"| '''Figure 6'''. The impact of layers deployment angle on bending stress values of steel beams reinforced by composite <br>fibers in unidirectional & bidirectional stat | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | ==6. Conclusions== | |
| − | + | 1. Increasing the thickness of composite fibers in unidirectional state decreases the flexural stress values due to the gravity loading of reinforced steel beams. However, the conversion of fibers from unidirectional to bi-directional modes has little effect on decreasing the values of bending stresses. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | 2. In the comparison of the numerical results of bending stresses of steel beams reinforced by unidirectional and bidirectional fiber, the use of bidirectional fiber in reducing bending stress values is effective than the corresponding bending fibers. | |
| − | + | 3. Changing the angle of the composite fibers in two-layer mode from zero value in both layers to 90 ° in the first layer and zero value in the second layer improve the flexural stress values only in unidirectional fiber mode. | |
| − | + | 4. By increasing the number of layers from one layer to three layers, in the case of unidirectional composite layers, the use of more layers with less thickness compared to one layer of equal thickness had a better effect on the flexural stress results. While in the bi-directional composite fibers, the use of a thick layer equivalent to the number of thinner layers will have a better effect on the calculated flexural stress results. | |
| − | < | + | ==References== |
| + | <div class="auto" style="text-align: left;width: auto; margin-left: auto; margin-right: auto;font-size: 85%;"> | ||
| − | + | [1] Selvaraj S., Madhavan M., Dongre S.U. Experimental studies on strength and stiffness enhancement in CFRP-strengthened structural steel chanel sections under flexure. J. Compos. Constr., 04016042:1-12, 2016. | |
| − | + | [2] Jun D, Yonghui J., Henghzhong Z. Theoretical and experimental study on notched steel beams strengthened with CFRP plate. Composite Structures, 136:450-459, 2016. | |
| − | + | [3] Zaho X.L., Alam M.I., Fawzia S. Experimental study on FRP-strengthened steel tubular members under lateral impact. J. Compos. Constr., 04017022:1-14, 2017. | |
| − | + | [4] Sweedan M.I., Alhadid M.A., EI-Sawy K.M. Experimental study response of steel beams strengthened with anchored hybrid composites. Thin-Walled Structures, 99:1-11, 2016. | |
| − | + | [5] Wang Z.Y., Zhang N., Wang Q.Y. Tensile behavaiour of open-hole and bolted steel plates reinforced by CFRP strips. Elsevier Composite Part B., 100:101-113, 2016. | |
| − | + | [6] Selvaraj S., Verma R., Sanap V., Madhavan M. Flexural strengthening of structural steel angle sections using CFRP: Experimental investigation. J. Compos. Constr., 04015018:1-10, 2015. | |
| − | + | [7] Rizkalla S., Kazem H., Guaderrama L., Selim H., Kobayashi A. Strengthening of steel plates subjected to uniaxial compression using small-diameter CFRP strands. Elsevier Construction and Building Materials, 111:223-236, 2016. | |
| − | + | [8] Zhao X.L., Nateghi-Alahi F., Khazaei Poul M. Experimental testing on CFRP strengthened thin steel plates under shear loading. Thin-Walled Structures., 109:217-226, 2016. | |
| − | + | [9] Harries K.A., Peck A.J., Abraham E.J. Enhancing of structural steel sections using FRP. Thin-Walled Structures, 47:1092-1101, 2009. | |
| − | + | [10] Rahghozar R., Narmashiri K., Nekoyee M., Keykha A.H. Numerically examined the increase in compressive capacity of long hollow steel columns reinforced with FRP-composite. Omran Ferdowsi Mashhad, 2:99-116, 2015. | |
| − | + | [11] Journal 345 of deputy of planning and strategic oversight of the President. | |
| − | + | [12] Reddy C.V., Raju C.J.S., Babu P.R., Ramnarayan R. Mechanical characterization of carbon/epoxy unidirectional and bidirectional composites for sructural aplication. Journal of Engineering Research and Application, 8:21-24, 2018. | |
| − | + | [13] Bennati S., Colonna D., Valvo P.S. Evaluation of the increased load bearing capacity of steel beams strengthened with pre-stressed FRP laminates. Frattura ed Integrita Strutturale, 38:377-391, 2016. | |
| − | + | </div> | |
Latest revision as of 16:32, 14 December 2021
Abstract
One of the most common methods of strengthening concrete structures is the use of composite fibers such as FRP. These fibers have found a special place in structural retrofitting methods due to a number of specific ability including lightness and ease of performance. Reinforced concrete structures have long been considered by design engineers for the possibility of retrofitting high strength composite steel structures. In this study, twenty-two steel beam models were modeled by ANSYS software. Variable parameters studied in the modeled steel beams can be referred to the number, orientation and thickness of composite layers.
Keywords: Steel beams, CFRP, unidirectional and bi-directional, bending stress
1. Introduction
Steel structures have certain advantages compared to the concrete structures due to two parameters of light weight and rapid performance. Nowadays, parameters such as changes in gravity and lateral loading code, changes in existing application, design and performance errors, corrosion and damage due to collision of random and environmental loads has caused the structures not to have adequate bearing capacity against the new loads and thus needs to be improved. Conventional retrofitting methods can be used to strengthening steel structures using a steel jacket coating method. In this method, by increasing the flexural, shear and axial load bearing capacity of the members, we can strengthen the weak members.
Although this method is effective, but due to the difficult application conditions and increase of the structural sections weight as well as the emergence of new materials such as composite fibers (FRP), design engineers have used structural strengthening method by polymeric composite fibers. These polymer fibers are now extensively growing and exploiting worldwide in a variety of industries, including the marine, aerospace, and automotive, road and building industries as shown in Figure 1.

|

|

| |
| Figure 1. Using of FRP composite fibers in industry | |
Important advantages of polymer fibers are their longevity and their good resistance to environmental conditions. In fact, polymer fibers can minimize the cost of maintenance of steel structures by their high resistance to corrosion and fatigue. In a comparison and field study, it is quite evident that the use of polymer fibers in reinforcing concrete structures is older than steel structures.
Selvaraj et al. [1] investigated the enhanced strength and hardness of CFRP-reinforced steel channel sections. They tested 210 laboratory models with different arrangements of polymer fibers under 4-point testing, which ultimately found that unidirectional polymer fibers were more effective in increasing the strength and stiffness of steel sections than in bi-directional polymer fibers. John et al. [2] investigated the theoretical and experimental study of CFRP-reinforced notched steel beams. The results of experiments have shown that the strength and ductility of the notched beams, twice reinforced by polymer fibers, have been improved. Zhao et al. [3] examined the sections of FRP-reinforced steel tubes under impact load. In this study, they posit 13 laboratory samples covered by composite fibers under impact load. Ultimately, the results of investigating bearing capacity and deformations indicated that due to the presence of polymer composite fiber coatings, the capacity of impulsivity capacity of sections is increased by 29% with the decrease of lateral displacement values compared to the non-coating composite fibers. In an experimental study, Sedan et al. [4] investigated the bending response of steel beams reinforced with anchored composite sheets. In this study, they impacted 11 beams by 3-point loading. The important results of their research are the increase in final bearing capacity of sections due to the increase in length and thickness of the composite fibers. In a study, Zhi-Yu Wang et al. [5] investigated the tensile behavior of CFRP-reinforced anchored steel sheets. In another study, Selvaraj et al. [6] investigated the flexural reinforcement of steel angular sections using CFRP fibers. They tested 30 laboratory models under 4-point loads in two states of with- and- without composite fiber coating, the most important of which can be significant increase in hardness and strength reinforced with composite fiber. Rizkalla et al [7] examined steel sheets reinforced with CFRP micro-strands. The results showed that the use of low-diameter composite fibers preserves the adhesion properties of the substrates under pressure and tension. In another experimental study, Zhao et al. [8] investigated thin CFRP-reinforced steel sheets affected by shear load. They reinforced three thin steel sheet specimens with different arrangement of polymer plates compared to the uncoated composite fiber sample. One of the important results of this study is the increase in the final strength and the increase in the hardness of the energy absorption sequence due to the reinforcement. In a study, Harris et al. [9] investigated the enhancement of the durability of steel structural sections with FRP fibers. The results show that the presence of composite fiber strips improves the dynamic behavior and provides a stable cyclic response of the steel sections under cyclic loads. Rahgozar et al. [10] numerically examined the increase in compressive capacity of long hollow box steel columns reinforced with FRP-composite. They investigate 62 steel column samples with abutment conditions of one end is fixed and one end is pinned. The results indicated an increase in critical load of hollow box steel columns due to the coating of composite fiber layers.
2. Materials properties
2.1 Steel beam
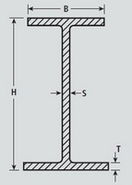
In this research, steel beams with geometrical and technical properties as shown in Figure 2 and in Table 1 are used as follows.
|
| Figure 2. Geometric properties of steel beam |
| l | h | b | t | E | Fy | Fu | ɣ | SX | IX | g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 600 | 27 | 13.5 | 1.02 | 2e6 | 2400 | 3700 | 7850e-6 | 429 | 5790 | 0.361 |
2.2 Composite fibers
In this study, based on the information available in Journal 345 of deputy of planning and strategic oversight of the President [11] and research by Reddy [12], the high-strength carbon composite properties available in Table 2 are used as follows.
| E | ƃ | Ɣ | µ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.4e6 | 5430 | 1.9e-3 | 0.2 |
3. Methodology
In this research, the results of bending stresses are investigated using the relation between theory and software modeling.
3.1 Theory relationship
In one study, Benati et al. [13] compute bearing capacity enhancements of steel beams reinforced by FRP-prestressed fiber. In this study, steel beams with conventional IPE sections were reinforced with FRP polymeric composite strips, which eventually bearing capacity of mentioned sections were investigated in two plastic and elastic states. Equation (1) indicates the flexural stresses caused by gravity loads in the presence of composite fibers in the beams:
|
|
(1) | |
|
|
(2) |
In Eq.(1), the value of (unit weight of steel beam length) has been studied while the value of is a permanent load from non-structural members that can be calculated based on the minimum value of below equation:
|
|
(3) |
It is noteworthy that in the aforementioned relationships, is steel beam compression wing area, is cross-sectional area of composite sheet, is tensile stress value due to composite fibers, and is the relationship coefficient value as shown in Eq.(2).
3.2 Software modeling
Today, with the advent of computer science, the accuracy of specialized software computing has increased dramatically. ANSYS software is one of the good soft wares that is used in engineering analysis such as structure and mechanics.
This software is finite element software that aims at analyzing the modeling. In this software, the basis of solving equations is to split the model into smaller elements. These types of elements can be structural, thermal, or other, depending on the number of degrees of freedom and the type of analysis method. One of the methods of analysis in this software is static nonlinear analysis. There are various ways to analyze nonlinear equations in this method, including Newton-Raphson iterative method. The basis of using a nonlinear static method is that the software gradually increases the amount of load until the structure reaches a failure and instability boundary and it is noteworthy that the convergence of the solutions obtained by this method is activated by automatic time step algorithm.
4. Validity
To evaluate the validity of the software model used in this study, the stress values obtained by software for steel beam model with unidirectional carbon fiber with 1mm thickness are compared with theoretical relationship in Section 3 that is described in equations (4) to (6):
|
|
(4) |
|
|
(5) |
|
|
(6) |
|
|
In this section and slight difference in Table 3 shows the validity of the software analysis.
| Theory bending stress | Software bending stress | Changing ratio |
|---|---|---|
| 77.04 | 77 | 0.5% |
5. Results and discussion
5.1 Numerical results of reinforced steel beam by one to three unidirectional CFRP composite layers
The specimens modeled in software with the results extracted from the presence of one to three unidirectional composite layers are described in Table 4, as shown in the results, the highest and the lowest increase in bending stress compared to the first model (one unidirectional composite layer with 1mm thickness) is equal to 155% and 45% respectively. As shown in Figures 3 and 4, increasing the thickness of composite fibers in unidirectional state decreases the flexural stress values due to the gravity loading of reinforced steel beams.
| Models NO | Layers NO | Layer Thickness | Angle Degree | Bending Stress | Increasing Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0.1 | 0 | 77 | 0 |
| 2 | 1 | 0.125 | 0 | 126 | 63% |
| 3 | 1 | 0.15 | 0 | 168 | 118% |
| 4 | 1 | 0.2 | 0 | 196 | 155% |
| 5 | 1 | 0.3 | 0 | 168 | 118% |
| 6 | 1 | 0.5 | 0 | 133 | 73% |
| 7 | 2 | 0.1 | 0,0 | 140 | 82% |
| 8 | 2 | 0.15 | 0,0 | 182 | 136% |
| 9 | 2 | 0.1 | 90,0 | 77 | 0% |
| 10 | 3 | 0.15 | 90,0 | 112 | 45% |
| 11 | 3 | 0.1 | 0,0,0 | 182 | 136% |

|
| Figure 3. The Results of bending stress in reinforced steel beam by unidirectional composite layer due to increased layer thickness |

|
| Figure 4. Numerical results of reinforced steel beam by one to three unidirectional CFRP composite layers |
5.2 Numerical results of reinforced steel beam with one to three layers of bi-directional CFRP composite
The characteristics of the modeled samples in software along with the results obtained from the presence of one to three bi-directional composite layers are presented in Table 5. The results showed that the highest and lowest increase in bending stress compared to the first model (one unidirectional composite layer with 1mm thickness) is equal 73% and 7% respectively. As illustrated in Figure 5, the use of bidirectional fiber in reducing bending stress values is effective than the corresponding bending fibers. As shown in Figures 6, changing the angle of the composite fibers improve the flexural stress values only in unidirectional fiber mode.
| Models NO | Layers NO | Layer Thickness | Angle Degree | Bending Stress | Increasing Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0.1 | 0 | 105 | 0 |
| 2 | 1 | 0.125 | 0 | 31.5 | -70% |
| 3 | 1 | 0.15 | 0 | 77 | -27% |
| 4 | 1 | 0.2 | 0 | 133 | 27% |
| 5 | 1 | 0.3 | 0 | 175 | 67% |
| 6 | 1 | 0.5 | 0 | 182 | 73% |
| 7 | 2 | 0.1 | 0,0 | 91 | -13% |
| 8 | 2 | 0.15 | 0,0 | 133 | 27% |
| 9 | 2 | 0.1 | 90,0 | 91 | -13% |
| 10 | 3 | 0.15 | 90,0 | 133 | 27% |
| 11 | 3 | 0.1 | 0,0,0 | 112 | 7% |

|
| Figure 5. The effect of number of layers direction on bending stress values of steel beams reinforced by composite fiber |

|

|
| Figure 6. The impact of layers deployment angle on bending stress values of steel beams reinforced by composite fibers in unidirectional & bidirectional stat |
6. Conclusions
1. Increasing the thickness of composite fibers in unidirectional state decreases the flexural stress values due to the gravity loading of reinforced steel beams. However, the conversion of fibers from unidirectional to bi-directional modes has little effect on decreasing the values of bending stresses.
2. In the comparison of the numerical results of bending stresses of steel beams reinforced by unidirectional and bidirectional fiber, the use of bidirectional fiber in reducing bending stress values is effective than the corresponding bending fibers.
3. Changing the angle of the composite fibers in two-layer mode from zero value in both layers to 90 ° in the first layer and zero value in the second layer improve the flexural stress values only in unidirectional fiber mode.
4. By increasing the number of layers from one layer to three layers, in the case of unidirectional composite layers, the use of more layers with less thickness compared to one layer of equal thickness had a better effect on the flexural stress results. While in the bi-directional composite fibers, the use of a thick layer equivalent to the number of thinner layers will have a better effect on the calculated flexural stress results.
References
[1] Selvaraj S., Madhavan M., Dongre S.U. Experimental studies on strength and stiffness enhancement in CFRP-strengthened structural steel chanel sections under flexure. J. Compos. Constr., 04016042:1-12, 2016.
[2] Jun D, Yonghui J., Henghzhong Z. Theoretical and experimental study on notched steel beams strengthened with CFRP plate. Composite Structures, 136:450-459, 2016.
[3] Zaho X.L., Alam M.I., Fawzia S. Experimental study on FRP-strengthened steel tubular members under lateral impact. J. Compos. Constr., 04017022:1-14, 2017.
[4] Sweedan M.I., Alhadid M.A., EI-Sawy K.M. Experimental study response of steel beams strengthened with anchored hybrid composites. Thin-Walled Structures, 99:1-11, 2016.
[5] Wang Z.Y., Zhang N., Wang Q.Y. Tensile behavaiour of open-hole and bolted steel plates reinforced by CFRP strips. Elsevier Composite Part B., 100:101-113, 2016.
[6] Selvaraj S., Verma R., Sanap V., Madhavan M. Flexural strengthening of structural steel angle sections using CFRP: Experimental investigation. J. Compos. Constr., 04015018:1-10, 2015.
[7] Rizkalla S., Kazem H., Guaderrama L., Selim H., Kobayashi A. Strengthening of steel plates subjected to uniaxial compression using small-diameter CFRP strands. Elsevier Construction and Building Materials, 111:223-236, 2016.
[8] Zhao X.L., Nateghi-Alahi F., Khazaei Poul M. Experimental testing on CFRP strengthened thin steel plates under shear loading. Thin-Walled Structures., 109:217-226, 2016.
[9] Harries K.A., Peck A.J., Abraham E.J. Enhancing of structural steel sections using FRP. Thin-Walled Structures, 47:1092-1101, 2009.
[10] Rahghozar R., Narmashiri K., Nekoyee M., Keykha A.H. Numerically examined the increase in compressive capacity of long hollow steel columns reinforced with FRP-composite. Omran Ferdowsi Mashhad, 2:99-116, 2015.
[11] Journal 345 of deputy of planning and strategic oversight of the President.
[12] Reddy C.V., Raju C.J.S., Babu P.R., Ramnarayan R. Mechanical characterization of carbon/epoxy unidirectional and bidirectional composites for sructural aplication. Journal of Engineering Research and Application, 8:21-24, 2018.
[13] Bennati S., Colonna D., Valvo P.S. Evaluation of the increased load bearing capacity of steel beams strengthened with pre-stressed FRP laminates. Frattura ed Integrita Strutturale, 38:377-391, 2016.
Document information
Published on 03/01/22
Accepted on 30/06/21
Submitted on 18/04/21
Volume 38, Issue 1, 2022
DOI: 10.23967/j.rimni.2021.12.005
Licence: CC BY-NC-SA license
Share this document
Keywords
claim authorship
Are you one of the authors of this document?